Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Einfache Methode zur Implementierung eines Dateimanagers für die Android-Entwicklung
Einfache Methode zur Implementierung eines Dateimanagers für die Android-Entwicklung
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-01-21 14:27:221491Durchsuche
Das Beispiel in diesem Artikel beschreibt die Implementierungsmethode eines einfachen Dateimanagers für die Android-Entwicklung. Teilen Sie es als Referenz mit allen. Die Details lauten wie folgt:
Hier werden Java I/O, ListActivity, Dialog, Bitmap usw. verwendet, um einen einfachen Dateimanager zu implementieren. Sie können Verzeichnisdateien anzeigen und Dateien ändern Namen hinzufügen, Dateien löschen und Dateien öffnen. Es ist relativ einfach, schauen Sie sich den Code direkt an:
Schauen Sie sich zuerst die Layoutdatei an:
layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ListView android:id="@android:id/list" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
Datei Listenlayout:
layout/file.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="14sp"> </TextView> </LinearLayout>
Ändern Sie die Dateinamen-Dialoglayoutdatei:
layout/rename_dialog.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <EditText android:id="@+id/editText" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
Hauptaktivität:
public class MainActivity extends ListActivity {
private static final String ROOT_PATH = "/";
//存储文件名称
private ArrayList<String> names = null;
//存储文件路径
private ArrayList<String> paths = null;
private View view;
private EditText editText;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//显示文件列表
showFileDir(ROOT_PATH);
}
private void showFileDir(String path){
names = new ArrayList<String>();
paths = new ArrayList<String>();
File file = new File(path);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
//如果当前目录不是根目录
if (!ROOT_PATH.equals(path)){
names.add("@1");
paths.add(ROOT_PATH);
names.add("@2");
paths.add(file.getParent());
}
//添加所有文件
for (File f : files){
names.add(f.getName());
paths.add(f.getPath());
}
this.setListAdapter(new MyAdapter(this,names, paths));
}
@Override
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
String path = paths.get(position);
File file = new File(path);
// 文件存在并可读
if (file.exists() && file.canRead()){
if (file.isDirectory()){
//显示子目录及文件
showFileDir(path);
}
else{
//处理文件
fileHandle(file);
}
}
//没有权限
else{
Resources res = getResources();
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("Message")
.setMessage(res.getString(R.string.no_permission))
.setPositiveButton("OK",new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
}).show();
}
super.onListItemClick(l, v, position, id);
}
//对文件进行增删改
private void fileHandle(final File file){
OnClickListener listener = new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// 打开文件
if (which == 0){
openFile(file);
}
//修改文件名
else if(which == 1){
LayoutInflater factory = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this);
view = factory.inflate(R.layout.rename_dialog, null);
editText = (EditText)view.findViewById(R.id.editText);
editText.setText(file.getName());
OnClickListener listener2 = new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String modifyName = editText.getText().toString();
final String fpath = file.getParentFile().getPath();
final File newFile = new File(fpath + "/" + modifyName);
if (newFile.exists()){
//排除没有修改情况
if (!modifyName.equals(file.getName())){
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this)
.setTitle("注意!")
.setMessage("文件名已存在,是否覆盖?")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
if (file.renameTo(newFile)){
showFileDir(fpath);
displayToast("重命名成功!");
}
else{
displayToast("重命名失败!");
}
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
})
.show();
}
}
else{
if (file.renameTo(newFile)){
showFileDir(fpath);
displayToast("重命名成功!");
}
else{
displayToast("重命名失败!");
}
}
}
};
AlertDialog renameDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).create();
renameDialog.setView(view);
renameDialog.setButton("确定", listener2);
renameDialog.setButton2("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
renameDialog.show();
}
//删除文件
else{
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this)
.setTitle("注意!")
.setMessage("确定要删除此文件吗?")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
if(file.delete()){
//更新文件列表
showFileDir(file.getParent());
displayToast("删除成功!");
}
else{
displayToast("删除失败!");
}
}
})
.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
}).show();
}
}
};
//选择文件时,弹出增删该操作选项对话框
String[] menu = {"打开文件","重命名","删除文件"};
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this)
.setTitle("请选择要进行的操作!")
.setItems(menu, listener)
.setPositiveButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
}
}).show();
}
//打开文件
private void openFile(File file){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
intent.setAction(android.content.Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
String type = getMIMEType(file);
intent.setDataAndType(Uri.fromFile(file), type);
startActivity(intent);
}
//获取文件mimetype
private String getMIMEType(File file){
String type = "";
String name = file.getName();
//文件扩展名
String end = name.substring(name.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, name.length()).toLowerCase();
if (end.equals("m4a") || end.equals("mp3") || end.equals("wav")){
type = "audio";
}
else if(end.equals("mp4") || end.equals("3gp")) {
type = "video";
}
else if (end.equals("jpg") || end.equals("png") || end.equals("jpeg") || end.equals("bmp") || end.equals("gif")){
type = "image";
}
else {
//如果无法直接打开,跳出列表由用户选择
type = "*";
}
type += "/*";
return type;
}
private void displayToast(String message){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
Benutzerdefinierter Adapter:
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private LayoutInflater inflater;
private Bitmap directory,file;
//存储文件名称
private ArrayList<String> names = null;
//存储文件路径
private ArrayList<String> paths = null;
//参数初始化
public MyAdapter(Context context,ArrayList<String> na,ArrayList<String> pa){
names = na;
paths = pa;
directory = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(),R.drawable.d);
file = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(),R.drawable.f);
//缩小图片
directory = small(directory,0.16f);
file = small(file,0.1f);
inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return names.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return names.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ViewHolder holder;
if (null == convertView){
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.file, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.text = (TextView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.textView);
holder.image = (ImageView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
else {
holder = (ViewHolder)convertView.getTag();
}
File f = new File(paths.get(position).toString());
if (names.get(position).equals("@1")){
holder.text.setText("/");
holder.image.setImageBitmap(directory);
}
else if (names.get(position).equals("@2")){
holder.text.setText("..");
holder.image.setImageBitmap(directory);
}
else{
holder.text.setText(f.getName());
if (f.isDirectory()){
holder.image.setImageBitmap(directory);
}
else if (f.isFile()){
holder.image.setImageBitmap(file);
}
else{
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
return convertView;
}
private class ViewHolder{
private TextView text;
private ImageView image;
}
private Bitmap small(Bitmap map,float num){
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(num, num);
return Bitmap.createBitmap(map,0,0,map.getWidth(),map.getHeight(),matrix,true);
}
}
Da die Datei bedient werden muss, erfolgt die Berechtigung in der Beschreibungsdatei:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.test.filemanager"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="10" />
<strong> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/></strong>
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Der Lauf Die Ergebnisse lauten wie folgt:
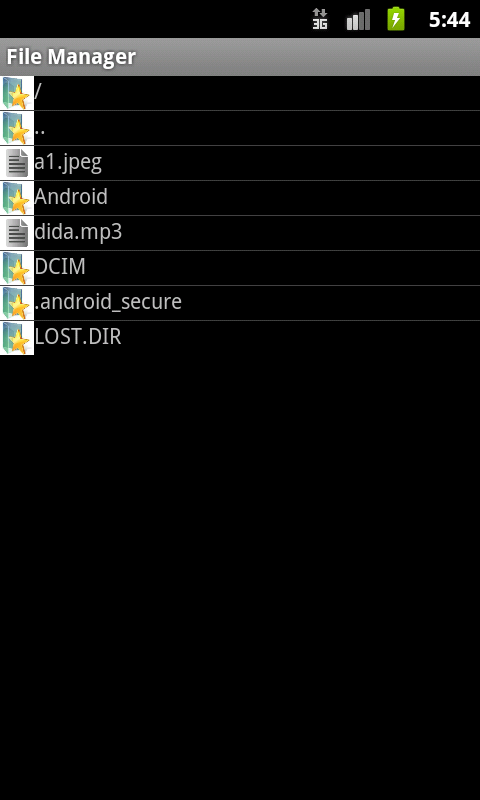
Verzeichnisdateien anzeigen
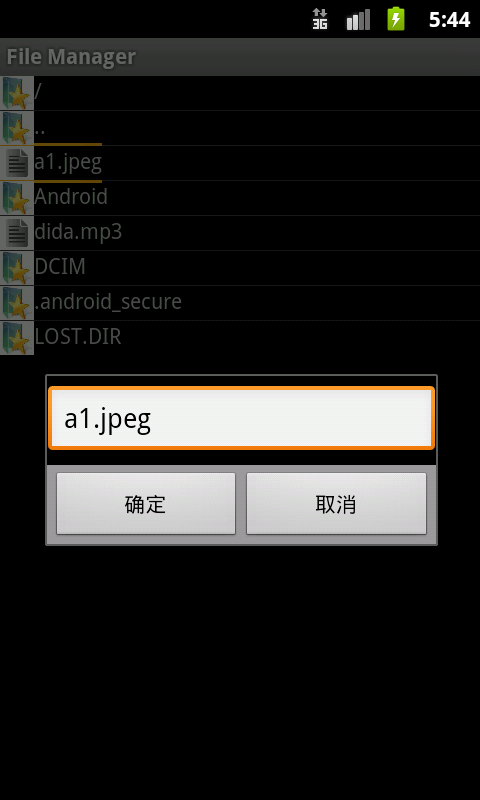
Dateien umbenennen:
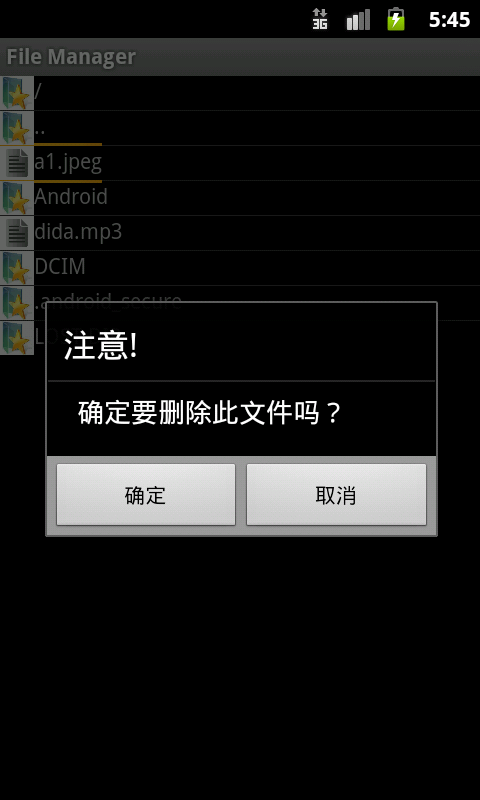
Dateien löschen:
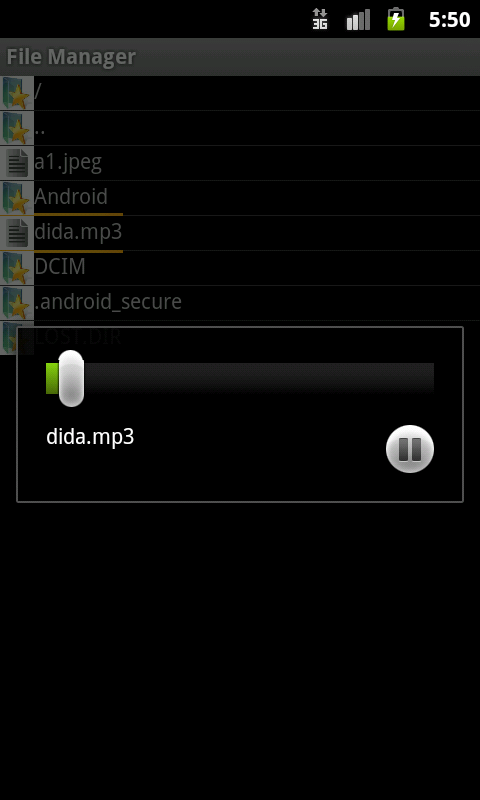
Datei öffnen:
Ich hoffe, dieser Artikel wird für alle hilfreich sein, die sich mit Android-Programmierung befassen.
Weitere Artikel zur einfachen Dateimanager-Implementierungsmethode für die Android-Entwicklung finden Sie auf der chinesischen PHP-Website!

