Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >C#.Net-Tutorial >Ausführliche Erläuterung des Beispiels für die Konfigurationsdatei web.config
Ausführliche Erläuterung des Beispiels für die Konfigurationsdatei web.config
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-09-01 14:33:593887Durchsuche
Dieser Artikel führt Sie hauptsächlich in die relevanten Informationen zur web.config-Konfigurationsdatei der .NET Core 2.0-Migrationsfähigkeiten ein. Der Artikel stellt sie anhand von Beispielcodes detailliert vor, die einen gewissen Referenzlernwert für alle Lern- oder Arbeitsfreunde haben Wer es braucht, folgt bitte dem Herausgeber, um gemeinsam zu lernen.
Vorwort
Ich glaube, jeder sollte wissen, dass .NET Core die ursprüngliche Konfigurationsdatei web.config nicht mehr unterstützt, sondern durch JSON oder XML ersetzt wurde Konfigurationsdatei. Die offiziell empfohlene Projektkonfigurationsmethode ist die Verwendung der Konfigurationsdatei appsettings.json, was für die Migration einiger vorhandener Projekte, die die web.cofig-Konfiguration stark nutzen, möglicherweise nicht akzeptabel ist.
Aber die gute Nachricht ist, dass wir die vorhandene web.config direkt im .NET Core 2.0-Projekt verwenden können. In diesem Artikel wird der relevante Inhalt der web.config-Konfigurationsdatei für die .NET Core 2.0-Migration ausführlich vorgestellt. Ich werde im Folgenden nicht auf Details eingehen, werfen wir einen Blick auf die detaillierte Einführung.
Migrationsmethode
1. Erst durch die Einführung können wir das Lesenetz erreichen .config-Code funktioniert.System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager
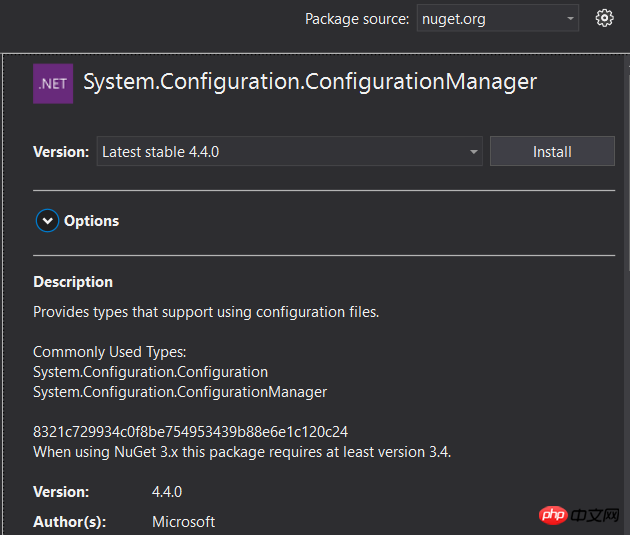
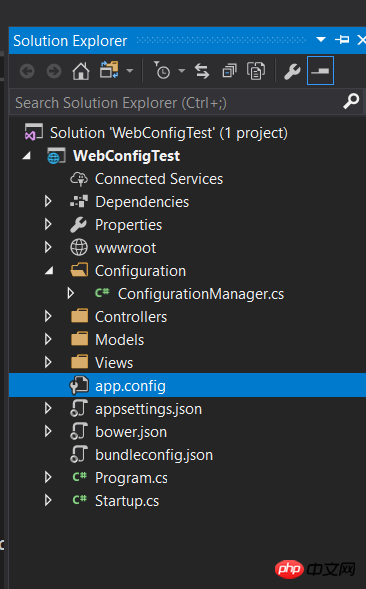
, 2dc15ec6bc814c3aa45b55d017848bed und 1dcc4c920d99d48189de261dfba48f61. 455f4645fc0f45153cc77129e16a328a
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <configSections> <!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 --> <section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false" /> </configSections> <connectionStrings> <add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=(LocalDb)\MSSQLLocalDB;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\aspnet-WebApplication24-20170824065102.mdf;Initial Catalog=aspnet-WebApplication24-20170824065102;Integrated Security=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings> <appSettings> <add key="webpages:Version" value="3.0.0.0" /> <add key="webpages:Enabled" value="false" /> <add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="true" /> <add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="true" /> <add key="MyKey" value="true"/> </appSettings> <system.web> <compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.7" /> <httpRuntime targetFramework="4.7" /> <httpModules> <add name="ApplicationInsightsWebTracking" type="Microsoft.ApplicationInsights.Web.ApplicationInsightsHttpModule, Microsoft.AI.Web" /> </httpModules> </system.web> <runtime> <assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1"> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="Newtonsoft.Json" culture="neutral" publicKeyToken="30ad4fe6b2a6aeed" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-6.0.0.0" newVersion="6.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Optimization" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.1.0.0" newVersion="1.1.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="WebGrease" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="0.0.0.0-1.5.2.14234" newVersion="1.5.2.14234" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Helpers" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.WebPages" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" /> </dependentAssembly> <dependentAssembly> <assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Mvc" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" /> <bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-5.2.3.0" newVersion="5.2.3.0" /> </dependentAssembly> </assemblyBinding> </runtime> <system.webServer> <validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration="false" /> <modules> <remove name="ApplicationInsightsWebTracking" /> <add name="ApplicationInsightsWebTracking" type="Microsoft.ApplicationInsights.Web.ApplicationInsightsHttpModule, Microsoft.AI.Web" preCondition="managedHandler" /> </modules> </system.webServer> <system.codedom> <compilers> <compiler language="c#;cs;csharp" extension=".cs" type="Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform.CSharpCodeProvider, Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform, Version=1.0.5.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" warningLevel="4" compilerOptions="/langversion:default /nowarn:1659;1699;1701" /> <compiler language="vb;vbs;visualbasic;vbscript" extension=".vb" type="Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform.VBCodeProvider, Microsoft.CodeDom.Providers.DotNetCompilerPlatform, Version=1.0.5.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35" warningLevel="4" compilerOptions="/langversion:default /nowarn:41008 /define:_MYTYPE=\"Web\" /optionInfer+" /> </compilers> </system.codedom> </configuration>Nach der Änderung:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <configSections> <!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 --> <section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false" /> </configSections> <connectionStrings> <add name="DefaultConnection" connectionString="Data Source=(LocalDb)\MSSQLLocalDB;AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|\aspnet-WebApplication24-20170824065102.mdf;Initial Catalog=aspnet-WebApplication24-20170824065102;Integrated Security=True" providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" /> </connectionStrings> <appSettings> <add key="webpages:Version" value="3.0.0.0" /> <add key="webpages:Enabled" value="false" /> <add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="true" /> <add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="true" /> <add key="MyKey" value="true"/> </appSettings> </configuration>4 . Testen Sie den ursprünglichen ASP.NET-Code und prüfen Sie, ob der gelesene Konfigurationswert korrekt ist:
using System.Configuration;
namespace WebConfigTest.Configuration
{
public class ConfigurationService
{
public static bool GetConfigValue(string key)
{
var result = false;
var val= ConfigurationManager.AppSettings[key];
if (val != null)
{
result = bool.Parse(val);
}
return result;
}
}
} Setzen Sie einen Haltepunkt, um zu sehen, ob der gelesene Konfigurationswert korrekt ist:
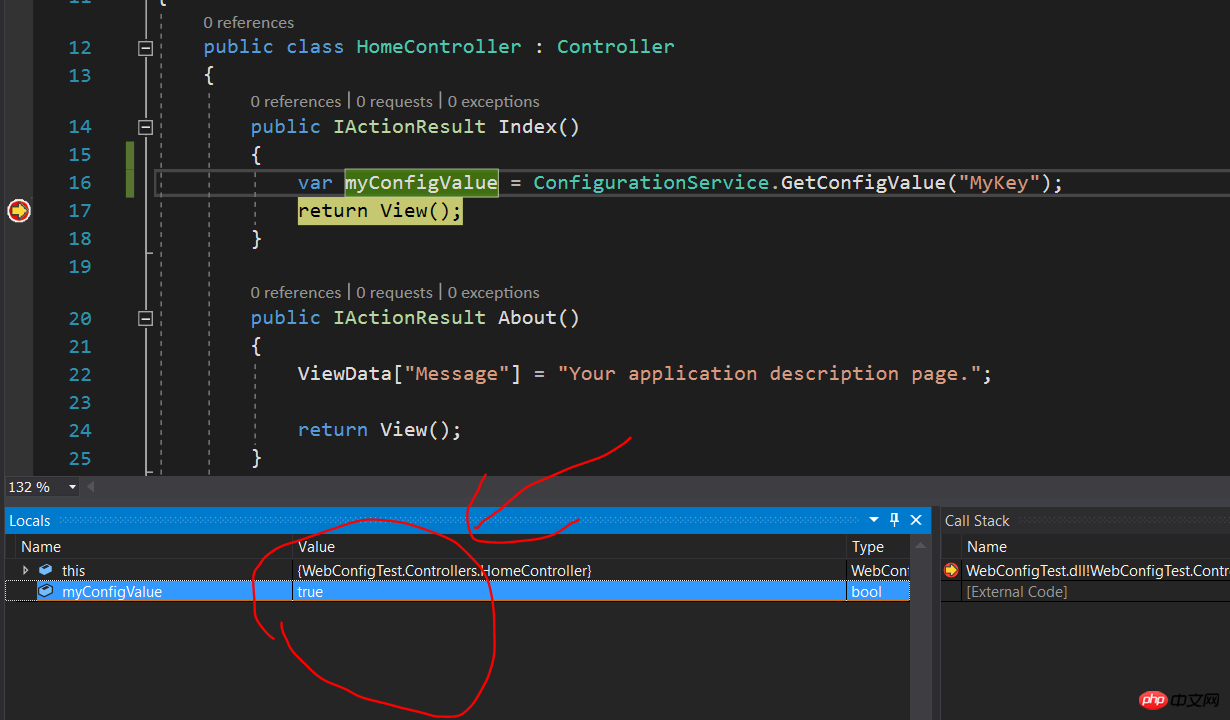
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonAusführliche Erläuterung des Beispiels für die Konfigurationsdatei web.config. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- .Net Core-Grafikverifizierungscode
- Laden der .NET Core-Konfigurationsdatei und DI-Injektion von Konfigurationsdaten
- Dokumentation zum .NET Core CLI-Tool dotnet-publish
- asp.net verwendet .net-Steuerelemente, um Dropdown-Navigationsmenüs zu erstellen
- So erhalten Sie den Namen des Controllers in Asp.net MVC

