Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Beispielanalyse verknüpfter Listen in Java
Beispielanalyse verknüpfter Listen in Java
- PHPznach vorne
- 2023-05-31 17:13:07805Durchsuche
Frage 1
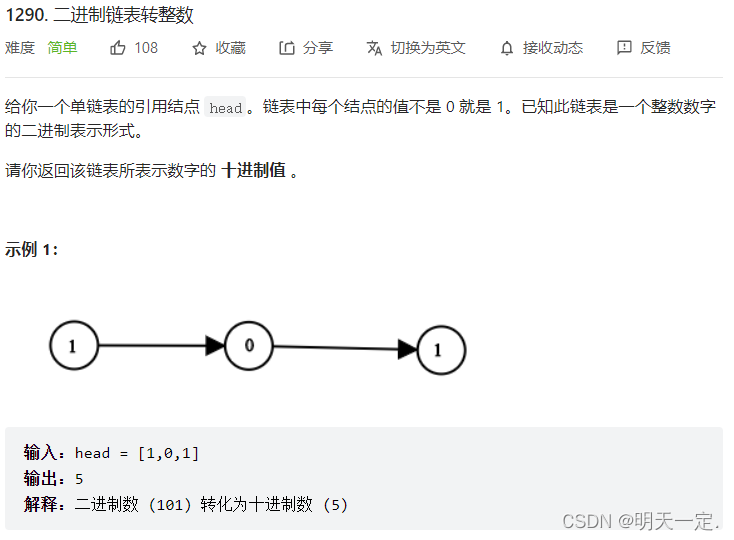
Lösung
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int getDecimalValue(ListNode head) {
int[] arr = new int[31];
int index = 0;
int ans = 0;
while(head!=null){
arr[index] = head.val;
index++;
head = head.next;
}
for(int i = 0;i<index;i++){
if(arr[i]==1){
ans+=(1<<(index-1-i));
}
}
return ans;
}
}Frage 2
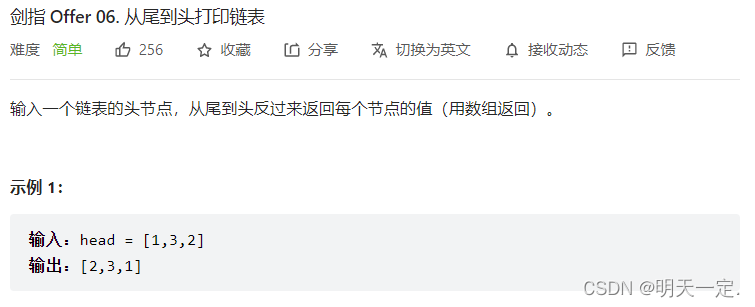
Lösung
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
int index = 0;
ListNode h = head;
while(head!=null){
head = head.next;
index++;
}
int[] arr = new int[index];
while(h!=null){
arr[index-1] = h.val;
index--;
h = h.next;
}
return arr;
}
}Frage 3
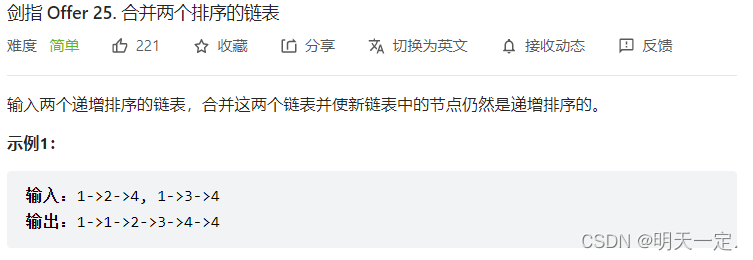
Lösung
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode ans = node;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val<=l2.val){
node.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
node.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
if(l1!=null){
node.next = l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
node.next = l2;
}
return ans.next;
}
}Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBeispielanalyse verknüpfter Listen in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
Stellungnahme:
Dieser Artikel ist reproduziert unter:yisu.com. Bei Verstößen wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn löschen
Vorheriger Artikel:Wie SpringBoot RabbitMQ integriertNächster Artikel:Wie SpringBoot RabbitMQ integriert

