Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Analyse von Beispielen für Java-String-, Array- und binäre Suchbäume
Analyse von Beispielen für Java-String-, Array- und binäre Suchbäume
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBnach vorne
- 2023-04-21 09:19:081503Durchsuche
Frage 1
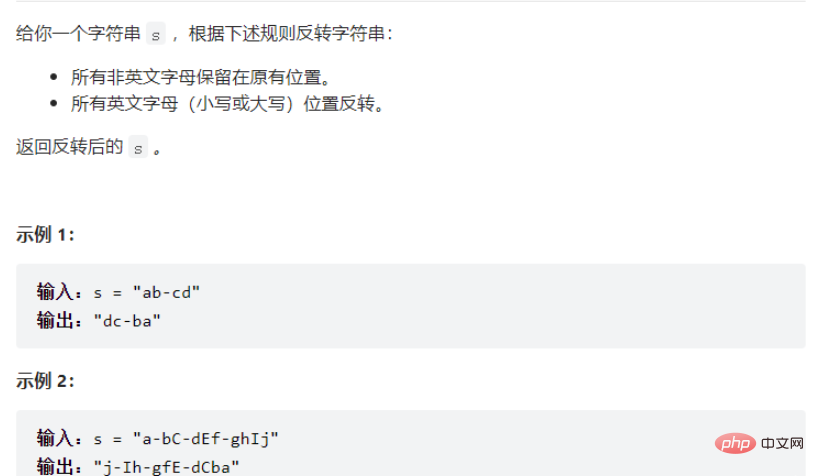
Lösung
class Solution {
public String reverseOnlyLetters(String s) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int left = 0;
int right = chars.length-1;
while(left<=right){
char tmp = 0;
if(chars[left]>='a'&&chars[left]<='z'||(chars[left]>='A'&&chars[left]<='Z')){
tmp = chars[left];
}else {
left++;
continue;
}
if(chars[right]>='a'&&chars[right]<='z'||(chars[right]>='A'&&chars[right]<='Z')){
chars[left] = chars[right];
chars[right] = tmp;
}else {
right--;
continue;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return new String(chars);
}
}Frage 2
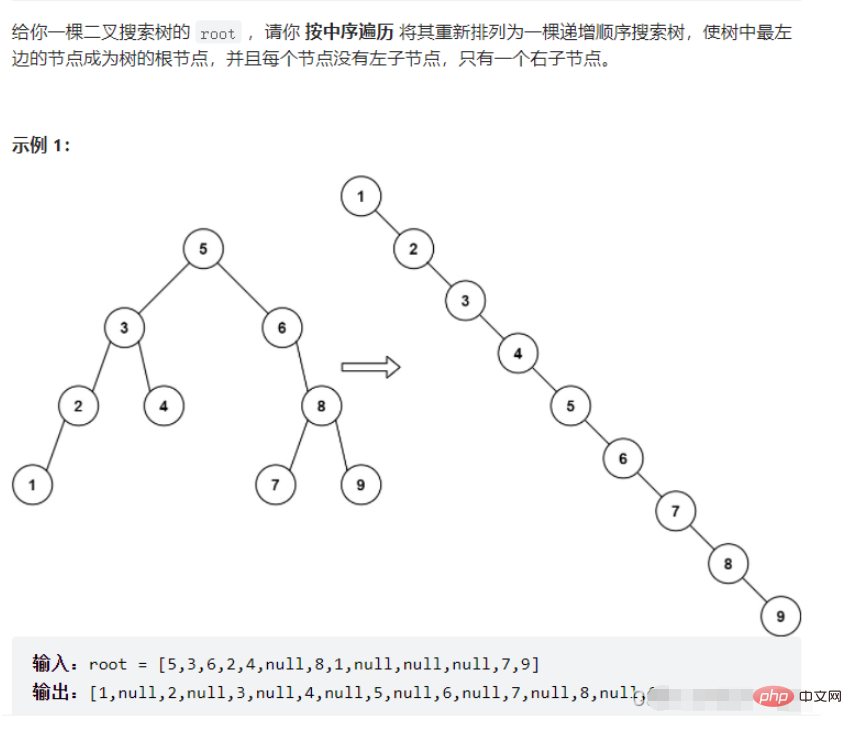
Lösung
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode increasingBST(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
method(root,list);
TreeNode ans = new TreeNode(-1);
TreeNode cur = ans;
for(int i:list){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
cur.right = node;
cur = cur.right;
}
return ans.right;
}
public void method(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){
if(root==null) return;
method(root.left,list);
list.add(root.val);
method(root.right,list);
}
}Frage 3

Lösung
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] nums) {
int[] ans = new int[nums.length];
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length-1;
for(int i : nums){
if(i%2==0){
ans[left] = i;
left++;
}else{
ans[right] = i;
right--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
if(nums[left]%2==0){
left++;
continue;
}
if(nums[right]%2!=0){
right--;
continue;
}
if(nums[left]%2!=0&&nums[right]%2==0){
int tmp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = tmp;
}
}
return nums;
}
} Frage 4

Lösung
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String s, String t) {
if(method(s).equals(method(t))) return true;
return false;
}
public static String method(String s){
int slow = 0;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if(chars[i]=='#'){
chars[i] = 0;
slow = i;
while (true){
if(slow-1<0) break;
if (chars[slow-1]!=0){
chars[slow-1] = 0;
break;
}
slow--;
}
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(char i : chars){
if(i!=0) sb.append(i);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonAnalyse von Beispielen für Java-String-, Array- und binäre Suchbäume. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
Stellungnahme:
Dieser Artikel ist reproduziert unter:yisu.com. Bei Verstößen wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn löschen
Vorheriger Artikel:Häufige Fehler und Vorsichtsmaßnahmen bei der Verwendung interner Java-KlassenNächster Artikel:Häufige Fehler und Vorsichtsmaßnahmen bei der Verwendung interner Java-Klassen
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Wie können Java-Assertions die Codequalität verbessern und Fehler verhindern?
- Beeinflusst die Deklaration von Strings als „final' in Java „=='-Vergleiche?
- String-Manipulation in Java
- Wie aktualisiere ich JLabel kontinuierlich mit den Ergebnissen einer lang andauernden Aufgabe?
- Wie konvertiere ich int[] in Integer[] zur Verwendung als Map-Schlüssel in Java?

