Java implementiert zwei Threads zum abwechselnden Drucken
- 王林nach vorne
- 2019-12-24 17:47:543526Durchsuche

Verwenden Sie ReentrantLock, um das abwechselnde Drucken von zwei Threads zu realisieren
Um Buchstaben vorne und Zahlen hinten zu realisieren
package com.study.pattern;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Demo2 {
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
private static CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "ABCDEFGHI";
char[] ca = c.toCharArray();
String n = "123456789";
char[] na = n.toCharArray();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
count.countDown();
for(char caa : ca) {
c1.signal();
System.out.print(caa);
c2.await();
}
c1.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
count.await();
lock.lock();
for(char naa : na) {
c2.signal();
System.out.print(naa);
c1.await();
}
c2.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}Endgültiges Ausgabeergebnis:
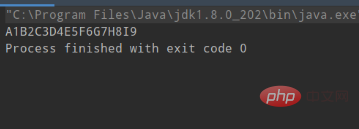
Empfohlene kostenlose Lernvideo-Tutorials: Java-Lehrvideo
Verwenden Sie LinkedTransferQueue, um das abwechselnde Drucken von zwei Threads zu realisieren
Um Buchstaben zuerst und Zahlen nachher zu realisieren
package com.study.pattern;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
public class Demo3 {
private static LinkedTransferQueue<Character> linkedC = new LinkedTransferQueue<Character>();
private static LinkedTransferQueue<Character> linkedN = new LinkedTransferQueue<Character>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "ABCDEFGHI";
char[] ca = c.toCharArray();
String n = "123456789";
char[] na = n.toCharArray();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char caa : ca) {
try {
linkedC.put(caa);
char a = linkedN.take();
System.out.print(a);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char naa : na) {
try {
char b = linkedC.take();
System.out.print(b);
linkedN.put(naa);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}Ausgabeergebnis:
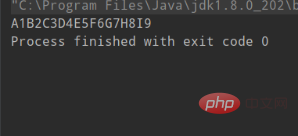
Verwenden Sie synchronisiert, um das abwechselnde Drucken von zwei Threads zu realisieren
Zu realisieren Buchstaben vorne und Zahlen hinten
package com.study.pattern;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class Demo4 {
private static CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "ABCDEFGHI";
char[] ca = c.toCharArray();
String n = "123456789";
char[] na = n.toCharArray();
Object lock = new Object();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
count.countDown();
for(char caa : ca) {
System.out.print(caa);
lock.notify();
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.notify();
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
count.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock) {
for(char naa : na) {
System.out.print(naa);
lock.notify();
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.notify();
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}Ausgabeergebnis:
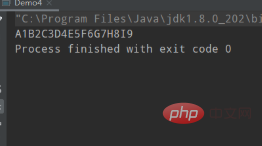
Verwenden Sie LockSupport, um das abwechselnde Drucken von zwei Threads zu realisieren
Zu Erkennen Sie Buchstaben vorne und Zahlen hinten
package com.study.pattern;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class Demo5 {
private static Thread t1;
private static Thread t2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String c = "ABCDEFGHI";
char[] ca = c.toCharArray();
String n = "123456789";
char[] na = n.toCharArray();
t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char caa : ca) {
System.out.print(caa);
LockSupport.unpark(t2);
LockSupport.park();
}
});
t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for(char naa : na) {
LockSupport.park();
System.out.print(naa);
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}Ausgabeergebnisse:
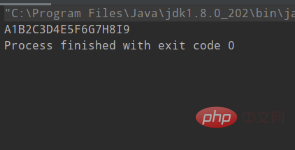
Empfohlene verwandte Artikel und Tutorials: Erste Schritte mit Java Zero Basics
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonJava implementiert zwei Threads zum abwechselnden Drucken. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

