 Web-Frontend
Web-Frontend H5-Tutorial
H5-Tutorial Multiperspektivische 3D-realistische HTML5-Wasserwellenanimation _html5-Tutorial-Fähigkeiten
Multiperspektivische 3D-realistische HTML5-Wasserwellenanimation _html5-Tutorial-FähigkeitenMultiperspektivische 3D-realistische HTML5-Wasserwellenanimation _html5-Tutorial-Fähigkeiten
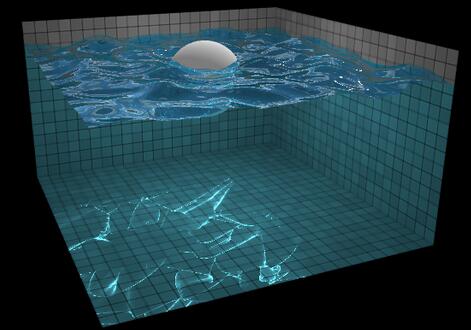
Dies ist ein 3D-Wasserwellen-Spezialeffekt, der auf HTML5 basiert. Sein Effekt ist sehr realistisch. Wir können die „G“-Taste drücken, um die Steine im Pool auf und ab zu schweben, und die „L“-Taste drücken Lichteffekte hinzufügen. Das Design ist ziemlich perfekt. Bitte beachten Sie gleichzeitig, dass diese 3D-Wasserwellenanimation auf der WebGL-Rendering-Technologie basiert. Sie können mehr über WebGL erfahren.
Online-Vorschau Quellcode-Download
HTML-Code
- img id="tiles" src="tiles.jpg">
- img id="xneg" src="xneg.jpg">
- img id="xpos" src="xpos.jpg">
- img id="ypos" src="ypos.jpg">
- img id="zneg" src="zneg.jpg">
- img id="zpos" src="zpos.jpg">
JavaScript-Code
- Funktion Water() {
- var vertexShader = '
- variierende vec2 koord;
- void main() {
- coord = gl_Vertex.xy * 0.5 0.5;
- gl_Position = vec4(gl_Vertex.xyz, 1.0);
- }
- ';
- this.plane = GL.Mesh.plane();
- if (!GL.Texture.canUseFloatingPointTextures()) {
- throw neu Fehler('Für diese Demo ist die Erweiterung OES_texture_float erforderlich');
- }
- var filter = GL.Texture.canUseFloatingPointLinearFiltering() ? gl.LINEAR : gl.NEAREST;
- this.textureA = new GL.Texture(256, 256, { type: gl.FLOAT, Filter: Filter});
- this.textureB = new GL.Texture(256, 256, { type: gl.FLOAT, Filter: Filter });
- this.dropShader = new GL.Shader(vertexShader, '
- const float PI = 3.141592653589793;
- einheitliche Sampler2D-Textur;
- einheitliches vec2 center;
- einheitlicher Schwimmradius;
- gleichmäßige Schwimmstärke;
- variierende vec2 koord;
- void main() {
- /* Scheitelpunktinformationen abrufen */
- vec4 info = texture2D(texture, coord);
- /* füge den Abfall zur Höhe hinzu */
- float drop = max(0.0, 1.0 - length(center * 0.5 0.5 - coord) / radius);
- drop = 0,5 - cos(drop * PI) * 0,5;
- info.r = drop * strength;
- gl_FragColor = info;
- }
- ');
- this.updateShader = new GL.Shader(vertexShader, '
- einheitliche Sampler2D-Textur;
- uniformes vec2 delta;
- variierende vec2 koord;
- void main() {
- /* Scheitelpunktinformationen abrufen */
- vec4 info = texture2D(texture, coord);
- /* durchschnittliche Nachbarngröße berechnen */
- vec2 dx = vec2(delta.x, 0.0);
- vec2 dy = vec2(0.0, delta.y);
- Float-Durchschnitt = (
- texture2D(texture, coord - dx).r
- texture2D(texture, coord - dy).r
- texture2D(texture, coord dx).r
- texture2D(texture, coord dy).r
- ) * 0,25;
- /* Ändere die Geschwindigkeit, um sich in Richtung des Durchschnitts zu bewegen.*/
- info.g = (average - info.r) * 2.0;
- /* Dämpft die Geschwindigkeit ein wenig, damit Wellen nicht ewig dauern.*/
- info.g *= 0,995;
- /* verschieben den Scheitelpunkt entlang der Geschwindigkeit */
- info.r = info.g;
- gl_FragColor = info;
- }
- ');
- this.normalShader = new GL.Shader(vertexShader, '
- einheitliche Sampler2D-Textur;
- uniformes vec2 delta;
- variierende vec2 koord;
- void main() {
- /* Scheitelpunktinformationen abrufen */
- vec4 info = texture2D(texture, coord);
- /* aktualisiere das normale */
- vec3 dx = vec3(delta.x, texture2D(texture, vec2(coord.x delta.x, coord.y)).r - info.r, 0.0);
- vec3 dy = vec3(0.0, texture2D(texture, vec2(coord.x, coord.y delta.y)).r - info.r, delta.y);
- info.ba = normalize(cross(dy, dx)).xz;
- gl_FragColor = info;
- }
- ');
- this.sphereShader = new GL.Shader(vertexShader, '
- einheitliche Sampler2D-Textur;
- uniform vec3 oldCenter;
- uniform vec3 newCenter;
- einheitlicher Schwimmradius;
- variierende vec2 koord;
- float volumeInSphere(vec3 center) {
- vec3 toCenter = vec3(coord.x * 2.0 - 1.0, 0.0, coord.y * 2.0 - 1.0) - center;
- float t = length(toCenter) / radius;
- float dy = exp(-pow(t * 1.5, 6.0));
- float ymin = min(0.0, center.y - dy);
- float ymax = min(max(0.0, center.y dy), ymin 2.0 * dy);
- return (ymax - ymin) * 0,1;
- }
- void main() {
- /* Scheitelpunktinformationen abrufen */
- vec4 info = texture2D(texture, coord);
- /* alte Volume hinzufügen */
- info.r = volumeInSphere(oldCenter);
- /* subtrahiere das neue Volumen */
- info.r -= volumeInSphere(newCenter);
- gl_FragColor = info;
- }
- ');
- }
- Water.prototype.addDrop = Funktion(x, y, Radius, Stärke) {
- var this_ = this;
- dieses.textureB.drawTo(function() {
- this_.textureA.bind();
- this_.dropShader.uniforms({
- Mitte: [x, y],
- Radius: Radius,
- Stärke: Stärke
- }).draw(this_.plane);
- });
- this.textureB.swapWith(this.textureA);
- };
- Water.prototype.moveSphere = Funktion(oldCenter, newCenter, radius) {
- var this_ = this;
- this.textureB.drawTo(function() {
- this_.textureA.bind();
- this_.sphereShader.uniforms({
- oldCenter: oldCenter,
- newCenter: newCenter,
- Radius: Radius
- }).draw(this_.plane);
- });
- this.textureB.swapWith(this.textureA);
- };
- Water.prototype.stepSimulation = function() {
- var this_ = this;
- this.textureB.drawTo(function() {
- this_.textureA.bind();
- this_.updateShader.uniforms({
- delta: [1 / this_.textureA.width, 1 / this_.textureA.height]
- }).draw(this_.plane);
- });
- this.textureB.swapWith(this.textureA);
- };
- Water.prototype.updateNormals = function() {
- var this_ = this;
- this.textureB.drawTo(function() {
- this_.textureA.bind();
- this_.normalShader.uniforms({
- delta: [1 / this_.textureA.width, 1 / this_.textureA.height]
- }).draw(this_.plane);
- });
- this.textureB.swapWith(this.textureA);
- };
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助.
 Dekonstruieren von H5 -Code: Tags, Elemente und AttributeApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Dekonstruieren von H5 -Code: Tags, Elemente und AttributeApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMDer HTML5 -Code besteht aus Tags, Elementen und Attributen: 1. Das Tag definiert den Inhaltstyp und ist von Winkelklammern umgeben, wie z. 2. Elemente bestehen aus Start -Tags, Inhalten und End -Tags wie Inhalten. 3. Attribute definieren Schlüsselwertpaare im Start-Tag und verbessern Funktionen, z. B.. Dies sind die grundlegenden Einheiten zum Aufbau von Webstruktur.
 H5 -Code verstehen: Die Grundlagen von HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5 -Code verstehen: Die Grundlagen von HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AMHTML5 ist eine Schlüsseltechnologie zum Aufbau moderner Webseiten und bietet viele neue Elemente und Funktionen. 1. HTML5 führt semantische Elemente wie usw. ein, die die Webseitenstruktur und die SEO verbessern. 2. Support Multimedia-Elemente und Einbetten von Medien ohne Plug-Ins. 3. Formulare verbessern neue Eingangstypen und Überprüfungseigenschaften und vereinfachen Sie den Überprüfungsprozess. 4. Bieten Sie Offline- und lokale Speicherfunktionen an, um die Leistung der Webseiten und die Benutzererfahrung zu verbessern.
 H5 -Code: Best Practices für WebentwicklerApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
H5 -Code: Best Practices für WebentwicklerApr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AMZu den Best Practices für den H5 -Code gehören: 1. Verwenden Sie korrekte DocType -Deklarationen und Zeichenkodierung; 2. Verwenden Sie semantische Tags; 3.. HTTP -Anfragen reduzieren; 4. Verwenden Sie asynchrone Laden; 5. Bilder optimieren. Diese Praktiken können die Effizienz, Wartbarkeit und Benutzererfahrung von Webseiten verbessern.
 H5: Die Entwicklung von Webstandards und TechnologienApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AM
H5: Die Entwicklung von Webstandards und TechnologienApr 15, 2025 am 12:12 AMWebstandards und -technologien haben sich bisher aus HTML4, CSS2 und einfachem JavaScript entwickelt und haben erhebliche Entwicklungen erfahren. 1) HTML5 führt APIs wie Leinwand und Webstorage ein, die die Komplexität und Interaktivität von Webanwendungen verbessern. 2) CSS3 fügt Animations- und Übergangsfunktionen hinzu, um die Seite effektiver zu gestalten. 3) JavaScript verbessert die Entwicklungseffizienz und die Lesbarkeit der Code durch moderne Syntax von Node.js und ES6, wie z. B. Pfeilfunktionen und Klassen. Diese Änderungen haben die Entwicklung von Leistungsoptimierung und Best Practices von Webanwendungen gefördert.
 Ist H5 eine Abkürzung für HTML5? Erforschen der DetailsApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Ist H5 eine Abkürzung für HTML5? Erforschen der DetailsApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMH5 ist nicht nur die Abkürzung von HTML5, sondern auch ein breiteres Ökosystem der modernen Webentwicklungstechnologie: 1. H5 enthält HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript und verwandte APIs und Technologien; 2. Es bietet eine reichhaltigere, interaktive und reibungslose Benutzererfahrung und kann nahtlos auf mehreren Geräten ausgeführt werden. 3. Mit dem H5 -Technologie -Stack können Sie reaktionsschnelle Webseiten und komplexe interaktive Funktionen erstellen.
 H5 und HTML5: häufig verwendete Begriffe in der WebentwicklungApr 13, 2025 am 12:01 AM
H5 und HTML5: häufig verwendete Begriffe in der WebentwicklungApr 13, 2025 am 12:01 AMH5 und HTML5 beziehen sich auf dasselbe, nämlich HTML5. HTML5 ist die fünfte Version von HTML, die neue Funktionen wie semantische Tags, Multimedia -Support, Leinwand und Grafiken, Offline -Speicher und lokaler Speicher bietet, die Ausdrucksfähigkeit und Interaktivität von Webseiten verbessert.
 Worauf bezieht sich H5? Erforschen des KontextesApr 12, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Worauf bezieht sich H5? Erforschen des KontextesApr 12, 2025 am 12:03 AMH5REFERSTOHTML5, ApivotaltechnologyInwebdevelopment.1) HTML5IntroducesNewelementsandapisrich, Dynamicwebapplications.2) ITSUPP ortsmultimediaWitHoutPlugins, BETHINGINGUSEREXPERICERCROSSDEVICES.3) SEMANTICELEMENTSIMPROVEPENTENTENTENTRUCTENTRUCTELUREANDSEO.4) H5'SRespo
 H5: Tools, Frameworks und Best PracticesApr 11, 2025 am 12:11 AM
H5: Tools, Frameworks und Best PracticesApr 11, 2025 am 12:11 AMZu den Tools und Frameworks, die in der H5 -Entwicklung gemeistert werden müssen, gehören Vue.js, React und WebPack. 1.Vue.js eignet sich zum Erstellen von Benutzeroberflächen und unterstützt die Komponentenentwicklung. 2. Die Rendern des Seitenrenders über virtuelle DOM optimiert, geeignet für komplexe Anwendungen. 3.Webpack wird zur Modulverpackung und zur Optimierung der Ressourcenlast verwendet.


Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

Dreamweaver Mac
Visuelle Webentwicklungstools

PHPStorm Mac-Version
Das neueste (2018.2.1) professionelle, integrierte PHP-Entwicklungstool

MantisBT
Mantis ist ein einfach zu implementierendes webbasiertes Tool zur Fehlerverfolgung, das die Fehlerverfolgung von Produkten unterstützen soll. Es erfordert PHP, MySQL und einen Webserver. Schauen Sie sich unsere Demo- und Hosting-Services an.

SAP NetWeaver Server-Adapter für Eclipse
Integrieren Sie Eclipse mit dem SAP NetWeaver-Anwendungsserver.

WebStorm-Mac-Version
Nützliche JavaScript-Entwicklungstools




