Heim >Betrieb und Instandhaltung >Sicherheit >So verwenden Sie sqlmapapi, um einen Scan zu starten
So verwenden Sie sqlmapapi, um einen Scan zu starten
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBnach vorne
- 2023-05-20 23:13:431617Durchsuche
sqlmap可谓是sql注入探测的神器,但是利用sqlmap测试SQL注入的效率很低,每一个url都需要手动测试。sqlmap的开发者新加了sqlmapapi.py,可以直接通过接口调用来操作,简化了sqlmap命令执行方式。
sqlmap api分为服务端和客户端,sqlmap api有两种模式,一种是基于HTTP协议的接口模式,一种是基于命令行的接口模式。
sqlmap源码下载地址:https://github.com/sqlmapproject/sqlmap/
一、查看帮助
python sqlmapapi.py -h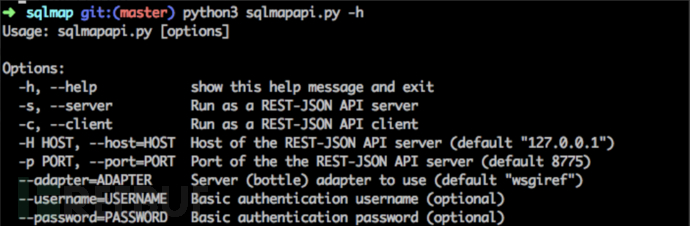
二、开启api服务端
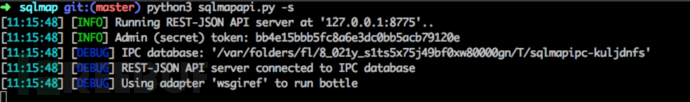
在使用API服务之前,需要先启动API服务器,无论是基于HTTP协议还是基于命令行的接口模式。要开启API服务端,只需运行以下命令:python sqlmapapi.py -s
命令成功后,在命令行中会返回一些信息。以下命令大概的意思是api服务端在本地8775端口上运行,admin token为c6bbb0c1f86b7d7bc2ed6ce3e3bbdcb5等
 但是通过上面的这种方式开启api服务端有一个缺点,当服务端和客户端不是一台主机会连接不上,因此如果要解决这个问题,可以通过输入以下命令来开启api服务端:python sqlmapapi.py -s -H "0.0.0.0" -p 8775
但是通过上面的这种方式开启api服务端有一个缺点,当服务端和客户端不是一台主机会连接不上,因此如果要解决这个问题,可以通过输入以下命令来开启api服务端:python sqlmapapi.py -s -H "0.0.0.0" -p 8775
命令成功后,远程客户端就可以通过指定远程主机IP和端口来连接到API服务端。
三、基于命令行的接口模式
3.1、开启客户端,发起注入命令
python sqlmapapi.py -c
如果是客户端和服务端不是同一台计算机的话,输入以下命令:
python sqlmapapi.py -c -H "192.168.1.101" -p 8775
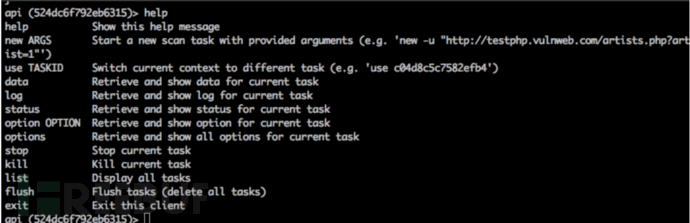
3.2、help命令,获取所有命令
help 显示帮助信息 new ARGS 开启一个新的扫描任务 use TASKID 切换 taskid data 获取当前任务返回的数据 log 获取当前任务的扫描日志 status 获取当前任务的扫描状态 option OPTION 获取当前任务的选项 options 获取当前任务的所有配置信息 stop 停止当前任务 kill 杀死当前任务 list 显示所有任务列表 flush 清空所有任务 exit 退出客户端
3.3、检测注入
3.3.1.new命令
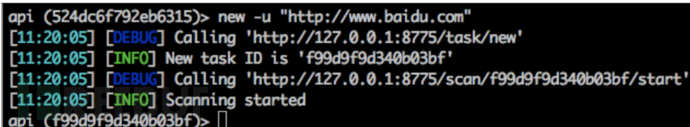
new -u "url"
实例:new -u "http://www.baidu.com"
虽然我们仅仅只指定了-u参数,但是从返回的信息中可以看出,输入new命令后,首先先请求了/task/new,来创建一个新的taskid,后又发起了一个请求去开始任务,因此可以发现该模式实质也是基于HTTP协议的。
3.3.2. status 命令
获取该任务的扫描状态,若返回内容中的status字段为terminated,说明扫描完成,若返回内容中的status字段为run,说明扫描还在进行中。下图是扫描完成的截图:
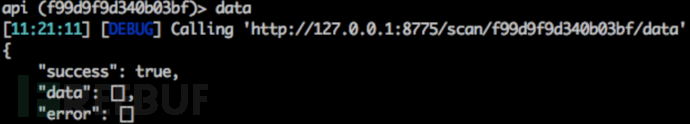
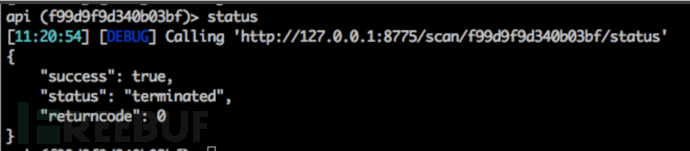 3.3.3. data 命令
3.3.3. data 命令
如果返回的数据中data字段非空,则可以得出注入已经成功。这个例子展示了一个含有 SQL 注入的返回内容,其中包含数据库类型、payload 和注入参数等信息。
四、基于HTTP协议的接口模式
简单介绍下sqlmapapi.py的h基于http接口调用模式的主要函数,进入到lib/utils/api.py的server类,可以发现通过向server提交数据进行与服务的交互。 一共分为3种类型。
Users' methods 用户方法
Admin function 管理函数
sqlmap core interact functions 核心交互函数
可以提交数据的种类如下:
4.1、用户方法
@get("/task/new")
@get("/task/new")
def task_new():
"""
Create a new task
"""
taskid = encodeHex(os.urandom(8), binary=False)
remote_addr = request.remote_addr
DataStore.tasks[taskid] = Task(taskid, remote_addr)
logger.debug("Created new task: '%s'" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True, "taskid": taskid})
@get("/task/delete")
@get("/task/<taskid>/delete")
def task_delete(taskid):
"""
Delete an existing task
"""
if taskid in DataStore.tasks:
DataStore.tasks.pop(taskid)
logger.debug("(%s) Deleted task" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True})
else:
response.status = 404
logger.warning("[%s] Non-existing task ID provided to task_delete()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Non-existing task ID"})</taskid>
4.2、核心交互函数
@get("/option/list")
@post("/option/get")
@post("/option/set")
@post("/option/<taskid>/set")
def option_set(taskid):
"""
Set value of option(s) for a certain task ID
"""
if taskid not in DataStore.tasks:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to option_set()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
if request.json is None:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid JSON options provided to option_set()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid JSON options"})
for option, value in request.json.items():
DataStore.tasks[taskid].set_option(option, value)
logger.debug("(%s) Requested to set options" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True})</taskid>
@post("/scan/start")
@post("/scan/<taskid>/start")
def scan_start(taskid):
"""
Launch a scan
"""
if taskid not in DataStore.tasks:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to scan_start()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
if request.json is None:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid JSON options provided to scan_start()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid JSON options"})
# Initialize sqlmap engine's options with user's provided options, if any
for option, value in request.json.items():
DataStore.tasks[taskid].set_option(option, value)
# Launch sqlmap engine in a separate process
DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_start()
logger.debug("(%s) Started scan" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True, "engineid": DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_get_id()})</taskid>
@get("/scan/stop")
@get("/scan/<taskid>/stop")
def scan_stop(taskid):
"""
Stop a scan
"""
if (taskid not in DataStore.tasks or DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_process() is None or DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_has_terminated()):
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to scan_stop()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_stop()
logger.debug("(%s) Stopped scan" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True})</taskid>
@get("/scan/kill")
@get("/scan/<taskid>/kill")
def scan_kill(taskid):
"""
Kill a scan
"""
if (taskid not in DataStore.tasks or DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_process() is None or DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_has_terminated()):
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to scan_kill()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_kill()
logger.debug("(%s) Killed scan" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True})</taskid>
@get("/scan/status")
@get("/scan/<taskid>/status")
def scan_status(taskid):
"""
Returns status of a scan
"""
if taskid not in DataStore.tasks:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to scan_status()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
if DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_process() is None:
status = "not running"
else:
status = "terminated" if DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_has_terminated() is True else "running"
logger.debug("(%s) Retrieved scan status" % taskid)
return jsonize({
"success": True,
"status": status,
"returncode": DataStore.tasks[taskid].engine_get_returncode()
})</taskid>
@get("/scan/data")
@get("/scan/<taskid>/data")
def scan_data(taskid):
"""
Retrieve the data of a scan
"""
json_data_message = list()
json_errors_message = list()
if taskid not in DataStore.tasks:
logger.warning("[%s] Invalid task ID provided to scan_data()" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": False, "message": "Invalid task ID"})
# Read all data from the IPC database for the taskid
for status, content_type, value in DataStore.current_db.execute("SELECT status, content_type, value FROM data WHERE taskid = ? ORDER BY id ASC", (taskid,)):
json_data_message.append({"status": status, "type": content_type, "value": dejsonize(value)})
# Read all error messages from the IPC database
for error in DataStore.current_db.execute("SELECT error FROM errors WHERE taskid = ? ORDER BY id ASC", (taskid,)):
json_errors_message.append(error)
logger.debug("(%s) Retrieved scan data and error messages" % taskid)
return jsonize({"success": True, "data": json_data_message, "error": json_errors_message})</taskid>
@get("/scan/log")
@get("/download/")
4.3、管理函数
@get("/admin/list")
@get("/admin/list")
@get("/admin/<token>/list")
def task_list(token=None):
"""
Pull task list
"""
tasks = {}
for key in DataStore.tasks:
if is_admin(token) or DataStore.tasks[key].remote_addr == request.remote_addr:
tasks[key] = dejsonize(scan_status(key))["status"]
logger.debug("(%s) Listed task pool (%s)" % (token, "admin" if is_admin(token) else request.remote_addr))
return jsonize({"success": True, "tasks": tasks, "tasks_num": len(tasks)})</token>
@get("/admin//flush")
@get("/admin/flush")
@get("/admin/<token>/flush")
def task_flush(token=None):
"""
Flush task spool (delete all tasks)
"""
for key in list(DataStore.tasks):
if is_admin(token) or DataStore.tasks[key].remote_addr == request.remote_addr:
DataStore.tasks[key].engine_kill()
del DataStore.tasks[key]
logger.debug("(%s) Flushed task pool (%s)" % (token, "admin" if is_admin(token) else request.remote_addr))
return jsonize({"success": True})</token>
从sqlmapapi.py文件分析,提取调用关系。这些操作可以充分满足我们的测试需求,因此可以利用它们来进行批量操作。
5. Verwenden Sie sqlmapapi, um einen Scan zu starten
sqlmapapi.py bietet praktischerweise einen HTTP-Anforderungseintrag, aber wenn Sie es verwenden, können Sie nur das Endergebnis erhalten, ob während der Injektion welche Art von Anforderungen initiiert werden sollen Scannen, und wie viele gibt es? Es ist schwierig, die Anfrage nach dem Durchkämmen des SQLMAP-Quellcodes zu erhalten. Anhand der Abbildung können Sie den spezifischen Speicherort der Anfrage auf Nutzlastebene ermitteln. Wenn Sie wissen möchten, welche Art von Anfrage initiiert wurde und wie viele Anfragen, müssen Sie hier nur benutzerdefinierten Code hinzufügen.
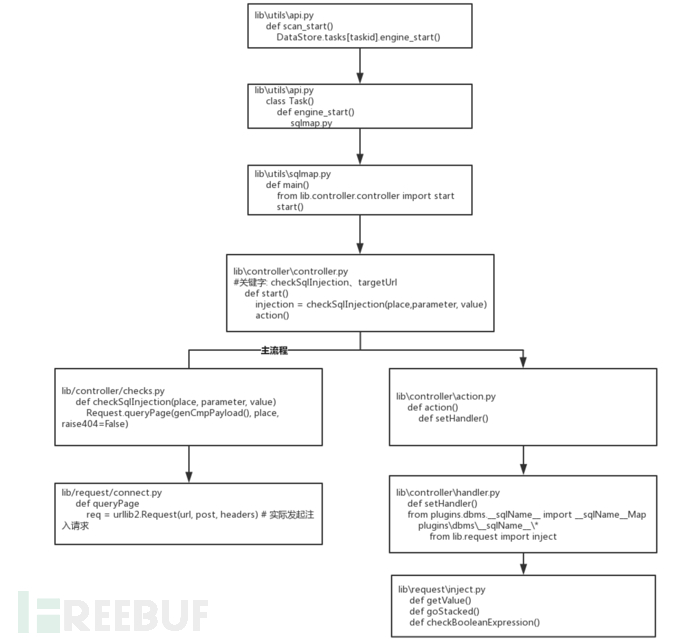
6. Implementierungsprozess der SQL-Injection-Automatisierung
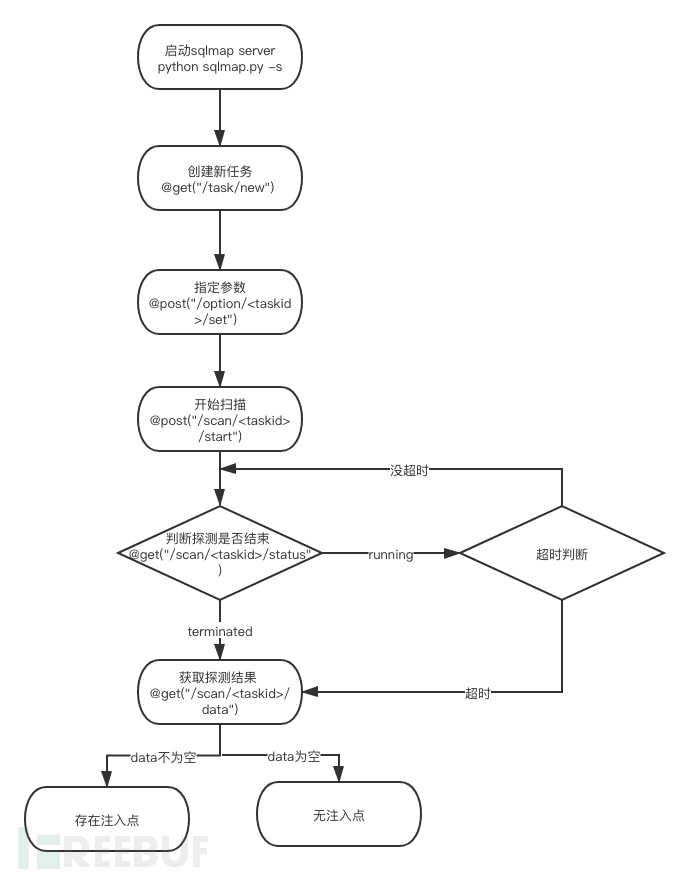
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo verwenden Sie sqlmapapi, um einen Scan zu starten. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Detaillierte Einführung in die Datenübertragungssicherheit von DSMM
- Zusammenfassung von 40 häufig genutzten Intrusion-Ports für Hacker, die es wert sind, gesammelt zu werden
- Drei Prozessinjektionstechniken in der Mitre ATT&CK-Matrix
- Grundsätze der sicheren Entwicklungspraxis
- So beheben Sie die Sicherheitslücke bei der Remote-Befehlsausführung in der Apache-Achsenkomponente

