Heim >Web-Frontend >js-Tutorial >Einführung in die grundlegenden Verpackungstypen von Javascript_Javascript-Kenntnissen
Einführung in die grundlegenden Verpackungstypen von Javascript_Javascript-Kenntnissen
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 16:04:451102Durchsuche
Um die Manipulation grundlegender Typwerte zu erleichtern, bietet ECMAScript drei spezielle Referenztypen: Boolean, Number und String. Diese Typen ähneln anderen Referenztypen, weisen jedoch auch ein spezielles Verhalten auf, das ihren jeweiligen Basistypen entspricht. Tatsächlich wird jedes Mal, wenn ein Basistypwert gelesen wird, im Hintergrund ein Objekt des entsprechenden Basisverpackungstyps erstellt, sodass einige Methoden aufgerufen werden können, um die Daten zu manipulieren.
1. Übersicht grundlegender Verpackungsarten
var box = 'Mr. Lee';//定义一个字符串 var box2 = box.substring(2);//截掉字符串前两位 alert(box2);//输出新字符串
Die Variable box ist ein Zeichenfolgentyp, und box.substring(2) zeigt an, dass es sich um ein Objekt handelt (PS: Nur Objekte rufen Methoden auf), und schließlich wird das Verarbeitungsergebnis box2 zugewiesen. „Mr. Lee“ ist logischerweise kein Objekt und sollte keine eigenen Methoden haben, wie zum Beispiel:
alert('Mr. Lee'.substring(2));//Rufen Sie die Methode direkt über den Wert auf
1. Wörtliches Schreiben:
var box = 'Mr. Lee';//字面量
box.name = 'Lee';//无效属性
box.age = function () {//无效方法
return 100;
};
alert(box);//Mr. Lee
alert(box.substring(2));//. Lee
alert(typeof box);//string
alert(box.name);//undefined
alert(box.age());//错误
2. neue Operator-Schreibmethode:
var box = new String('Mr. Lee');//new 运算符
box.name = 'Lee';//有效属性
box.age = function () {//有效方法
return 100;
};
alert(box);//Mr. Lee
alert(box.substring(2));//. Lee
alert(typeof box);//object
alert(box.name);//Lee
alert(box.age());//100
Die obige Literaldeklaration und die neue Operatordeklaration veranschaulichen den Unterschied zwischen ihnen gut. Eines ist jedoch sicher: Die integrierten Methoden können unabhängig von der Literalform oder der neuen Operatorform verwendet werden. Die Eigenschaften „Boolean“ und „Number“ sind mit String identisch, und die drei Typen können zu grundlegenden Verpackungstypen werden.
PS: Wenn Sie den neuen Operator zum Erstellen der oben genannten drei Objekttypen verwenden, können Sie sich selbst Eigenschaften und Methoden hinzufügen. Wir empfehlen jedoch, ihn nicht auf diese Weise zu verwenden, da dadurch nicht unterschieden werden kann, ob dies der Fall ist ein Basistypwert oder ein Referenztypwert.
2. Boolescher Typ
Der Typ Boolean hat keine spezifischen Eigenschaften oder Methoden.
3. Nummerntyp
Der Number-Typ verfügt über einige statische Eigenschaften (Eigenschaften, die direkt über Number ohne den neuen Operator aufgerufen werden) und Methoden.
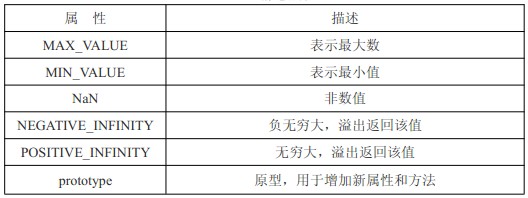
Statische Eigenschaft „Zahl“
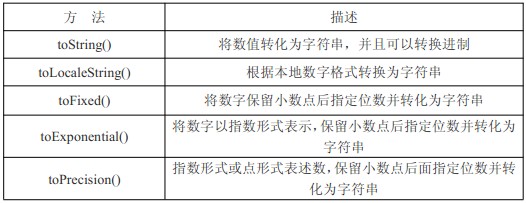
Methoden des Zahlenobjekts
var box = 1000.789; alert(box.toString());//转换为字符串,传参可以转换进制 alert(box.toLocaleString());//本地形式,1,000.789 alert(box.toFixed(2));//小数点保留,1000.78 alert(box.toExponential());//指数形式,传参会保留小数点 alert(box.toPrecision(3));//指数或点形式,传参保留小数点
4. String-Typ
Der String-Typ enthält drei Eigenschaften und eine große Anzahl verfügbarer integrierter Methoden.
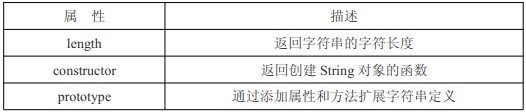
String-Objekteigenschaften
String enthält auch gängige Methoden von Objekten, wie z. B. die Methoden valueOf(), toLocaleString() und toString(), aber diese Methoden geben alle den Grundwert der Zeichenfolge zurück.
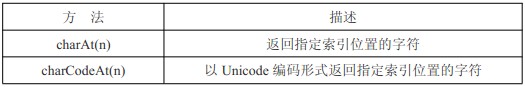
Zeichenmethoden
var box = 'Mr.Lee'; alert(box.charAt(1));//r alert(box.charCodeAt(1));//114 alert(box[1]);//r,通过数组方式截取
PS: Box[1] wird im IE-Browser undefiniert angezeigt, also verwenden Sie es mit Vorsicht.
String-Operationsmethoden
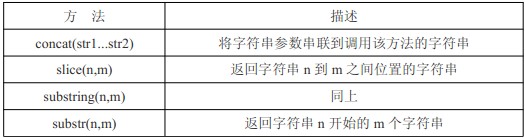
var box = 'Mr.Lee';
alert(box.concat(' is ', ' Teacher ', '!'));//Mr.Lee is Teacher !
alert(box.slice(3));//Lee
alert(box.slice(3,5));//Le
alert(box.substring(3));//Lee
alert(box.substring(3,5));//Le
alert(box.substr(3));//Lee
alert(box.substr(3,5));//Lee
var box = 'Mr.Lee';
alert(box.slice(-3));//Lee,6+(-3)=3 位开始
alert(box.substring(-3));//Mr.Lee 负数返回全部
alert(box.substr(-3));//Lee,6+(-3)=3 位开始
var box = 'Mr.Lee';
alert(box.slice(3, -1));//Le 6+(-1)=5, (3,5)
alert(box.substring(3, -1));//Mr. 第二参为负,直接转 0,并且方法会把较小的数字提前,(0,3)
alert(box.substr(3, -1));//'' 第二参数为负,直接转 0 ,(3,0)
PS: Die JavaScript-Implementierung des IE hat ein Problem bei der Verarbeitung negativer Werte, die an die Methode substr() übergeben werden. Sie gibt die ursprüngliche Zeichenfolge zurück. Denken Sie also daran, wenn Sie sie verwenden.
String-Position-Methode

var box = 'Mr.Lee is Lee';
alert(box.indexOf('L'));//3
alert(box.indexOf('L', 5));//10
alert(box.lastIndexOf('L'));//10
alert(box.lastIndexOf('L', 5));//3,从指定的位置向前搜索
PS: Wenn die gewünschte Zeichenfolge nicht gefunden wird, wird -1 zurückgegeben.
Beispiel: Finden Sie alle Ls.
var box = 'Mr.Lee is Lee';//包含两个 L 的字符串
var boxarr = [];//存放 L 位置的数组
var pos = box.indexOf('L');//先获取第一个 L 的位置
while (pos > -1) {//如果位置大于-1,说明还存在 L
boxarr.push(pos);//添加到数组
pos = box.indexOf('L', pos + 1);//从新赋值 pos 目前的位置
}
alert(boxarr);//输出
Fallkonvertierungsmethode

var box = 'Mr.Lee is Lee'; alert(box.toLowerCase());//全部小写 alert(box.toUpperCase());//全部大写 alert(box.toLocaleLowerCase()); alert(box.toLocaleUpperCase());
PS: Nur wenige Sprachen (z. B. Türkisch) verfügen über eine lokalspezifische Groß- und Kleinschreibung. Im Allgemeinen ist der Lokalisierungseffekt konsistent, unabhängig davon, ob er lokalisiert ist oder nicht.
String-Pattern-Matching-Methode

Die Anwendung regulärer Ausdrücke in Strings wurde in den vorherigen Kapiteln ausführlich besprochen und wird hier nicht wiederholt. Die oben genannten Funktionen match(), replace(), serach() und split() können auch in gewöhnlichen Zeichenfolgen verwendet werden.
var box = 'Mr.Lee is Lee';
alert(box.match('L'));//找到 L,返回 L 否则返回 null
alert(box.search('L'));//找到 L 的位置,和 indexOf 类型
alert(box.replace('L', 'Q'));//把 L 替换成 Q
alert(box.split(' '));//以空格分割成字符串
其他方法
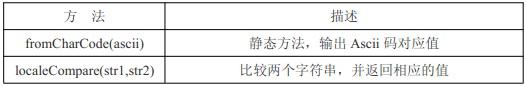
alert(String.fromCharCode(76));//L,输出 Ascii 码对应值
localeCompare(str1,str2)方法详解:比较两个字符串并返回以下值中的一个;
1.如果字符串在字母表中应该排在字符串参数之前,则返回一个负数。(多数-1)
2.如果字符串等于字符串参数,则返回 0。
3.如果字符串在自附表中应该排在字符串参数之后,则返回一个正数。(多数 1)
[task]var box = 'Lee';
alert(box.localeCompare('apple'));//1
alert(box.localeCompare('Lee'));//0
alert(box.localeCompare('zoo'));//-1
HTML 方法
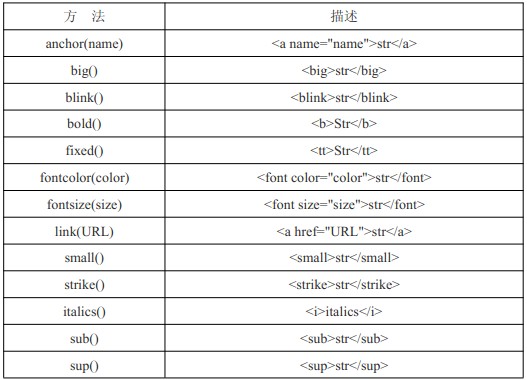
以上是通过 JS 生成一个 html 标签,根据经验,没什么太大用处,做个了解。
var box = 'Lee';
alert(box.link('http://www.jb51.net'));//超链接
教程内容来自 李炎恢老师JavaScript教程
下面是其它网友整理的文章:
一 基本包装类型概述
实际上,每当读取一个基本类型值的时候,后台就会创建一个对应的基本包装类型的对象,从而能够调用一些方法来操作这些数据;
var box = 'Mr.Lee'; // 定义一个String字符串;
var box2 = box.substring(2); // 截掉字符串前两位;
console.log(box2); // 输出新字符串;=>.Lee;
// 变量box是一个字符串String类型,而box.substring(2)又说明它是一个对象(只有对象才会调用方法);
console.log('Mr.Lee'.substring(3)); // 直接通过字符串值来调用方法=>Lee;
引用类型和基本包装类型的主要区别就是对象的生存期;
自动创建的基本包装类型的对象,则只存在于一行代码的执行瞬间,然后立即被销毁;
这意味着我们不能在运行时为基本类型值添加属性和方法;
var s1 = 'some text'; // => var s1 = new String('some text');
var s2 = s1.substring(5); // => var s2 = s1.substring(5);
// s1 = null; 销毁这个实例;后台自动执行;
1.字面量写法
var box = 'Mr.Lee'; // 字面量;
box.name = 'Lee'; // 无效属性;
box.age = function(){ // 无效方法;
return 100;
};
console.log(box.substring(3)); // =>Lee;
console.log(typeof box); // =>string;
console.log(box.name); // =>undefined;
console.lgo(box.age()); // =>错误;
2.new运算符写法
var box = new String('Mr.Lee');
box.name = 'Lee';
box.age = function(){
return 100;
};
console.log(box.substring(3)); // =>Lee;
console.log(typeof box); // =>object;
console.log(box.name); // =>Lee;
console.lgo(box.age()); // =>100;
// Die obige Literaldeklaration und die neue Operatordeklaration verdeutlichen den Unterschied zwischen ihnen;
// Unabhängig davon, ob es sich um ein Literal oder den neuen Operator handelt, können Sie dessen integrierte Methode (
) verwenden
Zwei boolesche Typen
//Der boolesche Typ hat keine spezifischen Eigenschaften oder Methoden;
Drei Zahlentypen
//Der Number-Typ verfügt über einige statische Eigenschaften (direkt über Number ohne den neuen Operator aufgerufen) und Methoden 1. Statische Eigenschaften des Number-ObjektsMAX_VALUE stellt die maximale Anzahl dar;
MIN_VALUE stellt den Mindestwert dar;
NaN Kein numerischer Wert;
NEGATIVE-INFINITY Negativ unendlich, Überlauf gibt diesen Wert zurück;
POSITIVE_INFINITY Unendlich, Überlauf gibt diesen Wert zurück;
Prototyp Prototyp, der zum Hinzufügen neuer Eigenschaften und Methoden verwendet wird;
toString() Konvertiert den Wert in eine Zeichenfolge und kann die Basis konvertieren; toLocaleString() String gemäß lokalem Zahlenformat konvertieren;
toFixed() Wandelt die Zahl in eine Zeichenfolge um, indem die angegebene Anzahl von Nachkommastellen beibehalten wird;
toExponential() stellt die Zahl in Exponentialform dar;
toPrecision() stellt Zahlen in Exponentialform oder Punktform dar;
Vier String-Typen
Der String-Typ enthält drei Attribute und eine große Anzahl verfügbarer integrierter Methoden
1.String-Objekteigenschaften
Länge Gibt die Zeichenlänge der Zeichenfolge zurück; Konstruktor Gibt die Funktion zurück, die ein String-Objekt erstellt;
Prototyp Erweitern Sie die String-Definition durch Hinzufügen von Attributen und Methoden. 2. String-Objekt-Zeichenmethode
charAt(n) Gibt das Zeichen an der angegebenen Indexposition zurück;
charCodeAt(n) Gibt die Kodierung des Zeichens an der angegebenen Indexposition in Unicode-Kodierung zurück;
var box = 'Mr.Lee';
console.log(box.charAt(1)); // =>r;
console.log(box.charCodeAt(1)); // =>114;
console.log(box[1]) // =>r;Interception through array; 3.String-Objekt-String-Operationsmethode
concat(str1...str2) Verkettet die String-Parameter mit dem String, der die Methode aufruft;
Slice(n,m) Gibt die Zeichenfolge zwischen Zeichenfolgenposition n und m;
substr(n,m) Gibt m Strings zurück, beginnend an der String-Position n;
var box = 'Mr.Lee';
console.log(box.concat('Ok!')); // =>Mr.Lee OK!;
console.log(box.slice(3)); // =>Lee;(Alle nachfolgenden Zeichen ab Index 3 abfangen);
console.log(box.substring(3,5)); // =>Le;(Intercept-Zeichen von Index 3 bis Index 5); 4.String-Objekt-String-Positionsmethode
indexOf(str,n) Durchsucht den ersten str rückwärts, beginnend mit Index n, und gibt den gesuchten Indexwert zurück;
lastIndexOf(str,n) Sucht vorwärts nach dem ersten str, beginnend mit Index n, und gibt den gesuchten Indexwert
zurück
var box = 'Mr.Lee ist Lee';
console.log(box.indexOf('L')); // =>3;(Der Indexwert des ersten gesuchten L von vorne nach hinten ist 3);
console.log(box.lastIndexOf('L')); // =>10;(Der Indexwert des ersten von hinten nach vorne gesuchten L ist 10);
console.log(box.indexOf('L',5)); // =>10;(Der Indexwert des ersten L, das vom 5. an rückwärts gesucht wird, ist 10);
//Wenn die zu durchsuchende Zeichenfolge nicht gefunden wird, geben Sie -1;
zurück
// Finde alle L;
var box = 'Mr.Lee ist Lee';
var boxarr = []; var boxarr
var pos = box.indexOf('L'); var pos = box.indexOf('L'); // Ermittelt die Position des ersten L;
boxarr.push(pos);
}
console.log(boxarr); // [3,10]
// trim()-Methode
// ECMAScript5 definiert die trim()-Methode für alle Zeichenfolgen. Diese Methode erstellt eine Kopie der Zeichenfolge, entfernt alle führenden Leerzeichen und Suffixe und gibt dann das Ergebnis zurück
var str = 'Hallo Welt';
var trimstr = str.trim();
console.log(trimstr); // =>hello world; console.log(str); // => Leerzeichen bleiben unverändert. 5. String-Objekt-String-Konvertierungsmethode
toLowerCase(str) Konvertiert alle Zeichenfolgen in Kleinbuchstaben;
toUpperCase(str) Konvertiert alle Zeichenfolgen in Großbuchstaben;
toLocaleLowerCase(str) Konvertiert alle Zeichenfolgen in Kleinbuchstaben und lokalisiert sie;
toLocaleLowerCase(str) Konvertiert alle Zeichenfolgen in Großbuchstaben und lokalisiert sie. 6. Mustervergleichsmethode des String-Objekts string
// Die spezifische Verwendungsmethode wird in den regulären Regeln eingeführt;
match(pattern) Gibt die Teilzeichenfolge in „pattern“ oder „null“ zurück. // Identisch mit „pattern.exec(str);“
ersetzen(Muster,Ersatz)Muster durch Ersatz ersetzen;
search(pattern) Gibt die Startposition des Musters in der Zeichenfolge zurück;
split(pattern) Gibt ein Array zurück, in dem die Zeichenfolge gemäß dem angegebenen Muster aufgeteilt wird;
var box = 'Mr.Lee ist Lee';
var p = /L/g;
console.log(box.match(p)); // =>[L,L];
console.log(box.search(p)); // =>3;
console.log(box.replace(p,'Q')); // =>Mr.Qee ist Qee;
console.log(box.split(' ')); // =>['Mr.Lee','is','Lee'];7
fromCharCode(ascii) Statische Methode, gibt den entsprechenden Wert des ASCII-Codes aus;
localeCompare(str1,str2) Vergleicht zwei Strings und gibt den entsprechenden Wert zurück; 8. String-Objekt-HTML-Methode
// Generiere ein HTML-Tag über JS, was wenig nützt;
var box = "Lee";
console.log(box.link('www.baidu.com')); //21cad4916aabd140f7c21f6d80e9a6bbLee5db79b134e9f6b82c0b36e0489ee08ed;
5 Zusammenfassung
// Aufgrund des grundlegenden Verpackungstyps kann auf grundlegende Typwerte in JS als Objekte zugegriffen werden
//Grundlegende Typmerkmale:
// 1. Jeder Verpackungstyp wird einem Basistyp mit demselben Namen zugeordnet;
// 2. Beim Zugriff auf einen Basistypwert im Lesemodus wird ein Objekt des entsprechenden Basisverpackungstyps erstellt, wodurch Datenoperationen erleichtert werden
// 3. Sobald die Anweisung ausgeführt wird, die den Basistypwert bedient, wird das neu erstellte Verpackungsobjekt sofort zerstört
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Eine eingehende Analyse der Bootstrap-Listengruppenkomponente
- Detaillierte Erläuterung des JavaScript-Funktions-Curryings
- Vollständiges Beispiel für die Generierung von JS-Passwörtern und die Erkennung der Stärke (mit Download des Demo-Quellcodes)
- Angularjs integriert WeChat UI (weui)
- Wie man mit JavaScript schnell zwischen traditionellem Chinesisch und vereinfachtem Chinesisch wechselt und wie Websites den Wechsel zwischen vereinfachtem und traditionellem Chinesisch unterstützen – Javascript-Kenntnisse

