Heim >Betrieb und Instandhaltung >Nginx >So stellen Sie CentOS7 Docker Nginx bereit und führen es aus
So stellen Sie CentOS7 Docker Nginx bereit und führen es aus
- WBOYnach vorne
- 2023-05-21 18:19:061383Durchsuche
1. Ressourcenvorbereitung
Dockerfile-Datei
# "ported" by adam miller <maxamillion@fedoraproject.org> from # https://github.com/fedora-cloud/fedora-dockerfiles # # originally written for fedora-dockerfiles by # scollier <scollier@redhat.com> from centos:centos7 maintainer the centos project <cloud-ops@centos.org> run yum -y update; yum clean all run yum -y install epel-release tar ; yum clean all run yum -y install nginx ; yum clean all add nginx.conf /opt/deploy/nginx/nginx.conf run echo "daemon off;" >> /opt/deploy/nginx/nginx.conf #run curl https://git.centos.org/sources/httpd/c7/acf5cccf4afaecf3afeb18c50ae59fd5c6504910 \ # | tar -xz -c /usr/local/nginx/html \ # --strip-components=1 #run sed -i -e 's/apache/nginx/g' -e '/apache_pb.gif/d' \ # /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html expose 80 #cmd [ "/usr/local/nginx/sbin" ]
Hinweis: Der Pfad muss auf dem System vorhanden sein und der Datei
nginx.conf entsprechen
# for more information on configuration, see:
# * official english documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * official russian documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /usr/logs/nginx/error.log;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /usr/logs/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
# load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# see http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
#include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
index index.html index.htm;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
autoindex on;
}
# redirect server error pages to the static page /40x.html
#
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
# proxy the php scripts to apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the php scripts to fastcgi server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param script_filename /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of ip-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# root html;
# location / {
# }
#}
# https server
#
#server {
# listen 443;
# server_name localhost;
# root html;
# ssl on;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_protocols sslv2 sslv3 tlsv1;
# ssl_ciphers high:!anull:!md5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# }
#}
}Hinweis: Der Pfad muss vorhanden sein und dem System entsprechen
2. Führen Sie den Build-Image-Befehl aus
Code kopieren Der Code lautet wie folgt:
[root@localhost nginx]# sudo docker build --rm --tag os7/nginx:centos7 .
Screenshot der Ausführung Ergebnis:
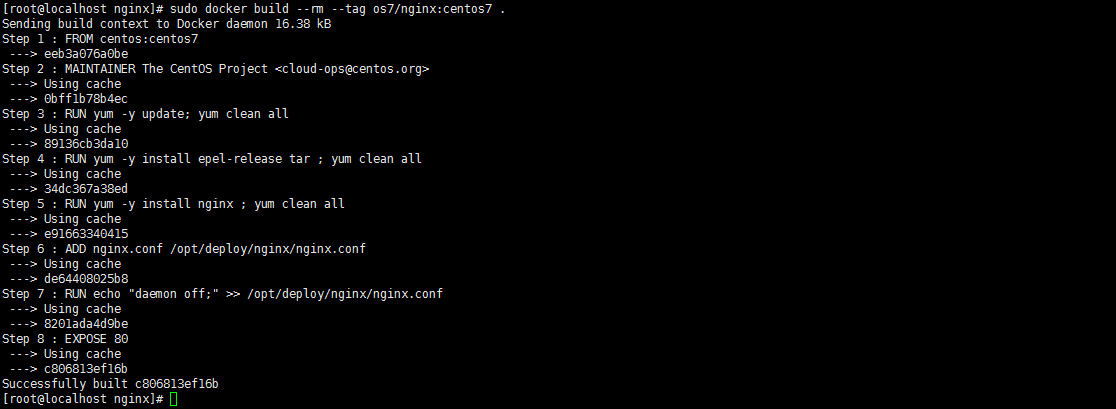
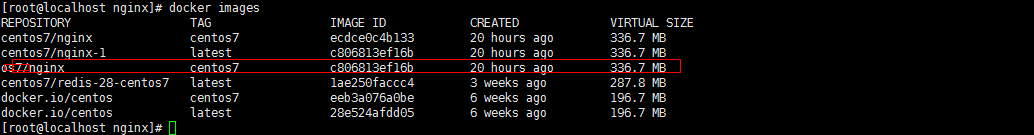
3. Sehen Sie sich das Bild an. Wurden Docker-Images erfolgreich installiert und erstellt? bin/bash
 Hinweis: Wenn die IP 192.168.32.129 ist, müssen Sie
Hinweis: Wenn die IP 192.168.32.129 ist, müssen Sie
192.168.32.129 zu /etc/hosts localhost hinzufügen
5. Überprüfen Sie, ob der Container erfolgreich erstellt wurde, und starten Sie Docker ps
6. Testen Sie, ob auf Curl http://192.168.32.129 erfolgreich zugegriffen wurde: 81

Diese Verbindung wurde abgelehnt. Was soll ich tun? Es gibt eine Möglichkeit, das Problem zu lösen: Geben Sie zuerst den Container ein. Geben Sie den Docker exec -i -t small_hodgkin /bin/sh ein.
 nginx
nginx

Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo stellen Sie CentOS7 Docker Nginx bereit und führen es aus. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

