Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >Einführung in Beispiele für die Implementierung von Einkaufssystemen in Python
Einführung in Beispiele für die Implementierung von Einkaufssystemen in Python
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-09-15 09:47:532700Durchsuche
下面小编就为大家带来一篇Python实现购物系统(示例讲解)。小编觉得挺不错的,现在就分享给大家,也给大家做个参考。一起跟随小编过来看看吧
要求:
用户入口
1、商品信息存在文件里
2、已购商品,余额记录。
商家入口
可以添加商品,修改商品价格
Code:
商家入口:
# Author:P J J
import os
ps = '''
1 >>>>>> 修改商品
2 >>>>>> 添加商品
按q为退出程序
'''
# 打开两个文件,f文件为原来存取商品文件,f_new文件为修改后的商品文件
f = open('commodit', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
f_new = open('commodit_update', 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
file_list = f.readlines()
# 打印商品信息
while True:
productslist = []
# 从商品文件中读取出来的数据存放到productslist列表里
for line in file_list:
productname = line.strip().split()
productname, oldprice = line.strip("\n").split()
productslist.append([productname, int(oldprice)])
choose = input("%s请选择:" %ps)
if choose =='1':
for index, item in enumerate(productslist):
print(index, item)
productindex = input("请输入要修改价格的商品序号:")
if productindex.isdigit():
productindex = int(productindex)
while True:
print('要修改商品信息:', productslist[productindex])
price = input("请输入要修改的价格:")
if price.isdigit():
price = int(price)
productslist[productindex][1]=price
break
else:
print("请正确的输入价格!")
continue
#已经修改好的商品列表循环写入f_new文件夹
for products in productslist:
insert_data = "%s %s" %(products[0],products[1])
f_new.write(insert_data+'\n')
print("商品价格已经修改!")
# 替换原来的文件
f_new = open('commodit_update', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
data = f_new.readlines()
f = open('commodit', 'w+', encoding='utf-8')
for line in data:
f.write(line)
f.close()
f_new.close()
#删除替换文件
os.remove('commodit_update')
elif choose =='2':
# 添加商品
f = open('commodit', 'a+', encoding='utf-8')
pricename = input("请输入商品名:")
while True:
price = input("请输入商品价格:")
if price.isdigit():
f.writelines('%s %s\n' % (pricename, price))
break
else:
print('输入错误请重新输入!')
continue
f.close()
continue
elif choose =='q':
break
else:
print("输入错误请重新输入")
continue买家入口:
# Author:P J J
productslist = []
f = open('commodit','r',encoding='utf-8')
for line in f:
productname,price = line.strip('\n').split()
productslist.append((productname,int(price)))
print(productslist)
shopping_list = []
salary = input("请输入你的现金:")
if salary.isdigit():
salary = int(salary)
while True:
# for item in productslist:
# print(productslist.index(item),item)
for index,item in enumerate(productslist):
print(index,item)
#判断用户要输入
user_choice = input("请选择要买什啥>>>:")
if user_choice.isdigit():
user_choice = int(user_choice)
if user_choice < len(productslist) and user_choice >= 0:
p_item = productslist[user_choice]
if p_item[1] <= salary: #买得起
shopping_list.append(p_item)
salary -=p_item[1]
print("加入 %s 购物车你的余额是\033[31;1m%s\033[0mRMB" %(p_item,salary))
else:
print("\033[32;1m 你的余额只剩[%s]RMB啦,还买个毛线\033[0m " %salary)
else:
print("\033[41;1m您输入的商品不存在,请重新输入!\033[0m")
elif user_choice == 'q':
print("----shopping_list----")
for p in shopping_list:
print(p)
print("你的余额:\033[31;1m%s\033[0mRMB" %salary)
#简单的余额记录
f = open('salary','w+',encoding='utf-8')
f.writelines(str(salary))
f.close
exit()
else:
print("错误选项")操作流程:
我的目录:
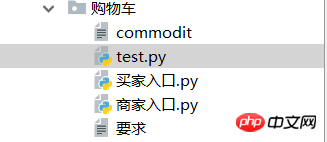
1、新建一个文件,名为 commodit 商品排列格式如下(自己可以更改商品名字或者价格)
2、运行商家入口测试功能

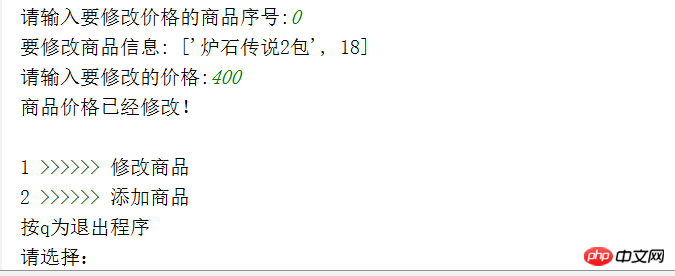
我们输入1,首先测试修改商品:

输入0,修改第一个商品价格为400:
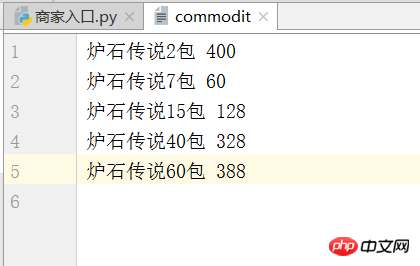
退出后查看 commodit 文件看见商品价格已经修改
--------------------------------------------------
测试添加商品:

查看 commodit文件
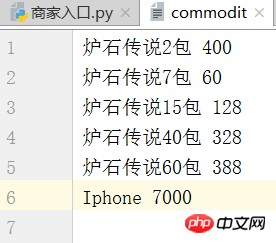
测试买家入口:

有钱了那就先来一台Iphone

再来60包炉石卡包

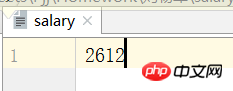
按q退出结账!并且有一个salary文件记录余额

此时目录会多一个salary文件
点开就能看到余额已经被记录
感想:
做完这个购物车花了2天,其实也不是整天都在弄,毕竟还要上课、学习。这次主要是熟悉文件的操作和一些基础知识的回顾,写完后能跑出功能就很开心了.因为中途遇到很多困难,解决了一个又出一个问题,不过通过上网查找和询问还是解决了。写完后感觉很low,毕竟自己敲得太少还是要多加练习,这个程序挺适合入门或者学完文件操作的亲来练练手。对了,自己测试程序的时候还出现bug,不过影响不是特别大,只是不要多次修改价格就行,这个问题我也想过怎么解决,就是把列表清空,这样数据就不会读出2遍,但又发现第二次读取的数据不是更改后的数据,我就在想,列表有没有刷新,清空功能。这里先留下这个问题吧。功能已经都实现了,但写的真的很low,等以后再掌握了新姿势,回头来改改!包括前面做的登录还有三级菜单!如果有跟我一样初学的可以一起学习Alex老师的python课程,如果有大神看到,并且能耐心看完,请大神再多指点指点小弟!
好了,Life is short,use python!
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEinführung in Beispiele für die Implementierung von Einkaufssystemen in Python. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

