Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >Allgemeine Wissenspunkte zu Python
Allgemeine Wissenspunkte zu Python
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-03-02 17:06:291399Durchsuche
1. Set-Basisdatentyp
a. Set-Set ist eine ungeordnete und sich nicht wiederholende Sammlung von Elementen
class set(object):
"""
set() -> new empty set object
set(iterable) -> new set object
Build an unordered collection of unique elements.
"""
def add(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Add an element to a set,添加元素
This has no effect if the element is already present.
"""
pass
def clear(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements from this set. 清楚内容"""
pass
def copy(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return a shallow copy of a set. 浅拷贝 """
pass
def difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the difference of two or more sets as a new set. A中存在,B中不存在
(i.e. all elements that are in this set but not the others.)
"""
pass
def difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Remove all elements of another set from this set. 从当前集合中删除和B中相同的元素"""
pass
def discard(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set if it is a member.
If the element is not a member, do nothing. 移除指定元素,不存在不保错
"""
pass
def intersection(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the intersection of two sets as a new set. 交集
(i.e. all elements that are in both sets.)
"""
pass
def intersection_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the intersection of itself and another. 取交集并更更新到A中 """
pass
def isdisjoint(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return True if two sets have a null intersection. 如果没有交集,返回True,否则返回False"""
pass
def issubset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether another set contains this set. 是否是子序列"""
pass
def issuperset(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Report whether this set contains another set. 是否是父序列"""
pass
def pop(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove and return an arbitrary set element.
Raises KeyError if the set is empty. 移除元素
"""
pass
def remove(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Remove an element from a set; it must be a member.
If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError. 移除指定元素,不存在保错
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the symmetric difference of two sets as a new set. 对称交集
(i.e. all elements that are in exactly one of the sets.)
"""
pass
def symmetric_difference_update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the symmetric difference of itself and another. 对称交集,并更新到a中 """
pass
def union(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return the union of sets as a new set. 并集
(i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
"""
pass
def update(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Update a set with the union of itself and others. 更新 """
pass
B. Beispiele für Datentypmodule
se = {11,22,33,44,55}
be = {44,55,66,77,88}
# se.add(66)
# print(se) #添加元素,不能直接打印!
#
#
#
# se.clear()
# print(se) #清除se集合里面所有的值,不能清除单个
#
#
#
# ce=be.difference(se) #se中存在,be中不存在的值,必须赋值给一个新的变量
# print(ce)
#
#
# se.difference_update(be)
# print(se) #在se中删除和be相同的值,不能赋值给一个新的变量,先输入转换,然后打印,也不能直接打印!
# se.discard(11)
# print(se) #移除指定元素,移除不存在的时候,不会报错
# se.remove(11)
# print(se) #移除指定的元素,移除不存在的会报错
# se.pop()
# print(se) #移除随机的元素
#
#
# ret=se.pop()
# print(ret) #移除元素,并且可以把移除的元素赋值给另一个变量
# ce = se.intersection(be)
# print(ce) #取出两个集合的交集(相同的元素)
# se.intersection_update(be)
# print(se) #取出两个集合的交集,并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.isdisjoint(be)
# print(ret) #判断两个集合之间又没有交集,如果有交集返回False,没有返回True
# ret=se.issubset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是否是be集合的子序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret = se.issuperset(be)
# print(ret) #判断se是不是be集合的父序列,如果是返回True,不是返回Flase
# ret=se.symmetric_difference(be)
# print(ret) #对称交集,取出除了不相同的元素
# se.symmetric_difference_update(be)
# print(se) #对称交集,取出不相同的元素并更新到se集合中
# ret = se.union(be)
# print(ret) #并集,把两个元素集合并在一个新的变量中2. Tiefe und flache Kopie
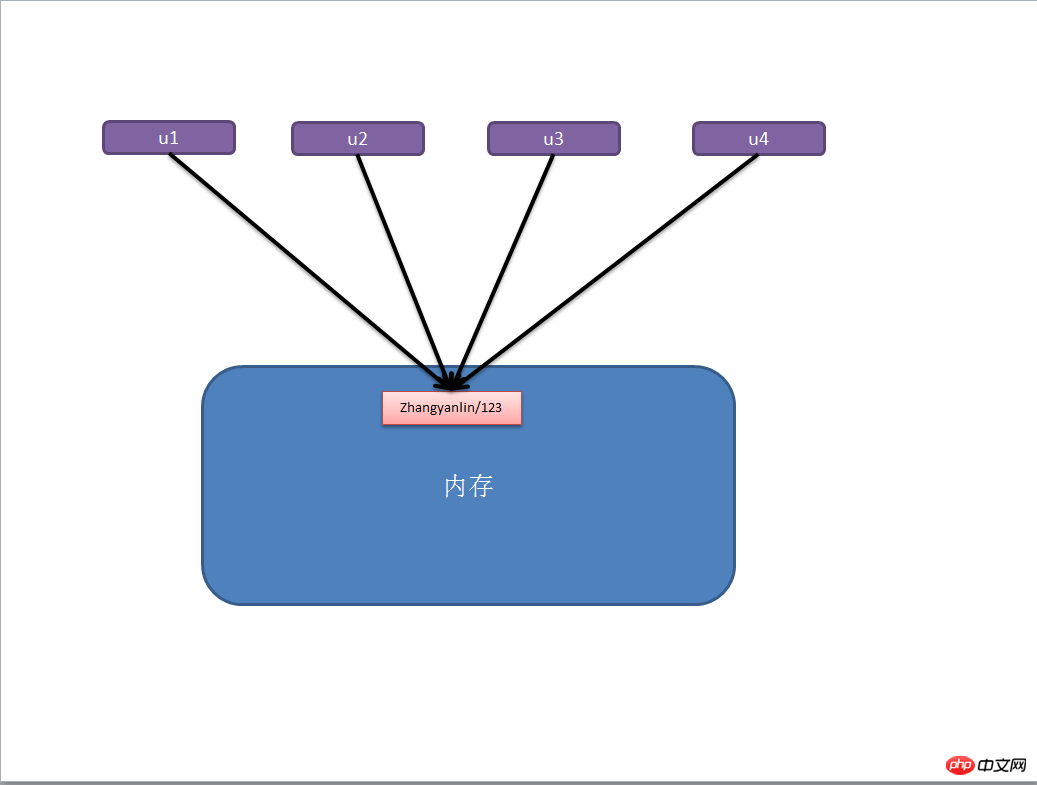
a, Zahlen und Strings
Bei Zahlen und Strings sind Zuweisung, flaches Kopieren und tiefes Kopieren bedeutungslos, da sie immer auf die gleiche Speicheradresse verweisen.
import copy # ######### 数字、字符串 ######### n1 = 123 # n1 = "i am alex age 10" print(id(n1)) # ## 赋值 ## n2 = n1 print(id(n2)) # ## 浅拷贝 ## n2 = copy.copy(n1) print(id(n2)) # ## 深拷贝 ## n3 = copy.deepcopy(n1) print(id(n3))
 b. Andere grundlegende Datentypen
b. Andere grundlegende Datentypen
Für Wörterbücher, Grundelemente und Listen , Die Änderungen der Speicheradresse sind unterschiedlich, wenn Zuweisung, flaches Kopieren und tiefes Kopieren durchgeführt werden.
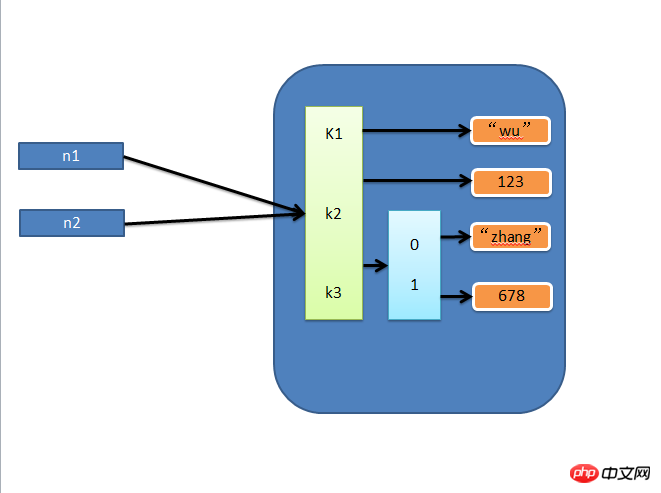
1. Zuweisung
Zuweisung erstellt lediglich eine Variable, die auf die ursprüngliche Speicheradresse zeigt, wie zum Beispiel:
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["Aylin", 456]}
n2 = n1
 2. Flache Kopie
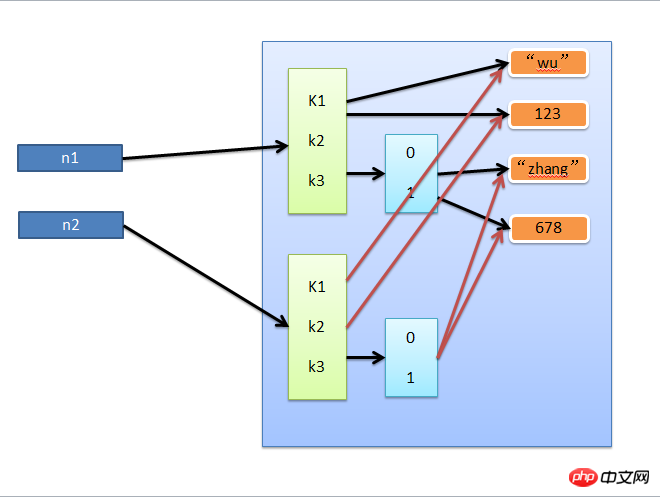
2. Flache Kopie
Flache Kopie, nur die erste Datenebene wird zusätzlich im Speicher erstellt
import copy
n1 = {"k1": "zhangyanlin", "k2": 123, "k3": ["aylin", 456]}
n3 = copy.copy(n1)3. Deep Copy
Deep Copy, erstellt eine Kopie aller Daten im Speicher (mit Ausnahme der letzten Ebene, d. h. Pythons interne Optimierung von Zeichenfolgen und Zahlen)
Funktional: Kapseln Sie einen bestimmten Funktionscode in eine Funktion, sodass Sie nicht schreiben müssen Nennen Sie es in Zukunft noch einmal. Funktionen können
“. Die Definition von Funktionen hauptsächlich hat die folgenden Punkte:
def: Schlüsselwort, das eine Funktion darstellt
Funktionsname: Der Name der Funktion wird in Zukunft basierend auf dem Funktionsnamen aufgerufen In der Funktion werden eine Reihe logischer Berechnungen durchgeführt, z. B. E-Mails senden, [11, 22, 38, 888, 2] berechnen usw. Parameter: Daten für den Funktionskörper bereitstellen
Rückgabewert: Wenn die Funktion ausgeführt wird, können Daten an den Aufrufer zurückgegeben werden. 🎜>1 Rückgabewert: Ob die Funktion erfolgreich ausgeführt wird oder nicht, muss dem Aufrufer mitgeteilt werden Rückgabewert.
Unter den oben genannten Punkten sind die Parameter und die wichtigsten:
def 发送短信():
发送短信的代码...
if 发送成功:
return True
else:
return False
while True:
# 每次执行发送短信函数,都会将返回值自动赋值给result
# 之后,可以根据result来写日志,或重发等操作
result = 发送短信()
if result == False:
短信发送失败... # Name wird als Formal bezeichnet Parameter der Funktion func, abgekürzt als: formaler Parameter
def func(name):print name
# ######### Funktion ausführen######## #
# 'zhangyanlin' wird als tatsächlicher Parameter der Funktion func bezeichnet, abgekürzt als: tatsächlicher Parameterfunc( 'zhangyanlin')
Standardparameter
def func(name, age = 18):
print "%s:%s" %(name,age)
# Parameter angeben
# Verwendung Standardparameter
func('nick')
Hinweis: Standardparameter müssen in der letzten Parameterliste platziert werden
Dynamische Parameter
def func(*args): print args # 执行方式一 func(11,33,4,4454,5) # 执行方式二 li = [11,2,2,3,3,4,54] func(*li)
def func(**kwargs):
print args
# 执行方式一
func(name='wupeiqi',age=18)
# 执行方式二
li = {'name':'wupeiqi', age:18, 'gender':'male'}
func(**li) E-Mail-Beispiel:
def func(*args, **kwargs): print args print kwargs
def email(p,j,k):
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.utils import formataddr
set = True
try:
msg = MIMEText('j', 'plain', 'utf-8') #j 邮件内容
msg['From'] = formataddr(["武沛齐",'wptawy@126.com'])
msg['To'] = formataddr(["走人",'424662508@qq.com'])
msg['Subject'] = "k" #k主题
server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.126.com", 25)
server.login("wptawy@126.com", "WW.3945.59")
server.sendmail('wptawy@126.com', [p], msg.as_string())
server.quit()
except:
set = False
return True
formmail = input("请你输入收件人邮箱:")
zhuti = input("请您输入邮件主题:")
neirong = input("请您输入邮件内容:")
aa=email(formmail,neirong,zhuti)
if aa:
print("邮件发送成功!")
else:
print("邮件发送失败!")Weitere Artikel zu allgemeinen Python-Wissenspunkten finden Sie unter die chinesische PHP-Website!

