Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Eine kurze Analyse des Prinzips und der einfachen Implementierung linearer Tabellen
Eine kurze Analyse des Prinzips und der einfachen Implementierung linearer Tabellen
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-06-26 11:38:012188Durchsuche
1. Lineare Tabelle
Prinzip: eine endliche Folge von null oder mehr ähnlichen Datenelementen
Prinzip:
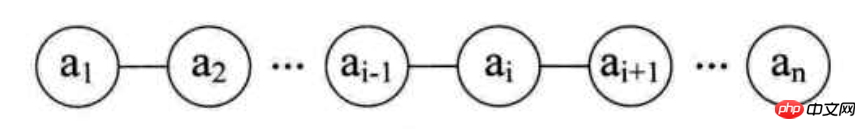
Merkmale:
1. Ordnung
3. Elemente des gleichen Typs
4 hat keinen Nachfolger und das mittlere Element hat einen Vorgänger und einen Nachfolger
Lineare Liste ist eine logische Datenstruktur. Es gibt im Allgemeinen zwei physische Implementierungen: sequentielle Implementierung und verknüpfte Listenimplementierung
2. Array-basierte lineare Tabellensequenzimplementierung
Prinzip: Verwenden Sie eine Speichereinheit mit einer kontinuierlichen Adresse, um lineare Tabellendatenelemente nacheinander zu speichern.
Prinzipdiagramm:
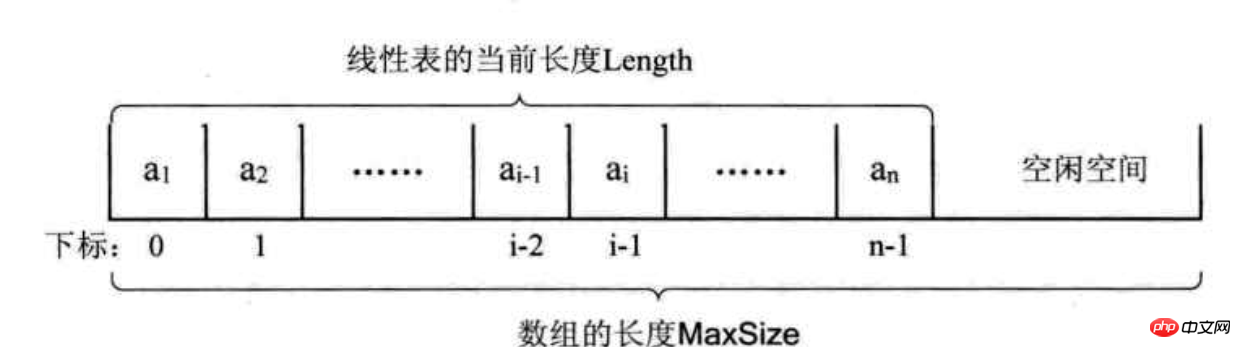 Algorithmusprinzip:
Algorithmusprinzip:
1. Initialisieren Sie ein Array mit fester Länge, RaumelementData[] und Speicherlänge Elemente
2. Schneller Zugriff auf Elemente durch Indizes
3. Einfügen und Löschen von Elementen durch Array-Kopie
1. Keine Notwendigkeit, zusätzliche Elemente hinzuzufügen Speicherplatz, um die logische Beziehung zwischen Elementen in der Tabelle auszudrücken
Sie können schnell auf Elemente an jeder Position in der Tabelle zugreifen
3. Das Einfügen und Löschen erfordert das Kopieren von Arrays (d. h. das Verschieben von a große Anzahl von Elementen)
4. Wenn sich die Länge der linearen Tabelle stark ändert, ist eine häufige Erweiterung erforderlich, was zu einer Fragmentierung des Speicherplatzes führt
Implementierungscode:
Schnittstellendefinition:

 Code anzeigen
Code anzeigen 1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-14 11:46 6 */ 7 8 public interface LineList <E>{ 9 10 /**11 * lineList 是否为空12 * @return13 */14 boolean isEmpty();15 16 /**17 * 清空 lineList18 */19 void clear();20 21 /**22 * 获取指定位置元素23 * @param index24 * @return25 */26 E get(int index);27 28 /**29 * 获取元素第一次出现的位置30 * @param e31 * @return32 */33 int indexOf(E e);34 35 /**36 * 判断 lineList是否包含指定元素37 * @param e38 * @return39 */40 boolean contains(E e);41 42 /**43 * 设置指定位置数据,如数据已存在 则覆盖原数据44 * @param index45 * @param e46 * @return47 */48 E set(int index, E e);49 50 /**51 * 移除指定位置元素52 * @param index53 * @return54 */55 E remove(int index);56 57 /**58 * 在lineList结尾插入元素59 * @param e60 * @return61 */62 E add(E e);63 64 /**65 * 在index后面插入元素66 * @param index67 * @param e68 * @return69 */70 E add(int index, E e);71 72 /**73 * 返回lineList长度74 * @return75 */76 int size();77 78 79 80 }
 Code anzeigen
Code anzeigen 1 package online.jfree.base; 2 3 /** 4 * author : Guo LiXiao 5 * date : 2017-6-15 13:44 6 */ 7 8 public class OrderedLineList<E> implements LineList<E> { 9 10 private static final int INIT_CAPACITY = 10; 11 12 private transient E[] elementData; 13 14 private transient int elementLength; 15 16 private int size; 17 18 public OrderedLineList() { 19 this(0); 20 } 21 22 public OrderedLineList(int initCapacity) { 23 init(initCapacity); 24 } 25 26 private void init(int initCapacity) { 27 if (initCapacity >= 0) { 28 this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[initCapacity]; 29 this.elementLength = initCapacity; 30 } else { 31 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + 32 initCapacity); 33 } 34 this.size = 0; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * 扩容 39 */ 40 private void dilatation() { 41 int oldCapacity = this.elementLength; 42 int newCapacity = oldCapacity; 43 if (oldCapacity <= this.size) { 44 newCapacity = oldCapacity + INIT_CAPACITY; 45 }else if(oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY > this.size){ 46 newCapacity = oldCapacity - INIT_CAPACITY; 47 } 48 if (oldCapacity != newCapacity){ 49 E[] newElementData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity]; 50 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newElementData, 0, oldCapacity); 51 this.elementLength = newCapacity; 52 this.elementData = newElementData; 53 } 54 } 55 56 /** 57 * 校验列表索引越界 58 * @param index 59 */ 60 private void checkCapacity(int index){ 61 if (index > this.size - 1 || index < 0) 62 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(new StringBuffer("[index : ").append(index).append("] , [size : ").append(size).append("] ").toString()); 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public boolean isEmpty() { 67 return this.size == 0; 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void clear() { 72 this.init(0); 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public E get(int index) { 77 this.checkCapacity(index); 78 return this.elementData[index]; 79 } 80 81 @Override 82 public int indexOf(E e) { 83 for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++){ 84 if (e == null && elementData[i] == null || e.equals(elementData[i])){ 85 return i; 86 } 87 } 88 return -1; 89 } 90 91 @Override 92 public boolean contains(E e) { 93 return this.indexOf(e) > 0; 94 } 95 96 @Override 97 public E set(int index, E e) { 98 this.checkCapacity(index); 99 this.dilatation();100 E oldElement = this.elementData[index];101 this.elementData[index] = e;102 return oldElement;103 }104 105 @Override106 public E remove(int index) {107 this.dilatation();108 E e = elementData[index];109 if (index == size - 1) elementData[index] = null;110 else {111 int length = size - index - 1;112 System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, length);113 }114 size --;115 return e;116 }117 118 @Override119 public E add(E e) {120 return this.add(size, e);121 }122 123 @Override124 public E add(int index, E e) {125 this.dilatation();126 if (index == size) elementData[index] = e;127 else {128 index++;129 int lastLength = size - index;130 E[] lastElementData = (E[]) new Object[lastLength];131 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, lastElementData, 0, lastLength);132 elementData[index] = e;133 System.arraycopy(lastElementData, 0, elementData, index + 1, lastLength);134 }135 size ++ ;136 return e;137 }138 139 @Override140 public int size() {141 return this.size;142 }143 144 }Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonEine kurze Analyse des Prinzips und der einfachen Implementierung linearer Tabellen. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

