Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >PHP-Tutorial >Wie richte ich eine LAMP-Umgebung ein? Detaillierter Prozess zum Aufbau einer LAMP-Umgebung
Wie richte ich eine LAMP-Umgebung ein? Detaillierter Prozess zum Aufbau einer LAMP-Umgebung
- 不言Original
- 2018-08-07 09:45:238193Durchsuche
Dieser Artikel stellt Ihnen den detaillierten Prozess zum Aufbau einer LAMP-Umgebung vor. Er hat einen gewissen Referenzwert. Ich hoffe, er wird Ihnen hilfreich sein.
Nach der Minimalinstallation von CentOS 7 geben Sie direkt den Befehl ifconfig ein und es erscheint die Meldung „ifconfig-Befehl nicht gefunden“.
, was darauf hinweist, dass bei der Minimalinstallation keine zugehörige Software installiert wird. Wir können ip addr anstelle von ifconfig verwenden, um die Netzwerkkartendetails anzuzeigen, oder wir können yum install verwenden
net-tools, um den Befehl ifconfig zu installieren. Geben Sie während des Installationsvorgangs zweimal y ein, um die Installation abzuschließen.
1. Apache
yum install httpd //Installieren Sie Apache
Total download size: 3.0 M Installed size: 10 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: //输入y,确认安装
Retrieving key from file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 Importing GPG key 0xF4A80EB5: Userid : "CentOS-7 Key (CentOS 7 Official Signing Key) <security>" Fingerprint: 6341 ab27 53d7 8a78 a7c2 7bb1 24c6 a8a7 f4a8 0eb5 Package : centos-release-7-5.1804.el7.centos.x86_64 (@anaconda) From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 Is this ok [y/N]: //验证GPG密钥是否正确,输入y</security>
Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : apr-1.4.8-3.el7_4.1.x86_64 1/5 Installing : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 2/5 Installing : httpd-tools-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1.x86_64 3/5 Installing : mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch 4/5 Installing : httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1.x86_64 5/5 Verifying : mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch 1/5 Verifying : httpd-tools-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1.x86_64 2/5 Verifying : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 3/5 Verifying : apr-1.4.8-3.el7_4.1.x86_64 4/5 Verifying : httpd-2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1.x86_64 5/5 Installed: httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1 Dependency Installed: apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-3.el7_4.1 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7 httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-80.el7.centos.1 mailcap.noarch 0:2.1.41-2.el7 Complete!
Aktivieren Sie den Apache-Dienst und stellen Sie den Dienst so ein, dass er automatisch startet, wenn Das System startet:systemctl start httpd.servicesystemctl enable httpd.service
Um von außen auf den Webserver zugreifen zu können, müssen die Ports HTTP (80) und HTTPS (443) geöffnet werden in der Firewall. Die Standard-Firewall unter CentOS ist firewalld, die mit dem Befehl firewalld-cmd konfiguriert werden kann. firewall-cmd --permanent --zone = public --add-service = http firewall-cmd --permanent --zone = public --add-service = https firewall-cmd --reload //Firewall neu startend
Überprüfen Sie, ob der Apache-Dienst geöffnet ist: systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-08-06 20:14:21 CST; 9s ago Docs: man:httpd(8) man:apachectl(8) Main PID: 1498 (httpd) Status: "Total requests: 0; Current requests/sec: 0; Current traffic: 0 B/sec" CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service ├─1498 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1499 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1500 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1501 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1502 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND └─1503 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND Aug 06 20:14:21 localhost systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server... Aug 06 20:14:21 localhost httpd[1498]: AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's f...sage Aug 06 20:14:21 localhost systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server. Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
Durchsuchen Geben Sie erneut die IP-Adresse des Servers in den Server ein:
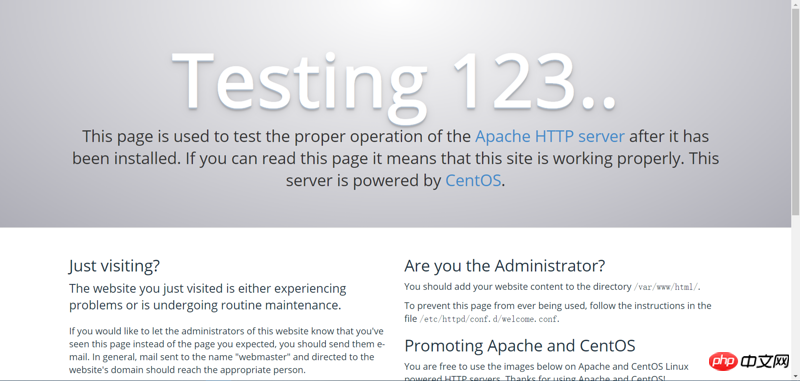
Wenn Sie die in der Abbildung gezeigte Schnittstelle sehen, ist die Installation abgeschlossen erfolgreich.
2. MySQL/MariaDB
Das Datenbankverwaltungssystem MariaDB ist ein Zweig von MySQL, der hauptsächlich von der Open-Source-Community gepflegt wird und unter der GPL lizenziert ist.
Einer der Gründe für die Entwicklung dieses Zweigs besteht darin, dass nach der Übernahme von MySQL durch Oracle das potenzielle Risiko bestand, MySQL als Quelle zu schließen. Daher hat die Community einen Zweigansatz gewählt, um dieses Risiko zu vermeiden.
MariaDB strebt eine vollständige Kompatibilität mit MySQL an, einschließlich API und Befehlszeile. Es ist das derzeit beliebteste MySQL-Datenbankderivat und gilt auch als Ersatz für die Open-Source-Datenbank MySQL.
Hier verwenden wir MariaDB anstelle von MySQL. Die MySQL-Installations- und Betriebsmethoden sind im Allgemeinen ähnlich.
Ersetzen Sie bei der Installation mariadb durch mysql.
Stoppen Sie zum Starten den Dienst und überprüfen Sie den Status. Ersetzen Sie mariadb.service durch mysql.service.
yum -y install mariadb-server mariadb //MariaDB installieren
Installed: mariadb.x86_64 1:5.5.56-2.el7 mariadb-server.x86_64 1:5.5.56-2.el7 Dependency Installed: perl.x86_64 4:5.16.3-292.el7 perl-Carp.noarch 0:1.26-244.el7 perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2.x86_64 0:2.061-3.el7 perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib.x86_64 1:2.061-4.el7 perl-DBD-MySQL.x86_64 0:4.023-6.el7 perl-DBI.x86_64 0:1.627-4.el7 perl-Data-Dumper.x86_64 0:2.145-3.el7 perl-Encode.x86_64 0:2.51-7.el7 perl-Exporter.noarch 0:5.68-3.el7 perl-File-Path.noarch 0:2.09-2.el7 perl-File-Temp.noarch 0:0.23.01-3.el7 perl-Filter.x86_64 0:1.49-3.el7 perl-Getopt-Long.noarch 0:2.40-3.el7 perl-HTTP-Tiny.noarch 0:0.033-3.el7 perl-IO-Compress.noarch 0:2.061-2.el7 perl-Net-Daemon.noarch 0:0.48-5.el7 perl-PathTools.x86_64 0:3.40-5.el7 perl-PlRPC.noarch 0:0.2020-14.el7 perl-Pod-Escapes.noarch 1:1.04-292.el7 perl-Pod-Perldoc.noarch 0:3.20-4.el7 perl-Pod-Simple.noarch 1:3.28-4.el7 perl-Pod-Usage.noarch 0:1.63-3.el7 perl-Scalar-List-Utils.x86_64 0:1.27-248.el7 perl-Socket.x86_64 0:2.010-4.el7 perl-Storable.x86_64 0:2.45-3.el7 perl-Text-ParseWords.noarch 0:3.29-4.el7 perl-Time-HiRes.x86_64 4:1.9725-3.el7 perl-Time-Local.noarch 0:1.2300-2.el7 perl-constant.noarch 0:1.27-2.el7 perl-libs.x86_64 4:5.16.3-292.el7 perl-macros.x86_64 4:5.16.3-292.el7 perl-parent.noarch 1:0.225-244.el7 perl-podlators.noarch 0:2.5.1-3.el7 perl-threads.x86_64 0:1.87-4.el7 perl-threads-shared.x86_64 0:1.43-6.el7 Complete!
MariaDB-Dienst aktivieren und festlegen, dass der Dienst beim Systemstart automatisch gestartet wird: systemctl start mariadb.servicesystemctl enable mariadb.service
Legen Sie das Passwort für das MySQL-Root-Konto fest: mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank, so you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none): //输入当前root用户密码,直接回车 OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. Set root password? [Y/n] New password: //输入密码 Re-enter new password: //确认密码 Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] //删除匿名用户,回车 ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] //不允许root用户远程登录,回车 ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] //删除测试数据库并访问它,回车 - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] //重新加载权限表,回车 ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB!
3. PHP
yum install php //PHP installieren
Total download size: 4.7 M Installed size: 17 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: //允许安装,输入y Downloading packages: (1/4): libzip-0.10.1-8.el7.x86_64.rpm | 48 kB 00:00:00 (2/4): php-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64.rpm | 1.4 MB 00:00:01 (3/4): php-common-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64.rpm | 565 kB 00:00:01 (4/4): php-cli-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64.rpm | 2.7 MB 00:00:02 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 2.1 MB/s | 4.7 MB 00:00:02 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : libzip-0.10.1-8.el7.x86_64 1/4 Installing : php-common-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 2/4 Installing : php-cli-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 3/4 Installing : php-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 4/4 Verifying : php-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 1/4 Verifying : php-cli-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 2/4 Verifying : libzip-0.10.1-8.el7.x86_64 3/4 Verifying : php-common-5.4.16-45.el7.x86_64 4/4 Installed: php.x86_64 0:5.4.16-45.el7 Dependency Installed: libzip.x86_64 0:0.10.1-8.el7 php-cli.x86_64 0:5.4.16-45.el7 php-common.x86_64 0:5.4.16-45.el7 Complete!
Um die Datenbank mit PHP zu verknüpfen, müssen wir auch php-mysql installieren: yum install php-mysql //Geben Sie während des Installationsvorgangs y ein, um die Installation abzuschließen
systemctl restart httpd.service //Nach der Installation von PHP den Apache-Dienst neu starten
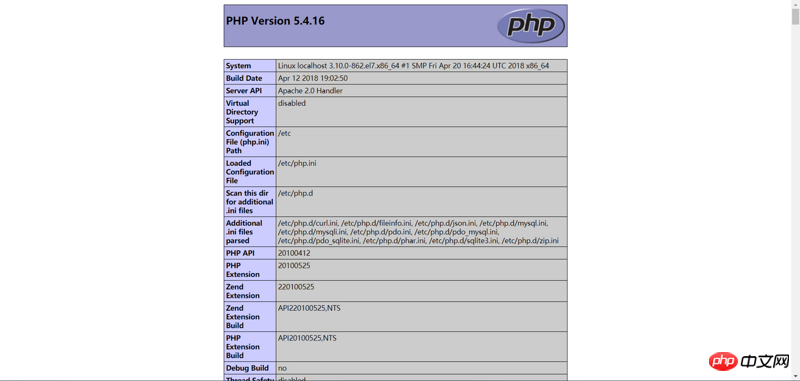
Testen Sie, ob PHP installiert ist: vi /var/www/html/index.php //Erstellen Sie eine neue PHP-Datei und füllen Sie den folgenden Inhalt aus
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Hinzufügen von /info .php nach der vorherigen URL. Wenn Sie die folgende Schnittstelle sehen, bedeutet dies, dass die Installation erfolgreich war.
Empfohlene verwandte Artikel:
Bedienungsschritte der Nginx-Konfigurationsdatei nginx.conf
Schritte zum Ändern der MySQL-Portnummer in der phpstudy-integrierten Umgebung unter Linux-System
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonWie richte ich eine LAMP-Umgebung ein? Detaillierter Prozess zum Aufbau einer LAMP-Umgebung. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- Alle Ausdruckssymbole in regulären Ausdrücken (Zusammenfassung)

