Heim >Betrieb und Instandhaltung >Nginx >So erstellen und konfigurieren Sie den Nginx-Dienst unter Ubuntu
So erstellen und konfigurieren Sie den Nginx-Dienst unter Ubuntu
- 王林nach vorne
- 2023-05-19 17:47:112669Durchsuche
1. Nginx
Nginx („Engine x“) ist ein leistungsstarker Web- und Reverse-Proxy-Server, der vom russischen Programmierer Igor Sysoev entwickelt wurde. Er ist auch ein IMAP/POP3/SMTP-Proxy-Server.
Einer der drei großen WEB-Server: Apache, Nginx, Lighttpd. Nginx ist eine gute Alternative und eignet sich besser als der Apache-Server, wenn Sie viele gleichzeitige Verbindungen verarbeiten müssen.
nginx-Anwendungsszenarien
statischer Server. (Bild- und Videodienst) Ein weiterer ist lighttpd. Zehntausende gleichzeitiger Vorgänge, HTML, JS, CSS, FLV, JPG, GIF usw.
Dynamischer Dienst, Nginx-Fastcgi-Modus zum Ausführen von PHP, JSP. (PHP-Parallelität beträgt 500–1500, MySQL-Parallelität beträgt 300–1500).
Reverse-Proxy, Lastausgleich. Wenn der tägliche PV unter 2000 W liegt, können Sie Nginx direkt als Proxy verwenden.
Caching-Dienst. Ähnlich wie SQUID, LACK.
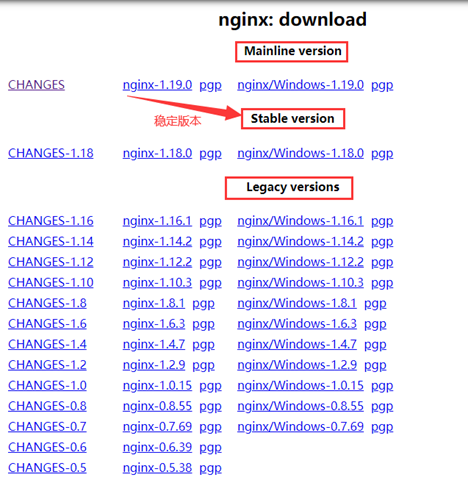
Die offizielle Website bietet drei Arten von Versionen:
Die offizielle Website von Nginx bietet drei Arten von Versionen.
Hauptversion: Mainline ist die Version, an der Nginx derzeit arbeitet. Man kann sagen, dass es sich um die Entwicklungsversion handelt.
Stabile Version : die neueste stabile Version, Produktionsumgebung. Die empfohlene Version ist
Legacy-Versionen: die stabile Version der alten Version
2. Nginx-Dienstkonstruktion
1. Verwenden Sie apt, um
sudo apt install nginx
2 zu installieren :
/usr/ sbin/nginx: Hauptprogramm
/etc/nginx: Konfigurationsdateien speichern
/usr/share/nginx: Statische Dateien speichern
/var/log/nginx : Protokolle speichern
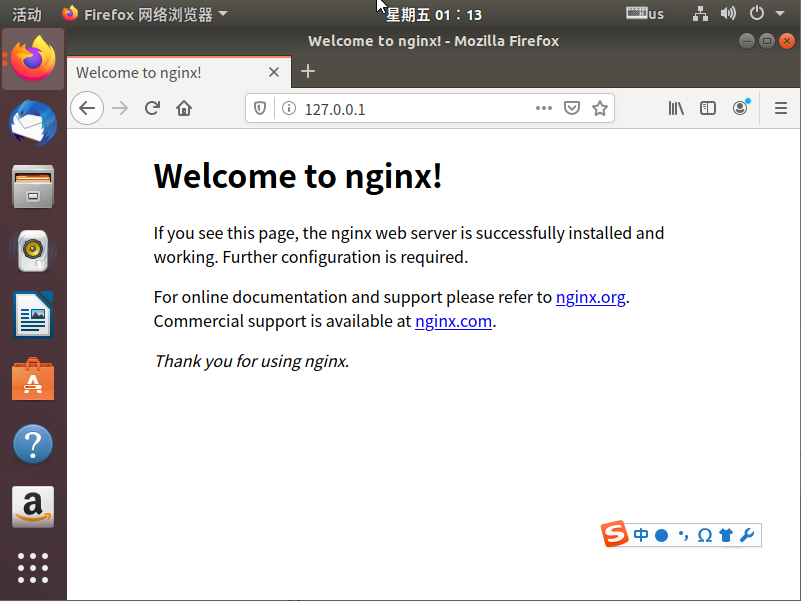
3, starten und den Effekt überprüfen
service nginx start # 启动nginx service nginx reload # 重新加载nginx配置文件
Geben Sie Ihre IP-Adresse in den Browser ein. Wenn „Willkommen bei Nginx“ angezeigt wird, ist die Konfiguration erfolgreich.
Weitere zwei Befehle
nginx -s reopen # 重启 Nginx
nginx -s stop # 停止 Nginx
3. Einführung in die Nginx-Konfigurationsdatei
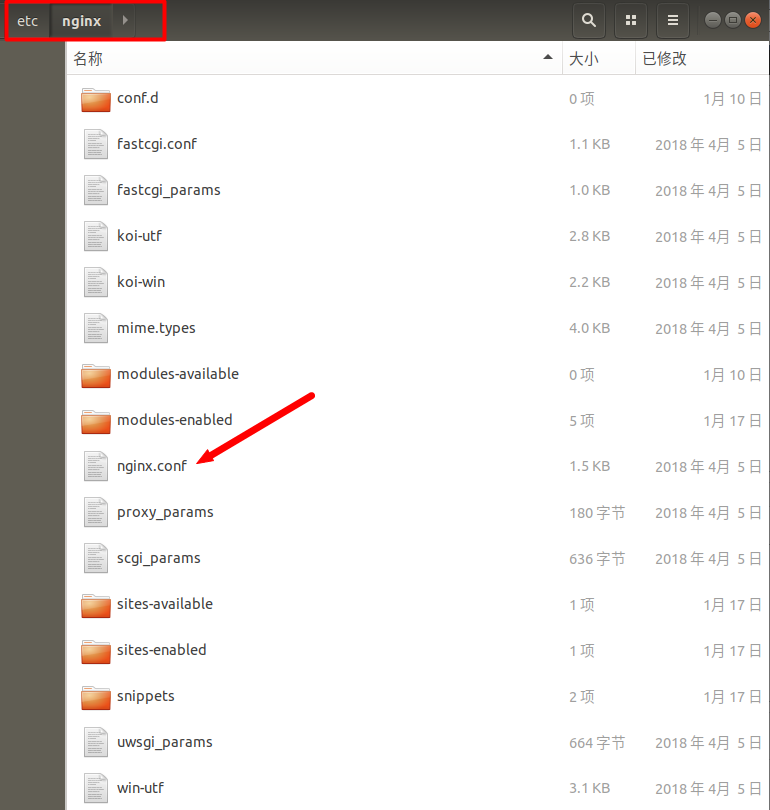
: Die Konfiguration wirkt sich auf Nginx aus globale Anweisungen. Im Allgemeinen gibt es eine Benutzergruppe zum Ausführen des Nginx-Servers, des Nginx-Prozess-PID-Speicherpfads, des Protokollspeicherpfads, der Einführung der Konfigurationsdatei, der Anzahl der Arbeitsprozesse, die generiert werden dürfen usw.
Ereignisblock: Konfiguration, die sich auf den Nginx-Server oder die Netzwerkverbindung zum Benutzer auswirkt. Es gibt die maximale Anzahl von Verbindungen pro Prozess, welches ereignisgesteuerte Modell zur Verarbeitung von Verbindungsanforderungen ausgewählt werden soll, ob die gleichzeitige Annahme mehrerer Netzwerkverbindungen zugelassen werden soll, ob die Serialisierung mehrerer Netzwerkverbindungen aktiviert werden soll usw.
http-Block: Sie können mehrere Server verschachteln, Proxys, Caches, Protokolldefinitionen und andere Funktionen sowie Modulkonfigurationen von Drittanbietern konfigurieren. Wie Dateieinführung, Mime-Typ-Definition, Protokollanpassung, ob sendfile zum Übertragen von Dateien verwendet werden soll, Verbindungszeitlimit, Anzahl einzelner Verbindungsanforderungen usw.
Serverblock: Konfigurieren Sie die relevanten Parameter des virtuellen Hosts. Es können mehrere Server in einem http vorhanden sein.
Standortblock: Konfigurieren Sie die Weiterleitung von Anfragen und die Verarbeitung verschiedener Seiten.
~$ nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.14.0 (Ubuntu)
2. Standardkonfiguration
... # 全局块。配置影响nginx全局的指令。 events { # events块。配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。 ... } http # http块。可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。 { ... # http全局块 server # server块。配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。 { ... # server全局块 location [PATTERN] # location块。配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。 { ... } location [PATTERN] { ... } } server { ... } ... # http全局块 }3. Nginx-Virtual-Host-Konfiguration## # You should look at the following URL's in order to grasp a solid understanding # of Nginx configuration files in order to fully unleash the power of Nginx. # https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/ # https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/ # https://wiki.debian.org/Nginx/DirectoryStructure # # In most cases, administrators will remove this file from sites-enabled/ and # leave it as reference inside of sites-available where it will continue to be # updated by the nginx packaging team. # # This file will automatically load configuration files provided by other # applications, such as Drupal or Wordpress. These applications will be made # available underneath a path with that package name, such as /drupal8. # # Please see /usr/share/doc/nginx-doc/examples/ for more detailed examples. ## # Default server configuration # server { listen 80 default_server; listen [::]:80 default_server; # SSL configuration # # listen 443 ssl default_server; # listen [::]:443 ssl default_server; # # Note: You should disable gzip for SSL traffic. # See: https://bugs.debian.org/773332 # # Read up on ssl_ciphers to ensure a secure configuration. # See: https://bugs.debian.org/765782 # # Self signed certs generated by the ssl-cert package # Don't use them in a production server! # # include snippets/snakeoil.conf; root /var/www/html; # Add index.php to the list if you are using PHP index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html; server_name _; location / { # First attempt to serve request as file, then # as directory, then fall back to displaying a 404. try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } # pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server # #location ~ \.php$ { # include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; # # # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets): # fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock; # # With php-cgi (or other tcp sockets): # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # Virtual Host configuration for example.com # # You can move that to a different file under sites-available/ and symlink that # to sites-enabled/ to enable it. # #server { # listen 80; # listen [::]:80; # # server_name example.com; # # root /var/www/example.com; # index index.html; # # location / { # try_files $uri $uri/ =404; # } #}Verifizierungskonfigurationsdatei:
########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。#################
#user administrator administrators; #配置用户或者组,默认为nobody nobody。
#worker_processes 2; #允许生成的进程数,默认为1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #指定nginx进程运行文件存放地址
error_log log/error.log debug; #制定日志路径,级别。这个设置可以放入全局块,http块,server块,级别以此为:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #设置网路连接序列化,防止惊群现象发生,默认为on
multi_accept on; #设置一个进程是否同时接受多个网络连接,默认为off
#use epoll; #事件驱动模型,select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #最大连接数,默认为512
}
http {
include mime.types; #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
default_type application/octet-stream; #默认文件类型,默认为text/plain
#access_log off; #取消服务日志
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #自定义格式
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined为日志格式的默认值
sendfile on; #允许sendfile方式传输文件,默认为off,可以在http块,server块,location块。
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #每个进程每次调用传输数量不能大于设定的值,默认为0,即不设上限。
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间,默认为75s,可以在http,server,location块。
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; #错误页
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #单连接请求上限次数。
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name 127.0.0.1; #监听地址
location ~*^.+$ { #请求的url过滤,正则匹配,~为区分大小写,~*为不区分大小写。
#root path; #根目录
#index vv.txt; #设置默认页
proxy_pass http://mysvr; #请求转向mysvr 定义的服务器列表
deny 127.0.0.1; #拒绝的ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #允许的ip
}
}
} Um Kunden zu erfassen Für die IP-Adresse des Clients können Sie $remote_addr und $http_x_forwarded_for
verwenden.$remote_user: wird zum Aufzeichnen des Client-Benutzernamens verwendet $request: wird verwendet, um die URL und das http-Protokoll der Anfrage aufzuzeichnen; - $status: wird verwendet, um den Anforderungsstatus aufzuzeichnen; Erfolg ist 200; die an den Client gesendete Datei;
- $http_referer: Wird verwendet, um den Zugriff über diesen Seitenlink aufzuzeichnen;
-
#下面是server虚拟主机的配置段 server { listen 80;#监听端口 server_name localhost;#域名 index index.html index.htm index.php; root /usr/local/webserver/nginx/html;#站点目录 location ~ .*\.(php|php5)?$ { #fastcgi_pass unix:/tmp/php-cgi.sock; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; include fastcgi.conf; } location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|ico)$ { expires 30d; #access_log off; } location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$ { expires 15d; #access_log off; } access_log off; }. Nginx-Hauptkonfiguration - 1. Konfiguration des statischen HTTP-Servers Zuerst Nginx Es ist ein HTTP-Server, der dem Client über das HTTP-Protokoll statische Dateien (wie HTML und Bilder) auf dem Server anzeigen kann. Konfiguration:
root@ubuntu: nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
2. Reverse-Proxy-Server-Konfiguration
Was ist ein Reverse-Proxy? - Der Client kann über das HTTP-Protokoll direkt auf einen Website-Anwendungsserver zugreifen. Wenn der Website-Administrator in der Mitte einen Nginx hinzufügt, fordert Nginx den Anwendungsserver an und gibt das Ergebnis dann an den Client zurück. Nginx ist der Reverse-Proxy-Server.
-
Reverse-Proxy-Konfiguration:
server { listen 80; location / { proxy_pass http://192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器HTTP地址 } }既然服务器可以直接HTTP访问,为什么要在中间加上一个反向代理,不是多此一举吗?反向代理有什么作用?继续往下看,下面的负载均衡、虚拟主机,都基于反向代理实现,当然反向代理的功能也不仅仅是这些。
3、负载均衡配置
当网站访问量非常大,也摊上事儿了。因为网站越来越慢,一台服务器已经不够用了。因此,可以将同一应用部署在多台服务器上,以将众多用户请求分配至多台机器进行处理。即使其中一台服务器故障,只要其他服务器正常运行,用户仍然可以正常使用,这是多台服务器带来的好处。Nginx可以通过反向代理来实现负载均衡。
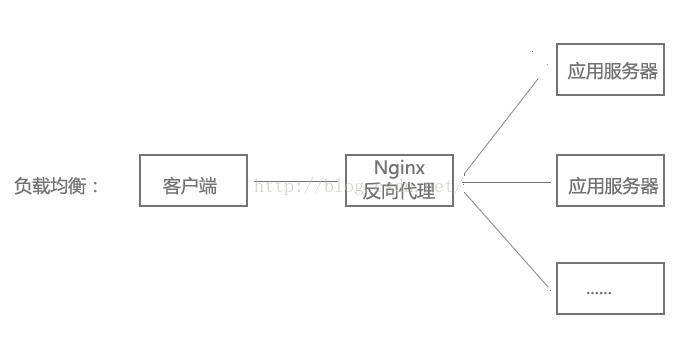
负载均衡配置:
upstream myapp { server 192.168.0.111:8080; # 应用服务器1 server 192.168.0.112:8080; # 应用服务器2 } server { listen 80; location / { proxy_pass http://myweb; } }4、虚拟主机配置
有的网站访问量大,需要负载均衡。然而并不是所有网站都如此出色,有的网站,由于访问量太小,需要节省成本,将多个网站部署在同一台服务器上。
例如将www.aaa.com和www.bbb.com两个网站部署在同一台服务器上,两个域名解析到同一个IP地址,但是用户通过两个域名却可以打开两个完全不同的网站,互相不影响,就像访问两个服务器一样,所以叫两个虚拟主机。虚拟主机配置:
server { listen 80 default_server; server_name _; return 444; # 过滤其他域名的请求,返回444状态码 } server { listen 80; server_name www.aaa.com; # www.aaa.com域名 location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; # 对应端口号8080 } } server { listen 80; server_name www.bbb.com; # www.bbb.com域名 location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8081; # 对应端口号8081 } }在服务器8080和8081分别开了一个应用,客户端通过不同的域名访问,根据server_name可以反向代理到对应的应用服务器。
虚拟主机的原理是通过HTTP请求头中的Host是否匹配server_name来实现的,有兴趣的同学可以研究一下HTTP协议。
另外,server_name配置还可以过滤有人恶意将某些域名指向你的主机服务器。
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonSo erstellen und konfigurieren Sie den Nginx-Dienst unter Ubuntu. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

