Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >So implementieren Sie ein Mensch-Computer-Backgammon-Spiel auf Basis von Python
So implementieren Sie ein Mensch-Computer-Backgammon-Spiel auf Basis von Python
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBnach vorne
- 2023-05-20 21:16:112323Durchsuche
Jeder spielt gegen jeden
Spielregeln: P1 ist der schwarze Stein, P2 ist der weiße Stein, der schwarze Stein übernimmt die Führung und eine Seite gewinnt, wenn fünf Steine verbunden sind.
Dynamische Demonstration
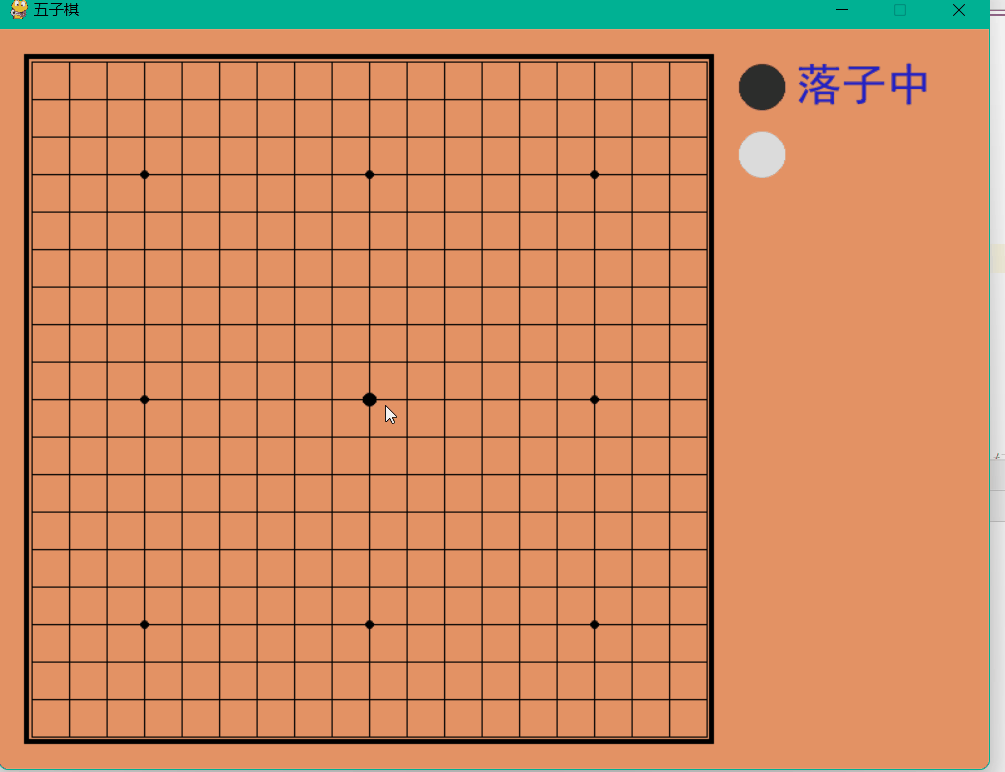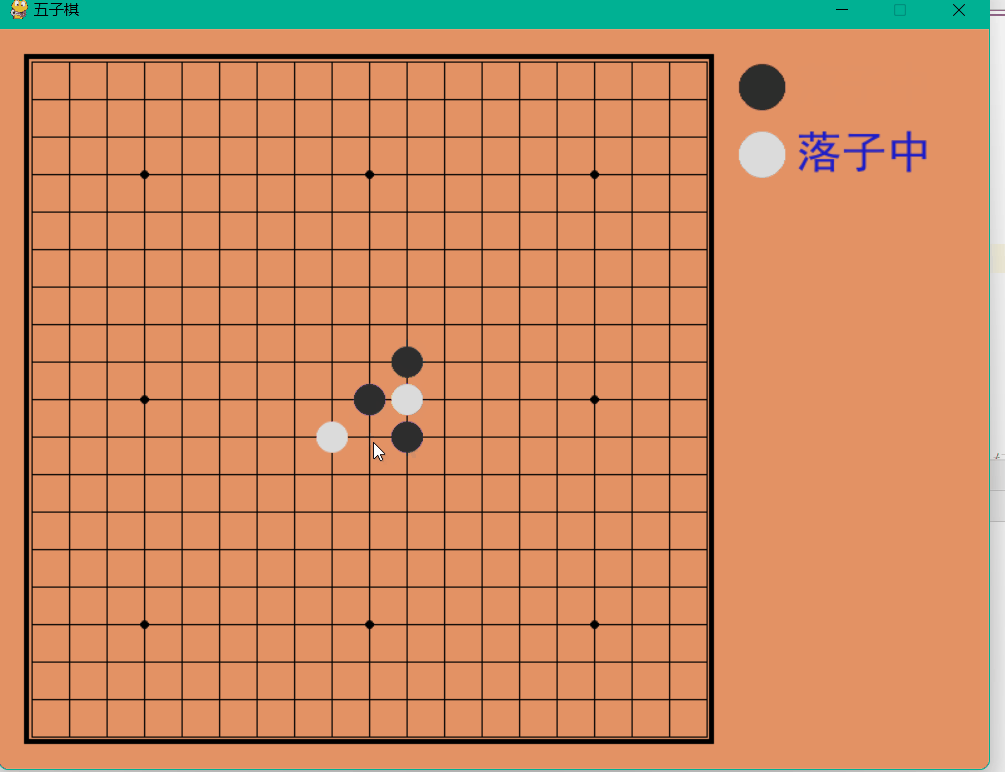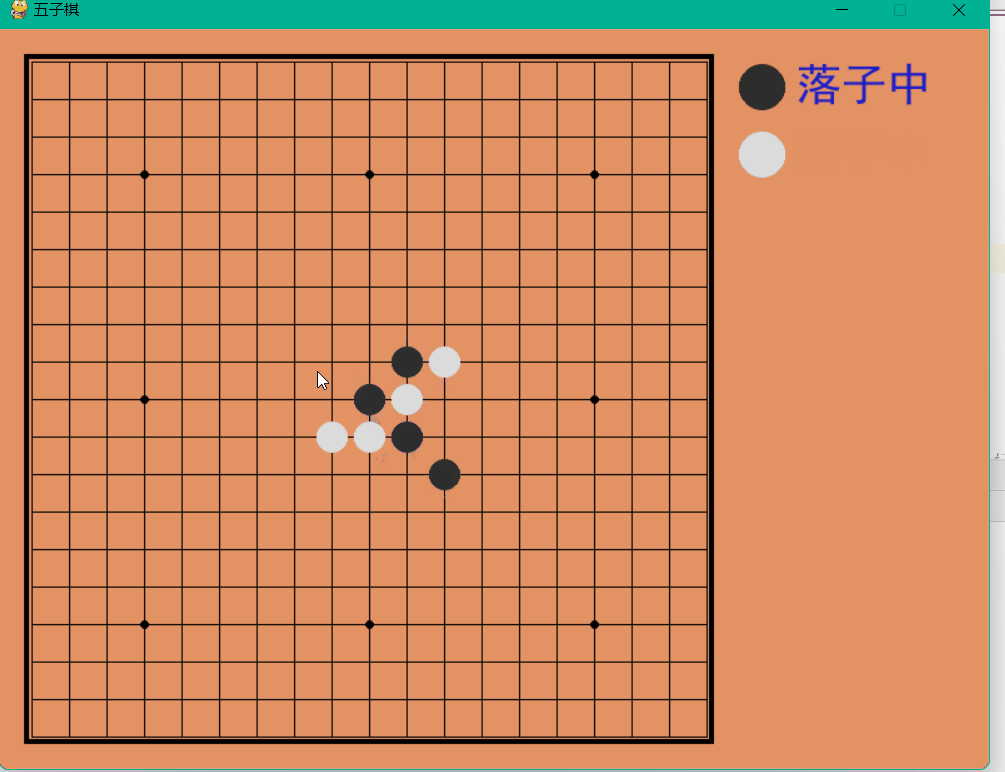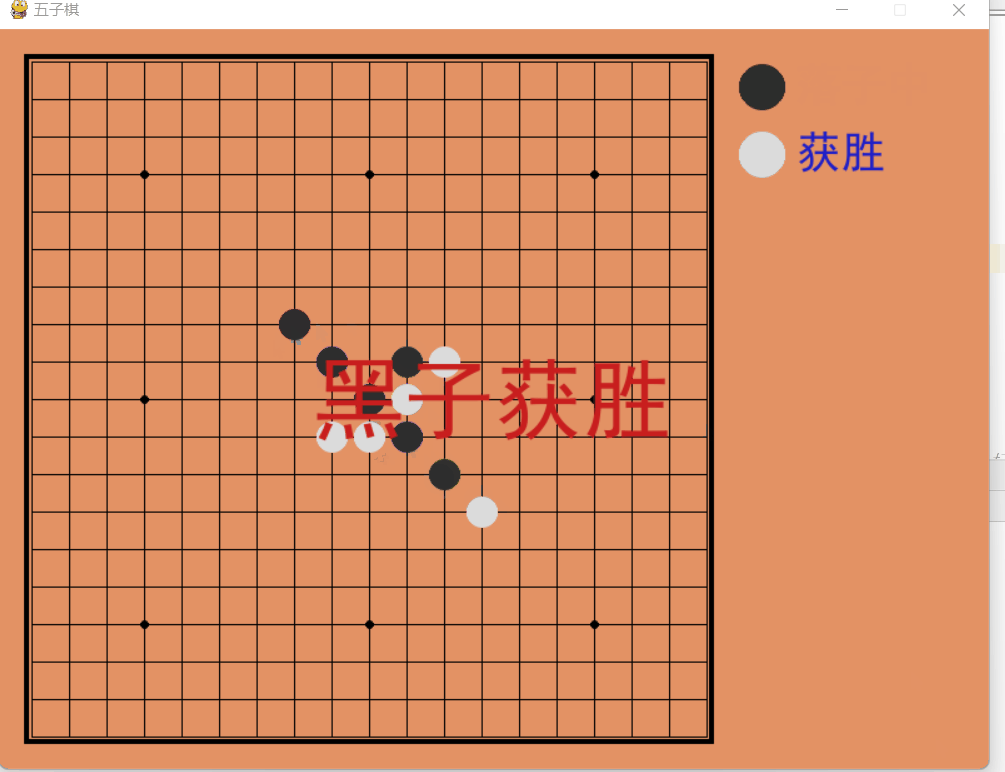
Quellcode-Sharing
cheackboard.py
Definieren Sie schwarze und weiße Steine, Platzierungs- und Gewinnregeln.
from collections import namedtuple
Chessman = namedtuple('Chessman', 'Name Value Color')
Point = namedtuple('Point', 'X Y')
BLACK_CHESSMAN = Chessman('黑子', 1, (45, 45, 45))
WHITE_CHESSMAN = Chessman('白子', 2, (219, 219, 219))
offset = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1), (1, -1)]
class Checkerboard:
def __init__(self, line_points):
self._line_points = line_points
self._checkerboard = [[0] * line_points for _ in range(line_points)]
def _get_checkerboard(self):
return self._checkerboard
checkerboard = property(_get_checkerboard)
# 判断是否可落子
def can_drop(self, point):
return self._checkerboard[point.Y][point.X] == 0
def drop(self, chessman, point):
"""
落子
:param chessman:
:param point:落子位置
:return:若该子落下之后即可获胜,则返回获胜方,否则返回 None
"""
print(f'{chessman.Name} ({point.X}, {point.Y})')
self._checkerboard[point.Y][point.X] = chessman.Value
if self._win(point):
print(f'{chessman.Name}获胜')
return chessman
# 判断是否赢了
def _win(self, point):
cur_value = self._checkerboard[point.Y][point.X]
for os in offset:
if self._get_count_on_direction(point, cur_value, os[0], os[1]):
return True
def _get_count_on_direction(self, point, value, x_offset, y_offset):
count = 1
for step in range(1, 5):
x = point.X + step * x_offset
y = point.Y + step * y_offset
if 0 <= x < self._line_points and 0 <= y < self._line_points and self._checkerboard[y][x] == value:
count += 1
else:
break
for step in range(1, 5):
x = point.X - step * x_offset
y = point.Y - step * y_offset
if 0 <= x < self._line_points and 0 <= y < self._line_points and self._checkerboard[y][x] == value:
count += 1
else:
break
return count >= 5Alle gegen py
Modul importieren
Wenn ein Modulfehler vorliegt, geben Sie den folgenden Befehl in das Pycharm-Terminal ein.
Um das entsprechende Modul zu installieren, verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl: „ pip installiert das entsprechende Modul -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple „
import sys import pygame from pygame.locals import * import pygame.gfxdraw from 小游戏.五子棋.checkerboard import Checkerboard, BLACK_CHESSMAN, WHITE_CHESSMAN, Point
Legen Sie die Parameter für das Schachbrett und die Schachfigur fest
SIZE = 30 # 棋盘每个点时间的间隔 Line_Points = 19 # 棋盘每行/每列点数 Outer_Width = 20 # 棋盘外宽度 Border_Width = 4 # 边框宽度 Inside_Width = 4 # 边框跟实际的棋盘之间的间隔 Border_Length = SIZE * (Line_Points - 1) + Inside_Width * 2 + Border_Width # 边框线的长度 Start_X = Start_Y = Outer_Width + int(Border_Width / 2) + Inside_Width # 网格线起点(左上角)坐标 SCREEN_HEIGHT = SIZE * (Line_Points - 1) + Outer_Width * 2 + Border_Width + Inside_Width * 2 # 游戏屏幕的高 SCREEN_WIDTH = SCREEN_HEIGHT + 200 # 游戏屏幕的宽 Stone_Radius = SIZE // 2 - 3 # 棋子半径 Stone_Radius2 = SIZE // 2 + 3 Checkerboard_Color = (0xE3, 0x92, 0x65) # 棋盘颜色 BLACK_COLOR = (0, 0, 0) WHITE_COLOR = (255, 255, 255) RED_COLOR = (200, 30, 30) BLUE_COLOR = (30, 30, 200) RIGHT_INFO_POS_X = SCREEN_HEIGHT + Stone_Radius2 * 2 + 10
Einstellungen für Schriftarten im Spiel
def print_text(screen, font, x, y, text, fcolor=(255, 255, 255)):
imgText = font.render(text, True, fcolor)
screen.blit(imgText, (x, y))
def main():
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT))
pygame.display.set_caption('五子棋')
font1 = pygame.font.SysFont('SimHei', 32)
font2 = pygame.font.SysFont('SimHei', 72)
fwidth, fheight = font2.size('黑方获胜')
checkerboard = Checkerboard(Line_Points)
cur_runner = BLACK_CHESSMAN
winner = None
computer = AI(Line_Points, WHITE_CHESSMAN)
black_win_count = 0
white_win_count = 0Schleifenkörper platzieren
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
sys.exit()
elif event.type == KEYDOWN:
if event.key == K_RETURN:
if winner is not None:
winner = None
cur_runner = BLACK_CHESSMAN
checkerboard = Checkerboard(Line_Points)
computer = AI(Line_Points, WHITE_CHESSMAN)
elif event.type == MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
if winner is None:
pressed_array = pygame.mouse.get_pressed()
if pressed_array[0]:
mouse_pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
click_point = _get_clickpoint(mouse_pos)
if click_point is not None:
if checkerboard.can_drop(click_point):
winner = checkerboard.drop(cur_runner, click_point)
if winner is None:
cur_runner = _get_next(cur_runner)
computer.get_opponent_drop(click_point)
AI_point = computer.AI_drop()
winner = checkerboard.drop(cur_runner, AI_point)
if winner is not None:
white_win_count += 1
cur_runner = _get_next(cur_runner)
else:
black_win_count += 1
else:
print('超出棋盘区域')Zeichnen Sie das Schachbrett
def _draw_checkerboard(screen):
# 填充棋盘背景色
screen.fill(Checkerboard_Color)
# 画棋盘网格线外的边框
pygame.draw.rect(screen, BLACK_COLOR, (Outer_Width, Outer_Width, Border_Length, Border_Length), Border_Width)
# 画网格线
for i in range(Line_Points):
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK_COLOR,
(Start_Y, Start_Y + SIZE * i),
(Start_Y + SIZE * (Line_Points - 1), Start_Y + SIZE * i),
1)
for j in range(Line_Points):
pygame.draw.line(screen, BLACK_COLOR,
(Start_X + SIZE * j, Start_X),
(Start_X + SIZE * j, Start_X + SIZE * (Line_Points - 1)),
1)
# 画星位和天元
for i in (3, 9, 15):
for j in (3, 9, 15):
if i == j == 9:
radius = 5
else:
radius = 3
# pygame.draw.circle(screen, BLACK, (Start_X + SIZE * i, Start_Y + SIZE * j), radius)
pygame.gfxdraw.aacircle(screen, Start_X + SIZE * i, Start_Y + SIZE * j, radius, BLACK_COLOR)
pygame.gfxdraw.filled_circle(screen, Start_X + SIZE * i, Start_Y + SIZE * j, radius, BLACK_COLOR)Führen Sie die Box aus, um zurückzukehren zu den Rahmenkoordinaten
def _get_clickpoint(click_pos):
pos_x = click_pos[0] - Start_X
pos_y = click_pos[1] - Start_Y
if pos_x < -Inside_Width or pos_y < -Inside_Width:
return None
x = pos_x // SIZE
y = pos_y // SIZE
if pos_x % SIZE > Stone_Radius:
x += 1
if pos_y % SIZE > Stone_Radius:
y += 1
if x >= Line_Points or y >= Line_Points:
return None
return Point(x, y) Ausführbare Datei
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()Mensch-Maschine-Kampf
Dynamische Demonstration
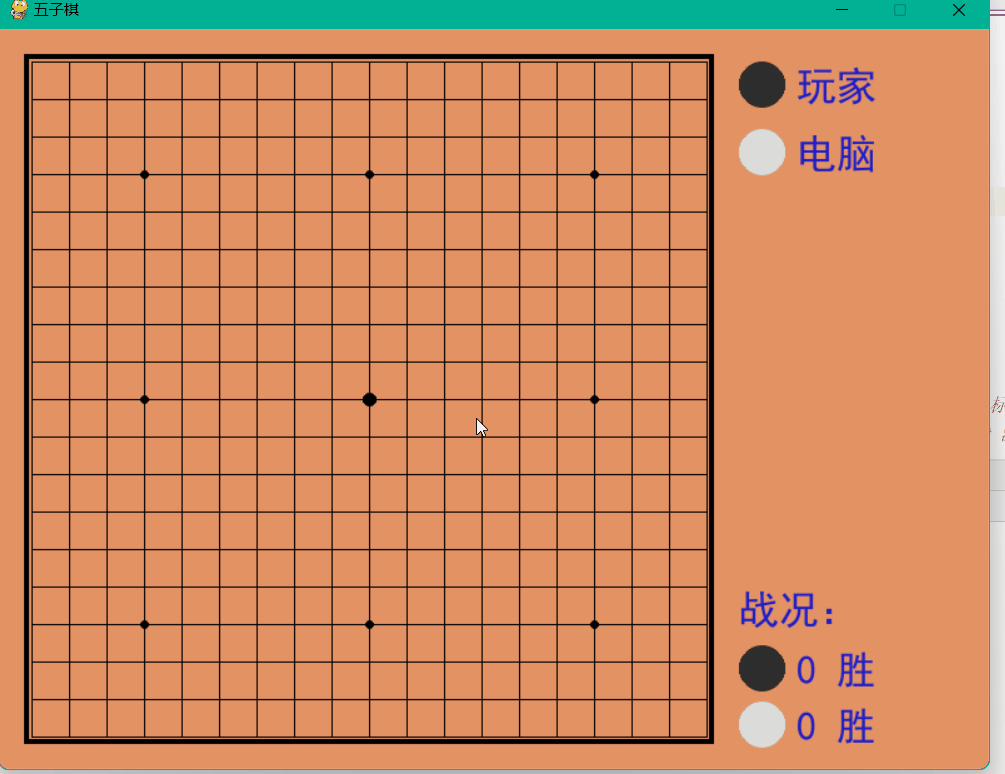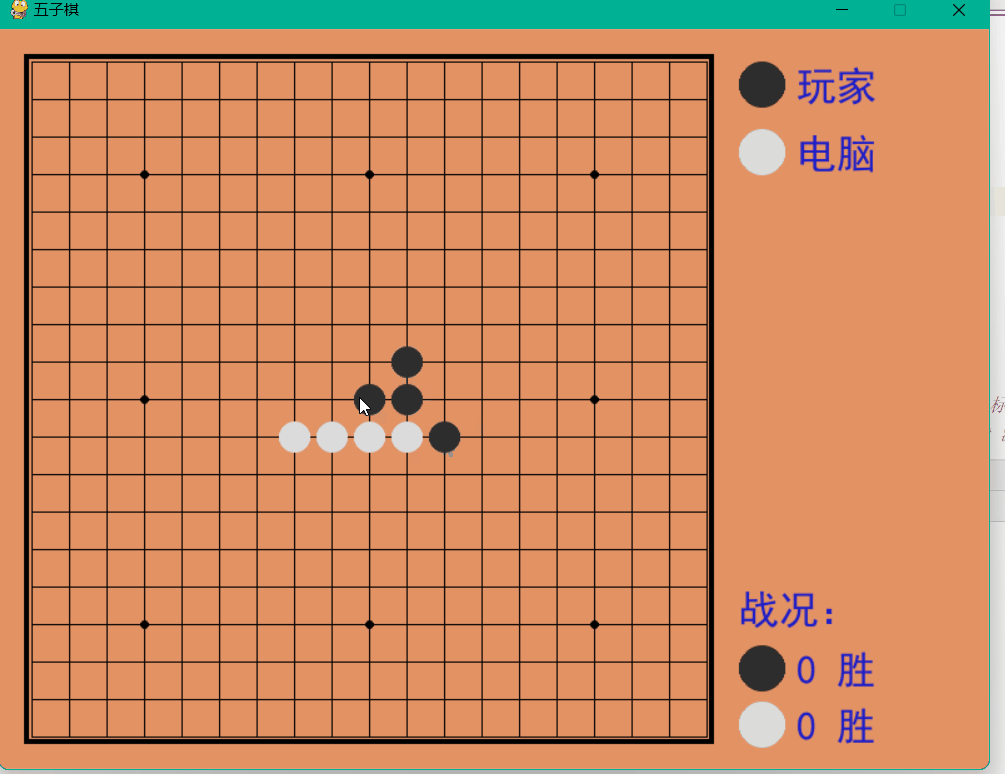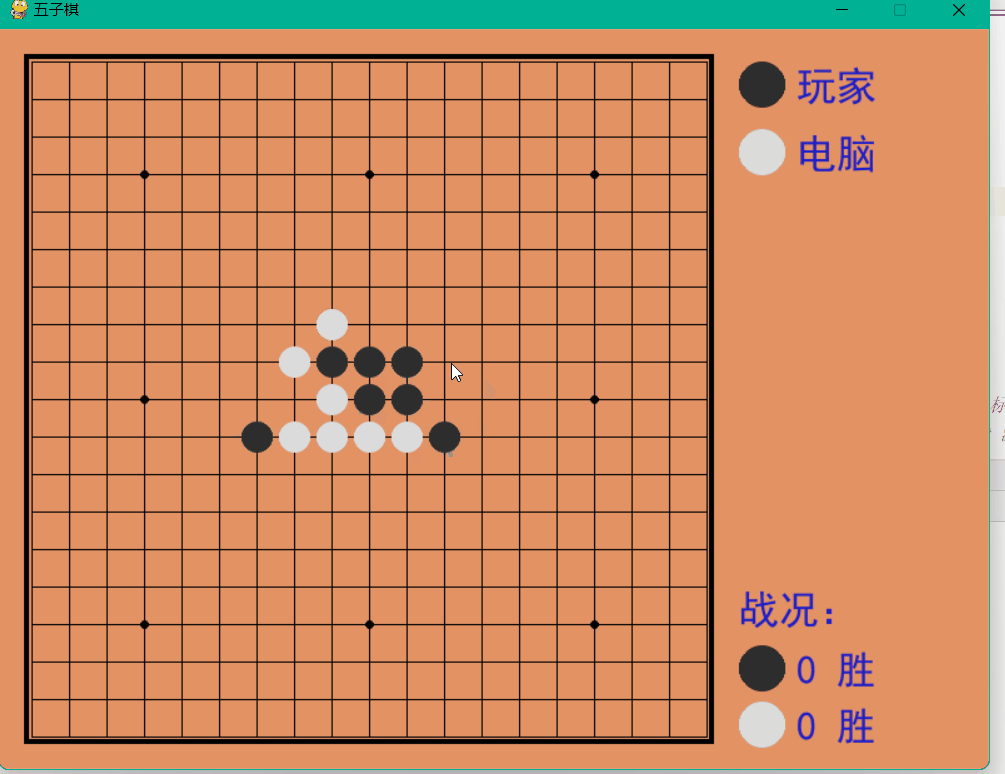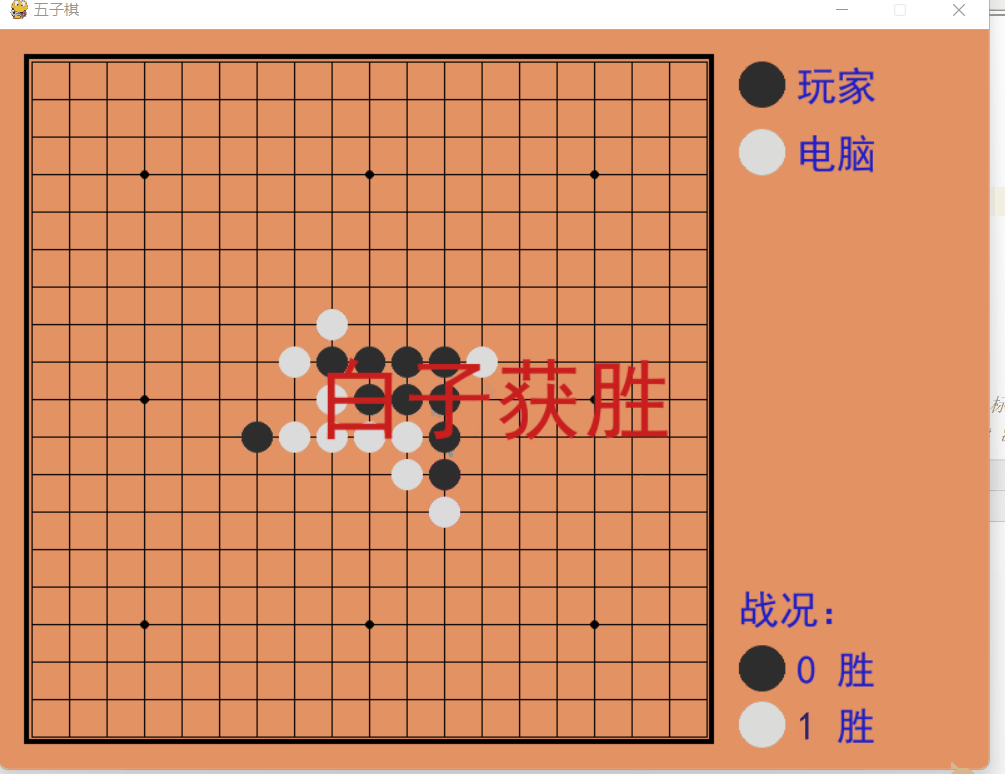
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo implementieren Sie ein Mensch-Computer-Backgammon-Spiel auf Basis von Python. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

