Heim >häufiges Problem >Was bedeutet template
Was bedeutet template?
- 爱喝马黛茶的安东尼Original
- 2019-07-25 15:12:3716230Durchsuche
Die Vorlagenklasse beginnt mit diesem Code: template
template
Klasse wird als Typname der Variablen betrachtet. Die Variable akzeptiert den Typ als ihren Wert.
Fügen Sie die Vorlageninformationen in eine Header-Datei ein und erstellen Sie stacktp.h
#ifndef STACKTP_H_
#define STACKTP_H_
// 建立模板
template<class Type>
class Stack
{
private:
enum {MAX=10};
Type items[MAX];
int top;
public:
Stack();
bool isempty();
bool isfull();
bool push(const Type & item);
bool pop(Type & item);
};
template<class Type>
Stack<Type>::Stack()
{
top=10;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::isempty()
{
return top==0;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::isfull()
{
return top==MAX;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::push(const Type &item)
{
if(top<MAX)
{
items[top++]=item;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
template<class Type>
bool Stack<Type>::pop(Type & item)
{
if(top>0)
{
item=items[--top];
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
#endifVerwandte Empfehlungen: "FAQ"
Erstellen Sie die Quelldatei stacktem . cpp;
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cctype>
#include"stacktp.h"
using namespace std;
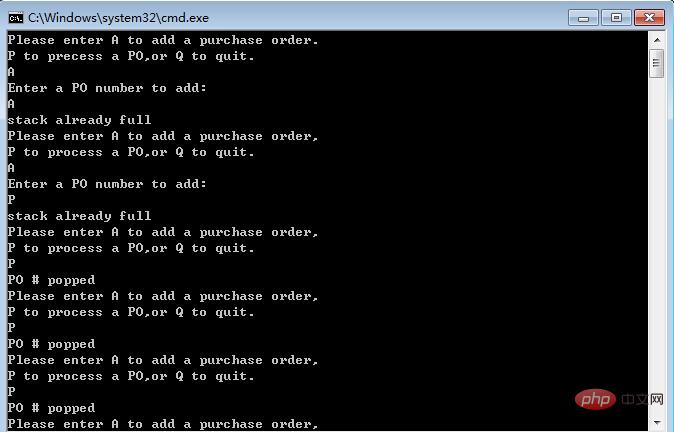
int main()
{
Stack<string> st;// 创建一个空的stack,和前面的模板联系起来
char ch;
string po;
cout<<"Please enter A to add a purchase order.\n"
<<"P to precess a PO,or Q to quit."<<endl;
while(cin>>ch && toupper(ch)!='Q' )
{
while(cin.get()!='\n')
{
continue;
}
if(!isalpha(ch))
{
cout<<'\a';
continue;
}
switch(ch)
{
case 'A':
case 'a':cout<<"Enter a PO number to add:"<<endl;
cin>>po;
if(st.isfull())
{
cout<<"stack already full"<<endl;
}
else
{
st.push(po);
}
break;
case 'P':
case 'p':
if(st.isempty())
{
cout<<"stack already empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
st.pop(po);
cout<<"PO #"<<po<<" popped\n";
break;
}
}
cout<<"Please enter A to add a purchase order,\n"
<<"P to process a PO,or Q to quit.\n";
}
cout<<"Bye!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonWas bedeutet template
Stellungnahme:
Der Inhalt dieses Artikels wird freiwillig von Internetnutzern beigesteuert und das Urheberrecht liegt beim ursprünglichen Autor. Diese Website übernimmt keine entsprechende rechtliche Verantwortung. Wenn Sie Inhalte finden, bei denen der Verdacht eines Plagiats oder einer Rechtsverletzung besteht, wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn
Vorheriger Artikel:Host Host bezieht sich aufNächster Artikel:Host Host bezieht sich auf

