I downloaded promise.js from the GIT source code library today and found that the source code is written based on Web front-end JavaScript and cannot be used directly for nodejs. Fortunately, there is not a lot of code and it is not very complicated. After analysis and integration, it is implemented as a framework of nodejs. The code is as follows:
(function(){
/**
* Copyright 2012-2013 (c) Pierre Duquesne <stackp@online.fr>
* script: promise.js
* description: promises的nodejs模块
* modified: https://github.com/stackp/promisejs
* authors: alwu007@sina.cn
* */
var Promise = exports.Promise = function(){
this._callbacks = [];
};
Promise.prototype.then = function(func, context){
//处理回调结果的方法
function doCallbackResults(r) {
if (r instanceof Promise) {
r.then(function(err, values){
p.done(err, values);
});
} else {
p.done(null, r);
}
}
var p = new Promise();
if (this._isdone) {
var results = func.apply(context, this.results);
doCallbackResults(results);
} else {
this._callbacks.push(function(){
var results = func.apply(context, arguments);
doCallbackResults(results);
});
}
return p;
};
Promise.prototype.done = function(){
this.results = arguments;
this._isdone = true;
for (var i=0; i<this._callbacks.length; i++) {
this._callbacks[i].apply(null, arguments);
}
this._callbacks = [];
};
Promise.join = function(promises){
var p = new Promise();
var results = [];
if (!promises || !promises.length) {
p.done(results);
return p;
}
var numdone = 0;
var total = promises.length;
function notifier(i) {
return function() {
numdone += 1;
results[i] = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
if (numdone === total) {
p.done(results);
}
};
}
for (var i = 0; i < total; i++) {
promises[i].then(notifier(i));
}
return p;
};
Promise.chain = function(funcs, args) {
var p = new Promise();
if (!funcs || !funcs.length) {
p.done.apply(p, args);
} else {
funcs[0].apply(null, args).then(function(){
funcs.splice(0, 1);
Promise.chain(funcs, arguments).then(function(){
p.done.apply(p, arguments);
});
});
}
return p;
};
})();
Attached is the test code as follows:
/**
* script: test.js
* description: promise.js测试代码
* */
var promise = require('./mypromise');
function asyncfoo() {
var p = new promise.Promise();
setTimeout(function(){
p.done();
}, 1000);
return p;
}
function syncfoo() {
var p = new promise.Promise();
p.done();
return p;
}
var o = {};
/*
asyncfoo().then(function(){
return 'Raymond';
}, o).then(function(err, name){
o.name = name;
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return 18;
});
});
}, o).then(function(err, age){
o.age = age;
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return 'boy';
});
}).then(function(err, sex){
return sex;
});
}).then(function(err, sex){
o.sex = sex;
return 'Hello, world!';
}).then(function(err, say){
o.say = say;
console.dir(o);
});
syncfoo().then(function(){
return 'Raymond';
}, o).then(function(err, name){
o.name = name;
return syncfoo().then(syncfoo).then(function(){
return syncfoo().then(syncfoo).then(function(){
return 18;
});
});
}, o).then(function(err, age){
o.age = age;
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return asyncfoo().then(asyncfoo).then(function(){
return 'boy';
});
}).then(function(err, sex){
return sex;
});
}).then(function(err, sex){
o.sex = sex;
return 'Hello, world!';
}).then(function(err, say){
o.say = say;
console.dir(o);
});
*/
function asyncfoo1(){
var p = new promise.Promise();
setTimeout(function(){
p.done(null, 'Raymond');
}, 1000);
return p;
}
function asyncfoo2(err, name){
o.name = name;
var p = new promise.Promise();
setTimeout(function(){
p.done(null, 18);
}, 1000);
return p;
}
function asyncfoo3(err, age){
o.age = age;
var p = new promise.Promise();
setTimeout(function(){
p.done(null, 'boy');
}, 1000);
return p;
}
function asyncfoo4(){
var p = new promise.Promise();
setTimeout(function(){
p.done(null, 'Hello, world!');
}, 1000);
return p;
}
promise.Promise.chain([asyncfoo1, asyncfoo2, asyncfoo3]).then(function(err, sex){
o.sex = sex;
return asyncfoo4();
}).then(function(err, say){
o.say = say;
}).then(function(){
console.dir(o);
});
 Vercel是什么?怎么部署Node服务?May 07, 2022 pm 09:34 PM
Vercel是什么?怎么部署Node服务?May 07, 2022 pm 09:34 PMVercel是什么?本篇文章带大家了解一下Vercel,并介绍一下在Vercel中部署 Node 服务的方法,希望对大家有所帮助!
 node.js gm是什么Jul 12, 2022 pm 06:28 PM
node.js gm是什么Jul 12, 2022 pm 06:28 PMgm是基于node.js的图片处理插件,它封装了图片处理工具GraphicsMagick(GM)和ImageMagick(IM),可使用spawn的方式调用。gm插件不是node默认安装的,需执行“npm install gm -S”进行安装才可使用。
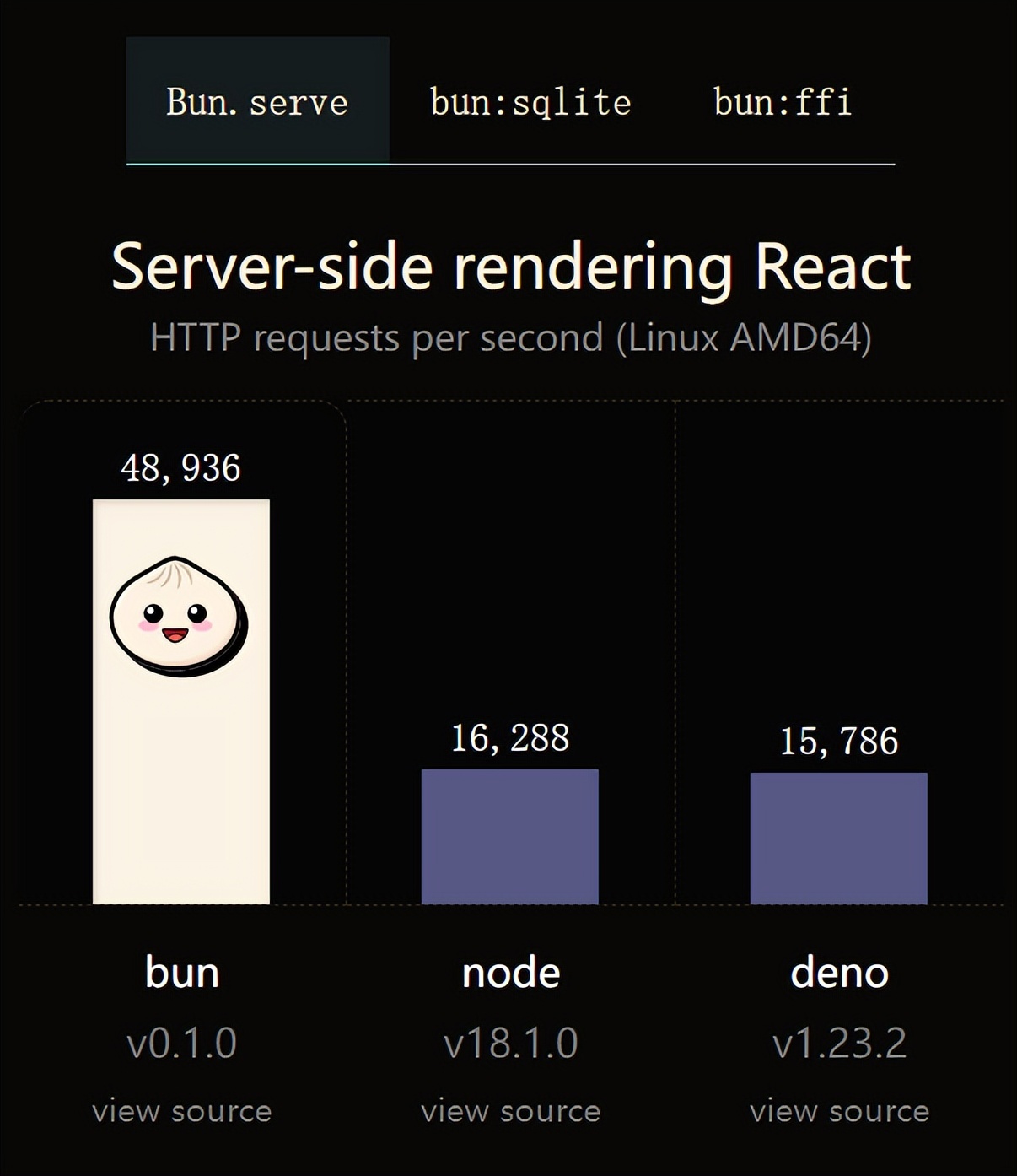 火了!新的JavaScript运行时:Bun,性能完爆NodeJul 15, 2022 pm 02:03 PM
火了!新的JavaScript运行时:Bun,性能完爆NodeJul 15, 2022 pm 02:03 PM今天跟大家介绍一个最新开源的 javaScript 运行时:Bun.js。比 Node.js 快三倍,新 JavaScript 运行时 Bun 火了!
 nodejs中lts是什么意思Jun 29, 2022 pm 03:30 PM
nodejs中lts是什么意思Jun 29, 2022 pm 03:30 PM在nodejs中,lts是长期支持的意思,是“Long Time Support”的缩写;Node有奇数版本和偶数版本两条发布流程线,当一个奇数版本发布后,最近的一个偶数版本会立即进入LTS维护计划,一直持续18个月,在之后会有12个月的延长维护期,lts期间可以支持“bug fix”变更。
 聊聊Node.js中的多进程和多线程Jul 25, 2022 pm 07:45 PM
聊聊Node.js中的多进程和多线程Jul 25, 2022 pm 07:45 PM大家都知道 Node.js 是单线程的,却不知它也提供了多进(线)程模块来加速处理一些特殊任务,本文便带领大家了解下 Node.js 的多进(线)程,希望对大家有所帮助!
 node爬取数据实例:聊聊怎么抓取小说章节May 02, 2022 am 10:00 AM
node爬取数据实例:聊聊怎么抓取小说章节May 02, 2022 am 10:00 AMnode怎么爬取数据?下面本篇文章给大家分享一个node爬虫实例,聊聊利用node抓取小说章节的方法,希望对大家有所帮助!


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.








