Docker image usage
When running a container, if the image used does not exist locally, docker will automatically download it from the docker image warehouse. The default is to download from the Docker Hub public image source.
Let’s learn:
1. Manage and use local Docker host images
2. Create images
List the image list
We can use docker images to list the images on the local host.
php@php:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE ubuntu 14.04 90d5884b1ee0 5 days ago 188 MB php 5.6 f40e9e0f10c8 9 days ago 444.8 MB nginx latest 6f8d099c3adc 12 days ago 182.7 MB mysql 5.6 f2e8d6c772c0 3 weeks ago 324.6 MB httpd latest 02ef73cf1bc0 3 weeks ago 194.4 MB ubuntu 15.10 4e3b13c8a266 4 weeks ago 136.3 MB hello-world latest 690ed74de00f 6 months ago 960 B training/webapp latest 6fae60ef3446 11 months ago 348.8 MB
Description of each option:
REPOSTITORY: Indicates the warehouse source of the image
TAG: Mirror tag
##IMAGE ID:Mirror ID
- ##CREATED:
Mirror creation time
- SIZE:
Mirror size
The same warehouse source can have multiple TAGs, representing this There are different versions of the warehouse source. For example, in the ubuntu warehouse source, there are many different versions such as 15.10, 14.04, etc. We use REPOSTITORY:TAG to define different images.
So, if we want to use the ubuntu system image of version 15.10 to run the container, the command is as follows:
php@php:~$ docker run -t -i ubuntu:15.10 /bin/bash root@d77ccb2e5cca:/#
If we want to use the ubuntu system image of version 14.04 to run the container, the command As follows:
php@php:~$ docker run -t -i ubuntu:14.04 /bin/bash root@39e968165990:/#
If you do not specify a version label for an image, for example, if you only use ubuntu, docker will use the ubuntu:latest image by default.
Get a new imageWhen we use a non-existent image on the local host, Docker will automatically download the image. If we want to download this image in advance, we can use the docker pull command to download it.
Cphp@php:~$ docker pull ubuntu:13.10 13.10: Pulling from library/ubuntu 6599cadaf950: Pull complete 23eda618d451: Pull complete f0be3084efe9: Pull complete 52de432f084b: Pull complete a3ed95caeb02: Pull complete Digest: sha256:15b79a6654811c8d992ebacdfbd5152fcf3d165e374e264076aa435214a947a3 Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:13.10
After the download is completed, we can directly use this image to run the container.
Find the imageWe can search for the image from the Docker Hub website. The Docker Hub URL is:
https://hub.docker.com/
We also You can use the docker search command to search for images. For example, we need an httpd mirror as our web service. We can search httpd through the docker search command to find the image that suits us.php@php:~$ docker search httpd
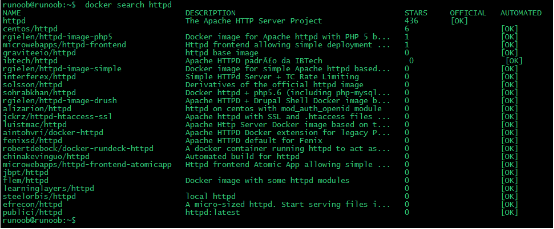
The name of the image warehouse source
DESCRIPTION:The description of the image
OFFICIAL:Whether docker is officially released
Drag the imageWe decided to use the official version of httpd image in the picture above, use the command docker pull to Download the image.
php@php:~$ docker pull httpd Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/httpd 8b87079b7a06: Pulling fs layer a3ed95caeb02: Download complete 0d62ec9c6a76: Download complete a329d50397b9: Download complete ea7c1f032b5c: Waiting be44112b72c7: Waiting
After the download is completed, we can use this image.
php@php:~$ docker run httpdCreate an image
When the image we download from the docker image warehouse cannot meet our needs, we can change the image in the following two ways.
- 1. Update the image from the already created container and submit the image
2. Use the Dockerfile command to create a new image
Update the image
Before updating the image, we need to use the image to create A container.php@php:~$ docker run -t -i ubuntu:15.10 /bin/bash root@e218edb10161:/#uses the apt-get update command within the running container to update.
After completing the operation, enter the exit command to exit the container.
The container with ID e218edb10161 at this time is a container that has been changed according to our needs. We can submit the container copy through the command docker commit.
php@php:~$ docker commit -m="has update" -a="php" e218edb10161 php/ubuntu:v2 sha256:70bf1840fd7c0d2d8ef0a42a817eb29f854c1af8f7c59fc03ac7bdee9545aff8
Description of each parameter:
-m:Submitted description information
-a:Specify the image author
##e218edb10161:Container ID
php/ubuntu :v2:Specify the target image name to be created
docker images command to view our new imagephp/ubuntu: v2:
php@php:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE php/ubuntu v2 70bf1840fd7c 15 seconds ago 158.5 MB ubuntu 14.04 90d5884b1ee0 5 days ago 188 MB php 5.6 f40e9e0f10c8 9 days ago 444.8 MB nginx latest 6f8d099c3adc 12 days ago 182.7 MB mysql 5.6 f2e8d6c772c0 3 weeks ago 324.6 MB httpd latest 02ef73cf1bc0 3 weeks ago 194.4 MB ubuntu 15.10 4e3b13c8a266 4 weeks ago 136.3 MB hello-world latest 690ed74de00f 6 months ago 960 B training/webapp latest 6fae60ef3446 12 months ago 348.8 MBUse our new image
php/ubuntu to start a container
php@php:~$ docker run -t -i php/ubuntu:v2 /bin/bash root@1a9fbdeb5da3:/#
Build the imageWe use Command
docker build to create a new image from scratch. To do this, we need to create a Dockerfile that contains a set of instructions to tell Docker how to build our image.
php@php:~$ cat Dockerfile FROM centos:6.7 MAINTAINER Fisher "fisher@sudops.com" RUN /bin/echo 'root:123456' |chpasswd RUN useradd php RUN /bin/echo 'php:123456' |chpasswd RUN /bin/echo -e "LANG=\"en_US.UTF-8\"" > /etc/default/local EXPOSE 22 EXPOSE 80 CMD /usr/sbin/sshd -DEach command will create a new layer on the image, and the prefix of each command must be uppercase. The first FROM specifies which image source to useThe RUN command tells docker to execute the command in the image and install what. . . Then, we use the Dockerfile file to build an image through the docker build command.
php@php:~$ docker build -t php/centos:6.7 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 17.92 kB Step 1 : FROM centos:6.7 ---> d95b5ca17cc3 Step 2 : MAINTAINER Fisher "fisher@sudops.com" ---> Using cache ---> 0c92299c6f03 Step 3 : RUN /bin/echo 'root:123456' |chpasswd ---> Using cache ---> 0397ce2fbd0a Step 4 : RUN useradd php ......Parameter description:
-t: Specify the target image name to be created
-
.: The directory where the Dockerfile file is located, you can specify the absolute path of the Dockerfile
php@php:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE php/centos 6.7 860c279d2fec About a minute ago 190.6 MB php/ubuntu v2 70bf1840fd7c 17 hours ago 158.5 MB ubuntu 14.04 90d5884b1ee0 6 days ago 188 MB php 5.6 f40e9e0f10c8 10 days ago 444.8 MB nginx latest 6f8d099c3adc 12 days ago 182.7 MB mysql 5.6 f2e8d6c772c0 3 weeks ago 324.6 MB httpd latest 02ef73cf1bc0 3 weeks ago 194.4 MB ubuntu 15.10 4e3b13c8a266 5 weeks ago 136.3 MB hello-world latest 690ed74de00f 6 months ago 960 B centos 6.7 d95b5ca17cc3 6 months ago 190.6 MB training/webapp latest 6fae60ef3446 12 months ago 348.8 MBWe can use the new image to create the container
php@php:~$ docker run -t -i php/centos:6.7 /bin/bash [root@41c28d18b5fb /]# id php uid=500(php) gid=500(php) groups=500(php)From the above we can see that the new image already contains the user php we created
Set the image labelWe can use the docker tag command to add a new tag to the image.
php@php:~$ docker tag 860c279d2fec php/centos:devdocker tag Image ID, here is 860c279d2fec, user name, image source name (repository name) and new tag name (tag). Using the docker images command, you can see that the image with the ID 860c279d2fec has one more label.
php@php:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE php/centos 6.7 860c279d2fec 5 hours ago 190.6 MB php/centos dev 860c279d2fec 5 hours ago 190.6 MB php/ubuntu v2 70bf1840fd7c 22 hours ago 158.5 MB ubuntu 14.04 90d5884b1ee0 6 days ago 188 MB php 5.6 f40e9e0f10c8 10 days ago 444.8 MB nginx latest 6f8d099c3adc 13 days ago 182.7 MB mysql 5.6 f2e8d6c772c0 3 weeks ago 324.6 MB httpd latest 02ef73cf1bc0 3 weeks ago 194.4 MB ubuntu 15.10 4e3b13c8a266 5 weeks ago 136.3 MB hello-world latest 690ed74de00f 6 months ago 960 B centos 6.7 d95b5ca17cc3 6 months ago 190.6 MB training/webapp latest 6fae60ef3446 12 months ago 348.8 MB








