Heim >Datenbank >MySQL-Tutorial >Beispielanalyse des Klassifizierungsrankings und der Gruppierung von TOP N in MySQL
Beispielanalyse des Klassifizierungsrankings und der Gruppierung von TOP N in MySQL
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBnach vorne
- 2023-05-28 23:10:041864Durchsuche
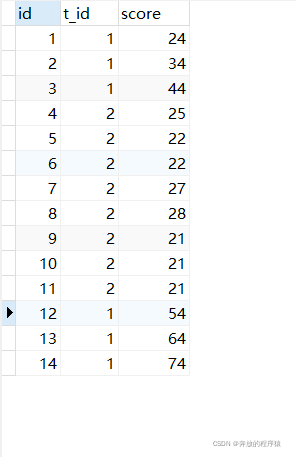
表结构
学生表如下:
CREATE TABLE `t_student` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `t_id` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学科id', `score` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '分数', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) );
数据如下:
题目一:获取每个科目下前五成绩排名(允许并列)
允许并列情况可能存在如4、5名成绩并列情况,会导致取前4名得出5条数据,取前5名也是5条数据。
SELECT s1.* FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score < s2.score GROUP BY s1.id HAVING COUNT( s2.id ) < 5 ORDER BY s1.t_id, s1.score DESC
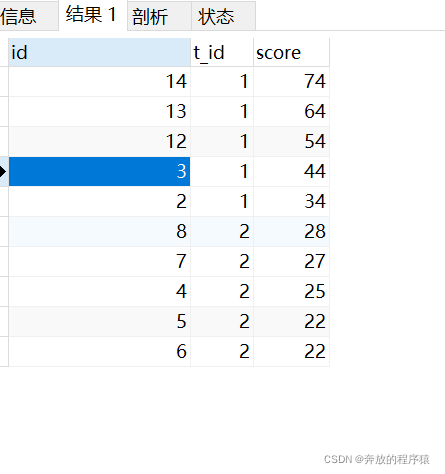
ps:取前4名时
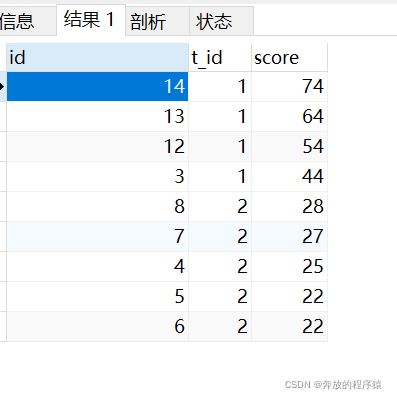
分析:
1.自身左外连接,得到所有的左边值小于右边值的集合。以t_id=1时举例,24有5个成绩大于他的(74、64、54、44、34),是第6名,34只有4个成绩大于他的,是第5名......74没有大于他的,是第一名。
SELECT * FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score < s2.score
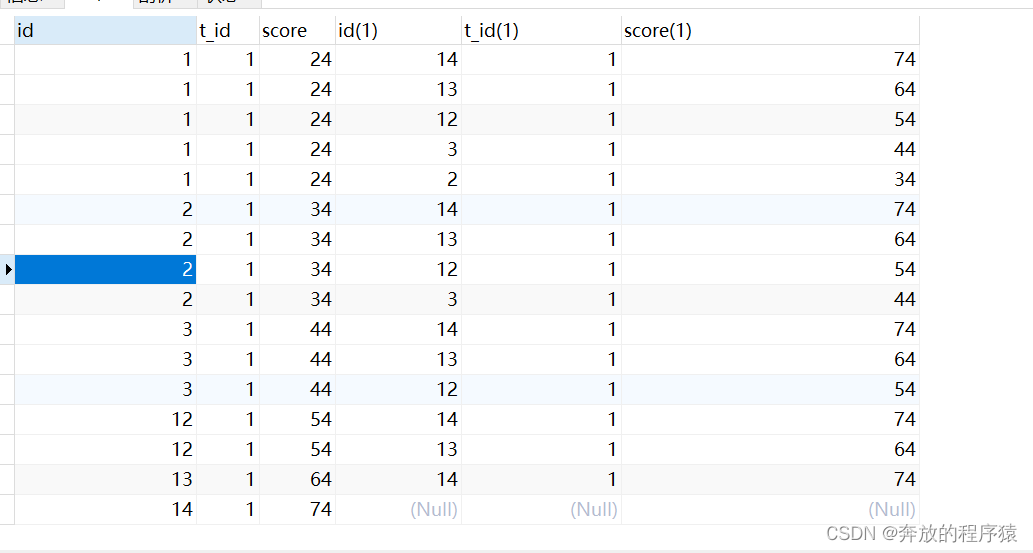
2. 把总结的规律转换成SQL表示出来,就是group by 每个student 的 id(s1.id),Having统计这个id下面有多少个比他大的值(s2.id)
SELECT s1.* FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score < s2.score GROUP BY s1.id HAVING COUNT( s2.id ) < 5
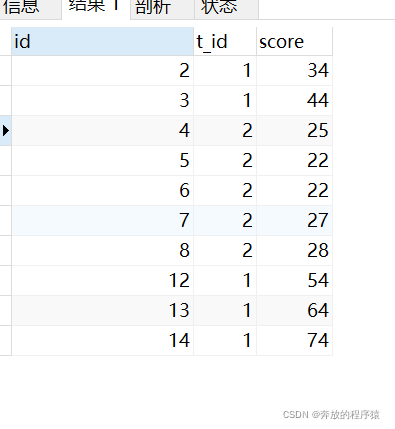
3. 最后根据 t_id 分类,score 倒序排序即可。
题目二:获取每个科目下最后两名学生的成绩平均值
取最后两名成绩
SELECT s1.* FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score GROUP BY s1.id HAVING COUNT( s1.id )< 2 ORDER BY s1.t_id, s1.score
并列存在情况下可能导致筛选出的同一t_id 下结果条数大于2条,但题目要求是取最后两名的平均值,多条平均后还是本身,故不必再对其处理,可以满足题目要求。
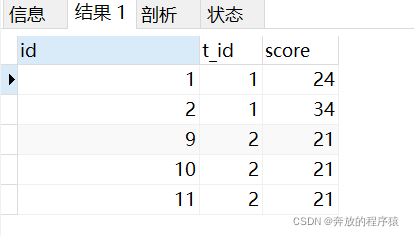
分组求平均值:
SELECT t_id,AVG(score) FROM ( SELECT s1.* FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score GROUP BY s1.id HAVING COUNT( s1.id )< 2 ORDER BY s1.t_id, s1.score ) tt GROUP BY t_id
结果:
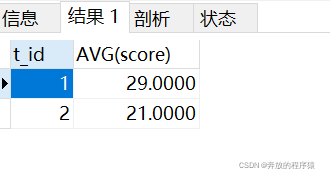
分析:
1. 查询出所有t1.score>t2.score 的记录
SELECT s1.*,s2.* FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score
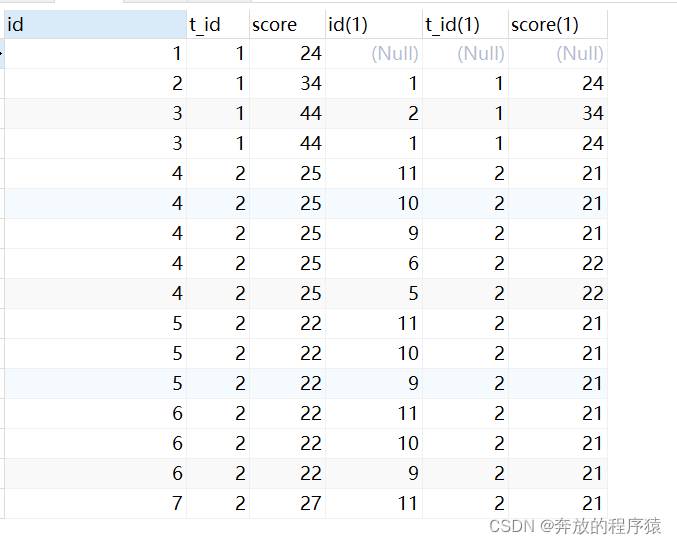
2. group by s.id 去重,having 计数取2条
3. group by t_id 分别取各自学科的然后avg取均值
题目三:获取每个科目下前五成绩排名(不允许并列)
SELECT * FROM ( SELECT s1.*, @rownum := @rownum + 1 AS num_tmp, @incrnum := CASE WHEN @rowtotal = s1.score THEN @incrnum WHEN @rowtotal := s1.score THEN @rownum END AS rownum FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score, ( SELECT @rownum := 0, @rowtotal := NULL, @incrnum := 0 ) AS it GROUP BY s1.id ORDER BY s1.t_id, s1.score DESC ) tt GROUP BY t_id, score, rownum HAVING COUNT( rownum )< 5
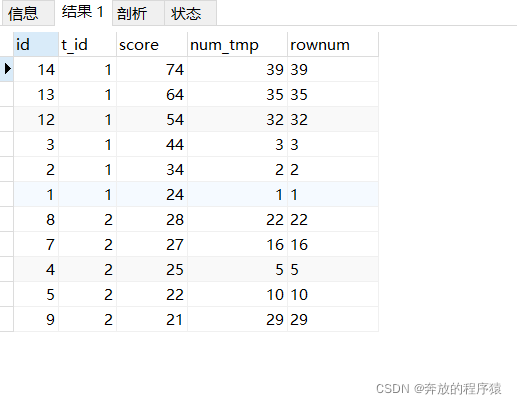
分析:
1.引入辅助参数
SELECT s1.*, @rownum := @rownum + 1 AS num_tmp, @incrnum := CASE WHEN @rowtotal = s1.score THEN @incrnum WHEN @rowtotal := s1.score THEN @rownum END AS rownum FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score, ( SELECT @rownum := 0, @rowtotal := NULL, @incrnum := 0 ) AS it
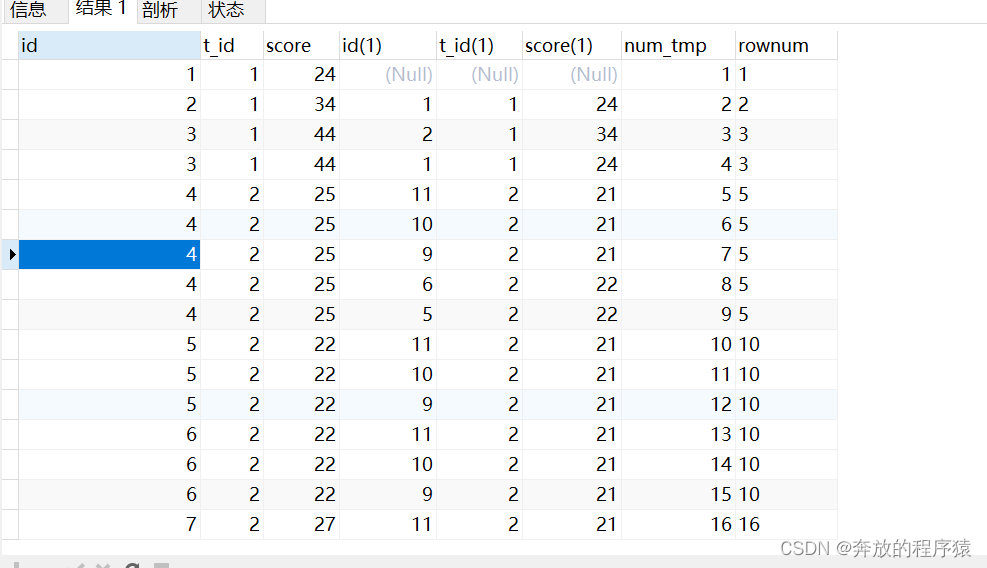
2.去除重复s1.id,分组排序
SELECT s1.*, @rownum := @rownum + 1 AS num_tmp, @incrnum := CASE WHEN @rowtotal = s1.score THEN @incrnum WHEN @rowtotal := s1.score THEN @rownum END AS rownum FROM student s1 LEFT JOIN student s2 ON s1.t_id = s2.t_id AND s1.score > s2.score, ( SELECT @rownum := 0, @rowtotal := NULL, @incrnum := 0 ) AS it GROUP BY s1.id ORDER BY s1.t_id, s1.score DESC
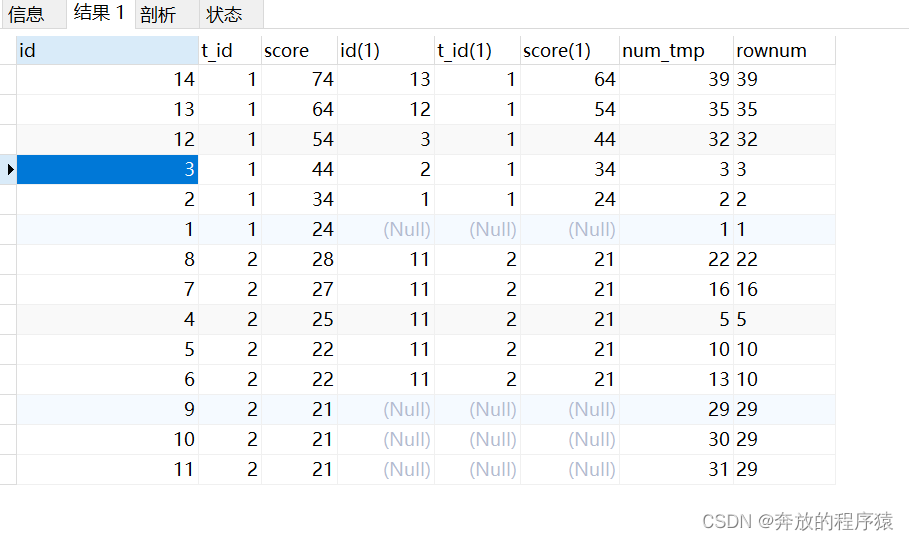
3.GROUP BY t_id, score, rownum 然后 HAVING 取前5条不重复的
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBeispielanalyse des Klassifizierungsrankings und der Gruppierung von TOP N in MySQL. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

