Heim >Web-Frontend >js-Tutorial >JS realisiert den Ebeneneffektcode, der mit der Bildlaufleiste auf der Webseite scrollt_Javascript-Fähigkeiten
JS realisiert den Ebeneneffektcode, der mit der Bildlaufleiste auf der Webseite scrollt_Javascript-Fähigkeiten
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-05-16 15:33:531241Durchsuche
Das Beispiel in diesem Artikel beschreibt die JS-Implementierung des Ebeneneffektcodes, der mit der Bildlaufleiste auf der Webseite scrollt. Teilen Sie es als Referenz mit allen. Die Details lauten wie folgt:
Der Bildlaufebenencode auf dieser Webseite folgt der Bildlaufleiste, um den Effekt zu sehen. Die schwebende Ebene auf der rechten Seite kann auch mit etwas Verarbeitung geschlossen werden . Implementieren Sie den Code für eine Floating-Anzeige, führen Sie ihn aus und sehen Sie sich zunächst die Wirkung an.
Der Screenshot des Laufeffekts sieht wie folgt aus:
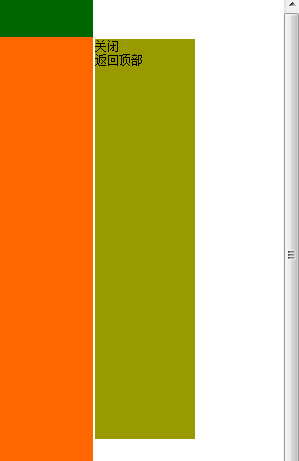
Die Online-Demo-Adresse lautet wie folgt:
http://demo.jb51.net/js/2015/js-web-fixed-scroll-adv-codes/
Der spezifische Code lautet wie folgt:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>随滚动条滚动的层</title>
<style>
body{ margin:0; padding:0; font-size:12px; font-family:"宋体",Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;}
div,p,ul,ol,li,dl,dt,dd,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,form,input,form{ margin:0; padding:0;}
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6{font-size:100%;font-weight:normal;}
img{ border:0;}
ol,ul{list-style:none;}
a{ text-decoration:none; color:#fff;}
a:hover{ text-decoration:none;}
#scroll_div{ width:100px; height:400px; background:#990; }
#btn_close,#btn_gotop{ cursor:pointer;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style=" width:1002px;height:42px;margin:0 auto; background-color:#060;">头</div>
<div style="width:1002px; margin:0 auto; background-color:#f60;">
我们提供各类编程源码、<br>素材、书籍教程、设计模板、<br>网页特效代码以及常用软件下载等,<br>做有质量的<br>学习型源码下载站。
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
</div>
<div style=" width:1002px;height:95px;margin:0 auto; background-color:#060;">底</div>
<div id="scroll_div">
<span id="btn_close">关闭</span><br />
<span id="btn_gotop">返回顶部</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var Bianyuan = {
//添加事件2(DOM-保证this指向对象是obj)
addEvent : function(obj, type, fn){
if (obj.attachEvent){
obj['e'+type+fn] = fn;
obj[type+fn] = function(){obj['e'+type+fn](window.event);}
obj.attachEvent('on'+type, obj[type+fn]);
}else{
obj.addEventListener(type, fn, false);
}
},
//获取id元素
$ : function(id){
return document.getElementById(id);
},
//取得浏览器可视区size
getBrowserSize : function(){
var pageWidth = window.innerWidth,
pageHeight = window.innerHeight;
if (typeof pageWidth != "number"){
if (document.compatMode == "CSS1Compat"){
pageWidth = document.documentElement.clientWidth;
pageHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight;
} else{
pageWidth = document.body.clientWidth;
pageWidth = document.body.clientHeight;
}
}
//ie减去17滚动条宽度
if(!window.ActiveXObject){
pageWidth -= 17;
}
return {
width : pageWidth,
height : pageHeight
}
},
//获取滚动条高度
getPageScroll : function(){
var yScroll;
if (self.pageYOffset) {
yScroll = self.pageYOffset;
} else if (document.documentElement && document.documentElement.scrollTop){
yScroll = document.documentElement.scrollTop;
} else if (document.body) {
yScroll = document.body.scrollTop;
}
return yScroll;
}
}
function scrollBar(scrollId, dir, headHeight, footHeight, areaWidth, o){
//滚动框宽高
var scrollBar = Bianyuan.$(scrollId),
barWidth = scrollBar.offsetWidth,
barHeight = scrollBar.offsetHeight;
//可视区宽高
var pageWidth = Bianyuan.getBrowserSize().width,
pageHeight = Bianyuan.getBrowserSize().height;
//内容宽高
var widthMore = document.documentElement.scrollWidth,
heightMore = document.body.scrollHeight||(document.documentElement.scrollHeight);
//最大宽高
var maxWidth = Math.max(pageWidth, widthMore),
maxHeight = Math.max(pageHeight, heightMore);
scrollBar.style.position = 'absolute';
//设置top--假设滚动框高度小于整个页面高度,如果大于直接将其隐藏
if (maxHeight < (barHeight + footHeight + footHeight + 4)){
scrollBar.style.display = 'none';
}else{
//不挡顶部---如果想改距顶高度,改下边的第一个2值
scrollBar.style.top = Bianyuan.getPageScroll() + headHeight + 2 + 'px';
//不挡底部
if ((heightMore - Bianyuan.getPageScroll() - barHeight) <= footHeight){
scrollBar.style.top = heightMore - footHeight - barHeight - 2 + 'px';
}
}
//无视主体内容-左右
if (dir == 'left' && areaWidth == 1){
scrollBar.style.left = 2 + 'px';
}else if (dir == 'right' && areaWidth == 1){
scrollBar.style.left = maxWidth - barWidth - 2 + 'px';
//根据主体内容宽-左右
}else if (dir == 'left' && areaWidth != 1){
if (pageWidth >= (barWidth*2 + areaWidth + 4)){
scrollBar.style.left = (pageWidth - areaWidth)/2 - barWidth - 2 + 'px';
}else{
scrollBar.style.left = 2 + 'px';
}
}else if (dir == 'right' && areaWidth != 1){
if (pageWidth >= (barWidth*2 + areaWidth + 4)){
scrollBar.style.left = (pageWidth - areaWidth)/2 + areaWidth + 2 + 'px';
}else{
scrollBar.style.left = maxWidth - barWidth - 2 + 'px';
}
}
//关闭和返回顶部
if (o){
if (o.btnClose){
var closeBtn = Bianyuan.$(o.btnClose);
Bianyuan.addEvent(closeBtn, 'click', function(){
scrollBar.style.display = 'none';
})
}
if (o.goTop){
var gotopBtn = Bianyuan.$(o.goTop);
Bianyuan.addEvent(gotopBtn, 'click', function(){
document.documentElement.scrollTop = 0;
document.body.scrollTop = 0;
})
}
}
//改变窗口大小或滚动条滚动
resizeWindow(scrollId, dir, headHeight, footHeight, areaWidth, o);
}
function resizeWindow(scrollId, dir, headHeight, footHeight, areaWidth, o){
window.onresize = function(){scrollBar(scrollId, dir, headHeight, footHeight, areaWidth, o);}
window.onscroll = function(){scrollBar(scrollId, dir, headHeight, footHeight, areaWidth, o);}
}
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
scrollBar("scroll_div", "right", 42, 95, 1002, {btnClose:"btn_close",goTop:"btn_gotop"});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Ich hoffe, dass dieser Artikel für alle hilfreich ist, die sich mit der JavaScript-Programmierung befassen.
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Eine eingehende Analyse der Bootstrap-Listengruppenkomponente
- Detaillierte Erläuterung des JavaScript-Funktions-Curryings
- Vollständiges Beispiel für die Generierung von JS-Passwörtern und die Erkennung der Stärke (mit Download des Demo-Quellcodes)
- Angularjs integriert WeChat UI (weui)
- Wie man mit JavaScript schnell zwischen traditionellem Chinesisch und vereinfachtem Chinesisch wechselt und wie Websites den Wechsel zwischen vereinfachtem und traditionellem Chinesisch unterstützen – Javascript-Kenntnisse

