Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Beispielanalyse des Java Spring Bean-Lebenszyklusmanagements
Beispielanalyse des Java Spring Bean-Lebenszyklusmanagements
- 王林nach vorne
- 2023-04-18 09:13:441631Durchsuche
Lebenszyklusmanagement von Frühlingsbohnen
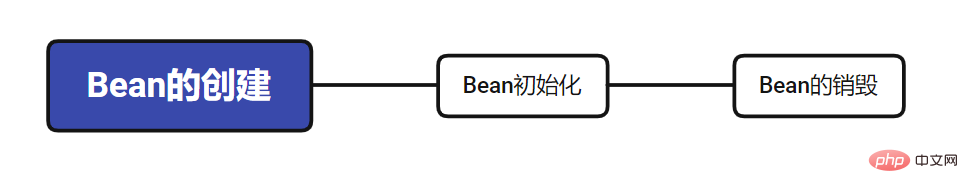
1. Lebenszyklus von Frühlingsbohnen
# 🎜🎜 #
通过以下方式来指定Bean的初始化和销毁方法, 当Bean为单例时,Bean归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,就会调用Bean的销毁方法 当Bean为多例时,Bean不归Spring容器管理,Spring容器关闭,不会调用Bean的销毁方法2. Geben Sie die Initialisierungs- und Zerstörungsmethoden der Bean über @Bean-Parameter an (initMethod, destroyMethod) 1 Projektstruktur
#🎜🎜 #
 2, Person
2, Person
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}3, Bean-Registrierungskonfigurationsklasse (einzelne Instanz)
import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}4, Testklasse#🎜 🎜 #import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import com.dashu.config.BeanConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//加载配置类获取容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
//获取Bean
Person bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
//关闭容器
annotationConfigApplicationContext.close();
}
}
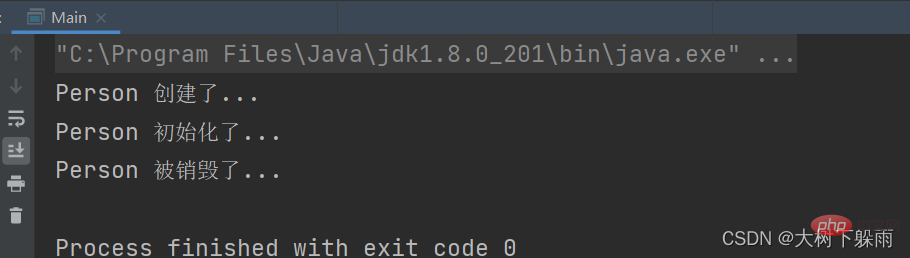
5. Testergebnisse
6. Bean-Registrierungskonfigurationsklasse (mehrere Instanzen)import com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
} 7 . Testergebnisse
3. Bean-Implementierungsschnittstelle InitializingBean, EinwegBean
7 . Testergebnisse
3. Bean-Implementierungsschnittstelle InitializingBean, EinwegBean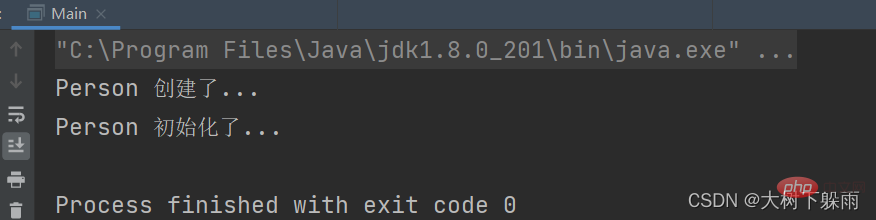 1, Person
1, Person
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}#🎜 🎜 #2. Bean-Registrierungskonfigurationsklasseimport com.dashu.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
3. Testergebnisse
4. Durch die Anmerkungen @PostConstruct und @PreDestroy @PostConstruct:标注在Bean的初始化方法上
@PreDestroy:标注在Bean的销毁方法上
1, Personimport javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}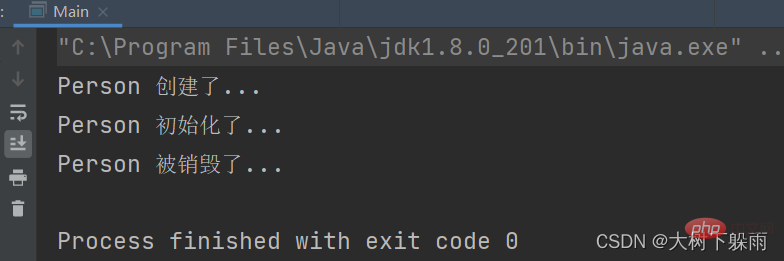 2, Testergebnisse
5. Verwenden Sie die Schnittstelle BeanPostProcessor-Implementierungsklasse (Postprozessor)1, Projektstruktur
2, Testergebnisse
5. Verwenden Sie die Schnittstelle BeanPostProcessor-Implementierungsklasse (Postprozessor)1, Projektstruktur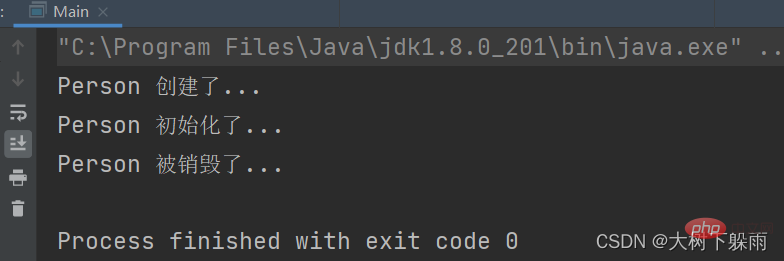
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
@Component
public class Person {
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person 创建了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person 初始化了...");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Person 被销毁了...");
}
}#🎜 🎜#3. Bean-Registrierungskonfigurationsklasse
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.dashu"})
public class BeanConfig {
}4. BeanPostProcessor-Implementierungsklasse (Postprozessor)
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化之前工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之前..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
/**
* 初始化之后工作
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("初始化之后..."+beanName+"=["+bean+"]");
return bean;
}
}5. Testergebnisse# 🎜 🎜#
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBeispielanalyse des Java Spring Bean-Lebenszyklusmanagements. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
Stellungnahme:
Dieser Artikel ist reproduziert unter:yisu.com. Bei Verstößen wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn löschen
Vorheriger Artikel:Wie man Maven in Java verstehtNächster Artikel:Wie man Maven in Java versteht

