Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >Erfahren Sie mehr über das OS-Modul in Python
Erfahren Sie mehr über das OS-Modul in Python
- 零到壹度Original
- 2018-04-14 11:51:451732Durchsuche
本篇文章给大家分享的内容是深入了解python中的os模块 ,有着一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下
在自动化测试中,经常需要查找操作文件,比如说查找配置文件(从而读取配置文件的信息),查找测试报告(从而发送测试报告邮件),经常要对大量文件和大量路径进行操作,这就依赖于os模块,所以今天整理下比较常用的几个方法。网上这方面资料也很多,每次整理,只是对自己所学的知识进行梳理,从而加深对某个模块的使用。
1.当前路径及路径下的文件
os.getcwd():查看当前所在路径。
os.listdir(path):列举目录下的所有文件。返回的是列表类型。
>>> import os >>> os.getcwd() 'D:\\pythontest\\ostest' >>> os.listdir(os.getcwd()) ['hello.py', 'test.txt']
2.绝对路径
os.path.abspath(path):返回path的绝对路径。
>>> os.path.abspath('.') 'D:\\pythontest\\ostest' >>> os.path.abspath('..') 'D:\\pythontest'
3.查看路径的文件夹部分和文件名部分
os.path.split(path):将路径分解为(文件夹,文件名),返回的是元组类型。可以看出,若路径字符串最后一个字符是\,则只有文件夹部分有值;若路径字符串中均无\,则只有文件名部分有值。若路径字符串有\,且不在最后,则文件夹和文件名均有值。且返回的文件夹的结果不包含\.
os.path.join(path1,path2,...):将path进行组合,若其中有绝对路径,则之前的path将被删除。
>>> os.path.split('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\Hello.py') ('D:\\pythontest\\ostest', 'Hello.py') >>> os.path.split('.') ('', '.') >>> os.path.split('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\') ('D:\\pythontest\\ostest', '') >>> os.path.split('D:\\pythontest\\ostest') ('D:\\pythontest', 'ostest') >>> os.path.join('D:\\pythontest', 'ostest') 'D:\\pythontest\\ostest' >>> os.path.join('D:\\pythontest\\ostest', 'hello.py') 'D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py' >>> os.path.join('D:\\pythontest\\b', 'D:\\pythontest\\a')'D:\\pythontest\\a'
os.path.dirname(path):返回path中的文件夹部分,结果不包含'\'
>>> os.path.dirname('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py' )'D:\\pythontest\\ostest' >>> os.path.dirname('.') '' >>> os.path.dirname('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\') 'D:\\pythontest\\ostest' >>> os.path.dirname('D:\\pythontest\\ostest') 'D:\\pythontest'
os.path.basename(path):返回path中的文件名。
>>> os.path.basename('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py') 'hello.py' >>> os.path.basename('.') '.' >>> os.path.basename('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\') '' >>> os.path.basename('D:\\pythontest\\ostest') 'ostest'
4.查看文件时间
os.path.getmtime(path):文件或文件夹的最后修改时间,从新纪元到访问时的秒数。
os.path.getatime(path):文件或文件夹的最后访问时间,从新纪元到访问时的秒数。
os.path.getctime(path):文件或文件夹的创建时间,从新纪元到访问时的秒数。
>>> os.path.getmtime('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py') 1481695651.857048 >>> os.path.getatime('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py') 1481687717.8506615 >>> os.path.getctime('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py') 1481687717.8506615
5.查看文件大小
os.path.getsize(path):文件或文件夹的大小,若是文件夹返回0。
>>> os.path.getsize('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py' 58L >>> os.path.getsize('D:\\pythontest\\ostest') 0L
6.查看文件是否存在
os.path.exists(path):文件或文件夹是否存在,返回True 或 False。
>>> os.listdir(os.getcwd()) ['hello.py', 'test.txt'] >>> os.path.exists('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\hello.py') True >>> os.path.exists('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\Hello.py') True >>> os.path.exists('D:\\pythontest\\ostest\\Hello1.py') False
7.一些表现形式参数
os中定义了一组文件、路径在不同操作系统中的表现形式参数,如:
>>> os.sep '\\' >>> os.extsep '.' >>> os.pathsep ';' >>> os.linesep '\r\n'
8.实例说明
在自动化测试过程中,常常需要发送邮件,将最新的测试报告文档发送给相关人员查看,这是就需要查找最新文件的功能。
举例:查找文件夹下最新的文件。
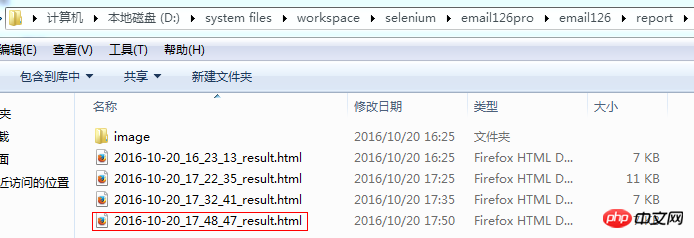
代码如下:
import os
def new_file(test_dir):
#列举test_dir目录下的所有文件(名),结果以列表形式返回。
lists=os.listdir(test_dir) #sort按key的关键字进行升序排序,lambda的入参fn为lists列表的元素,获取文件的最后修改时间,所以最终以文件时间从小到大排序
#最后对lists元素,按文件修改时间大小从小到大排序。
lists.sort(key=lambda fn:os.path.getmtime(test_dir+'\\'+fn)) #获取最新文件的绝对路径,列表中最后一个值,文件夹+文件名
file_path=os.path.join(test_dir,lists[-1])
return file_path
#返回D:\pythontest\ostest下面最新的文件
print new_file('D:\\system files\\workspace\\selenium\\email126pro\\email126\\report')运行结果:

最后再啰嗦一句,关于lambda的用法(python中单行的最小函数):
key=lambda fn:os.path.getmtime(test_dir+'\\'+fn)
#相当于
def key(fn):
return os.path.getmtime(test_dir+'\\'+fn)相关推荐:
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonErfahren Sie mehr über das OS-Modul in Python. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

