JavaScript Study Notes (7) Ajax and Http Status Code_Basic Knowledge
Ajax and how it works
AJAX is a technology that exchanges data with the server without refreshing the web page. It was first used by Google in Google Maps and quickly became popular.
AJAX cannot cross domain. If you need to cross domain, you can use document.domain='a.com'; or use a server proxy to proxy the XMLHttpRequest file
AJAX is based on existing Internet standards and uses them in conjunction:
XMLHttpRequest object (asynchronously exchange data with the server)
JavaScript/DOM (information display/interaction)
CSS (define styles for data)
XML (as a format for transforming data)
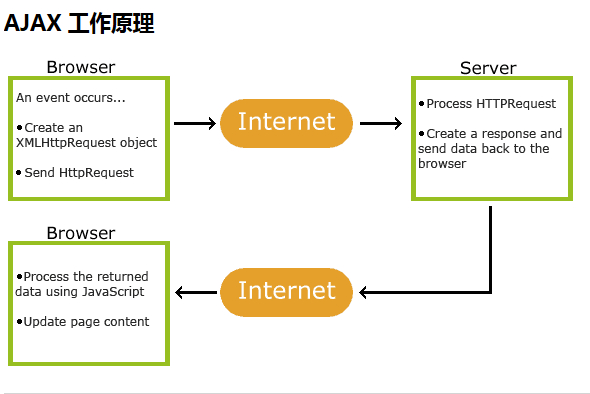
Create XMLHttpRequest object
All modern browsers (IE7, Firefox, Chrome, Safari and Opera) have built-in XMLHttpRequest objects.
Create Ajax object:
//IE6 and above
var oAjax = new XMLHttpRequest();
//IE6
var oAjax =new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP")
Connect to server
oAjax.open(method, url, whether asynchronous)
We all know that Ajax means "Asynchronous Javascript And XML" (asynchronous JavaScript and XML), which refers to a web development technology for creating interactive web applications. Therefore, Ajax naturally works in asynchronous mode (asynchronous is true, synchronous is false)
Synchronous and asynchronous
Synchronization refers to the communication method in which the sender sends data and waits for the receiver to send back a response before sending the next data packet.
Asynchronous refers to the communication method in which the sender sends data, waits for the receiver to send back a response, and then sends the next data packet.
(To put it simply: synchronization means that you can only do one thing, while asynchronous means that you can do multiple things at the same time)
Send request send()
GET or POST?
Compared to POST, GET is simpler and faster, and works in most cases.
However, please use POST requests in the following situations:
Cache files (updating files or databases on the server) cannot be used
Send large amounts of data to the server (POST has no data size limit)
POST is more stable and reliable than GET when sending user input containing unknown characters
Receive return information
oAjax.onreadystatechange = function(){ //Event handler to be called when the request state changes
alert(oAjax.readystate);
}
As long as the value of the readyState attribute changes, a readyStatechange event will be triggered. This event can be used to detect the value of readyState after each state change. Typically, we are only interested in the stage with a readyState value of 4, since all data is ready at this time, however, the onreadystatechange event handler must be specified before calling open() to ensure cross-browser compatibility. Let’s look at an example:
var xhr = createXHR();
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
If (xhr.readyState == 4) {
If ((xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status alert(xhr.statusText);
} else {
alert("Request was unsuccessful: " xhr.status);
}
}
};
xhr.open("get", "example.txt", true);
xhr.send(null);
XHR Object
When the XHR object sends an HTTP request to the server, it will go through several states until the request is processed and then receives a response. readyState is the status attribute of the XHR request. It has 5 attribute values:
0 (not initialized) The open() method has not been called yet
1 (Loading) The send() method has been called and the request is being sent
2 (Loading completed) The send() method is completed and all response content has been received
3 (Parsing) Parsing response content
4 (Complete) The response content is parsed and can be used on the client
status
The status attribute represents the response status code returned from the server. For example: 200 means success, 404 means not found.
1 prefix: message. This type of status code means that the request has been accepted and needs to continue processing.
2 prefix: success. This type of status code means that the request has been successfully received, understood, and accepted by the server.
Prefix 3: Redirect. This type of status code indicates that the client needs to take further action to complete the request.
Prefix 4: client error. This type of status code represents an error that appears to have occurred on the client side, preventing the server from processing it.
Prefix 5: Server error. This type of status code represents that an error or abnormal state occurred during the server's processing of the request
Attached: Detailed explanation of http status code
statusText
StatusText is the text information returned by the response, which can only be used when the readyState value is 3 or 4. When readyState is other values, the view's access to the statusText property will throw an exception.
XHR method
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| abort() | 导致当前正在执行的请求被取消 |
| getAllResponseHeaders() | 返回包含所有响应头的名称和值的单个字符|串 |
| getResponseHeader(name) | 返回响应头中指定的名称和值 |
| open(method,url,async,username,pwd) | 设置HTTP方法(get或post)等 |
| send(content) | 发出带有指定主体内容的请求 |
| setRequestHeader(name,value) | 使用指定的名称和值设置请求头 |
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






