Heim >Web-Frontend >H5-Tutorial >【HTML5】Canvas implementiert einen Lupeneffekt
【HTML5】Canvas implementiert einen Lupeneffekt
- 高洛峰Original
- 2016-10-12 10:07:542055Durchsuche
Inhaltsverzeichnis

Bildlupe
Effekte

Online-Demonstrations-Quellcode
Prinzip
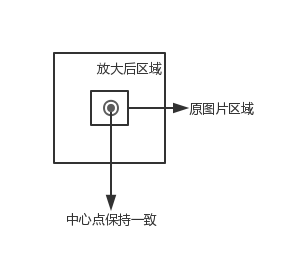
Wählen Sie zuerst einen Bereich des Bildes aus, vergrößern Sie dann diesen Bereich und zeichnen Sie ihn dann auf das Originalbild, um sicherzustellen, dass die Mittelpunkte der beiden Bereiche wie gezeigt konsistent sind in der folgenden Abbildung:
Initialisieren
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" height="500"> </canvas> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="image.png" class="lazy" style="max-width:90%" id="img" alt="【HTML5】Canvas implementiert einen Lupeneffekt" >
, um die Leinwand- und Bildobjekte zu erhalten. Verwenden Sie hier das Tag 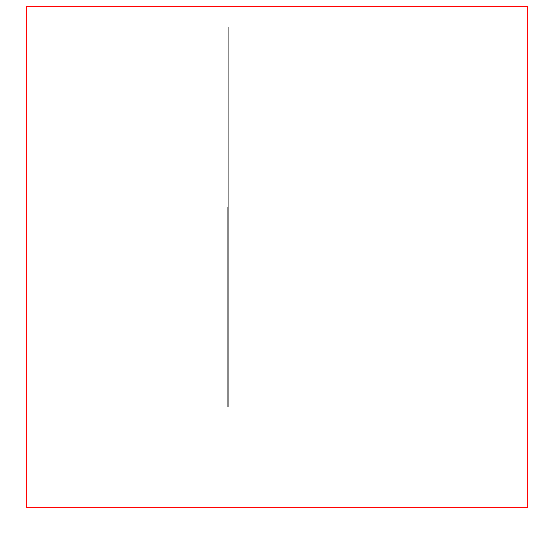 , um Bilder vorab zu laden Das Vorladen von Bildern können Sie hier sehen
, um Bilder vorab zu laden Das Vorladen von Bildern können Sie hier sehen
var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
var context = canvas.getContext("2d");
var img = document.getElementById("img"); Zugehörige Variablen festlegen
// 图片被放大区域的中心点,也是放大镜的中心点
var centerPoint = {};
// 图片被放大区域的半径
var originalRadius = 100;
// 图片被放大区域
var originalRectangle = {};
// 放大倍数
var scale = 2;
// 放大后区域
var scaleGlassRectangleEin Hintergrundbild zeichnen
function drawBackGround() {
context.drawImage(img, 0, 0);
}Berechnen Sie den Bereich des Bereichs, in dem sich das Bild befindet vergrößert
Hier verwenden wir die Position der Maus als zu vergrößernden Bereich. Der Mittelpunkt des Bereichs (die Lupe bewegt sich mit der Mausbewegung), da die Leinwand die Koordinaten der oberen linken Ecke kennen muss und die Breite und Höhe des Bereichs beim Zeichnen eines Bildes, daher berechnen wir hier den Bereich des Bereichs
function calOriginalRectangle(point) {
originalRectangle.x = point.x - originalRadius;
originalRectangle.y = point.y - originalRadius;
originalRectangle.width = originalRadius * 2;
originalRectangle.height = originalRadius * 2;}Zeichnen Sie den Vergrößerungsglasbereich
Zuschneidebereich
Die Lupe ist im Allgemeinen kreisförmig. Hier verwenden wir die Clip-Funktion, um einen kreisförmigen Bereich zuzuschneiden und dann das vergrößerte Bild in diesen Bereich zu zeichnen. Sobald ein bestimmter Bereich abgeschnitten ist, werden alle zukünftigen Zeichnungen auf diesen Bereich beschränkt. Hier verwenden wir die Methoden zum Speichern und Wiederherstellen, um die Auswirkungen des abgeschnittenen Bereichs zu löschen. save speichert den aktuellen Canvas-Status, einschließlich der Kontextattribute des Canvas, wie Stil, Linienbreite usw., und verschiebt diesen Status dann in einen Stapel. „restore“ wird verwendet, um den Status des letzten Speichervorgangs wiederherzustellen und den obersten Status vom Stapel zu entfernen.
context.save(); context.beginPath(); context.arc(centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false); context.clip(); ...... context.restore();
Berechnen Sie den Vergrößerungsglasbereich
Erhalten Sie die Koordinaten der oberen linken Ecke des Bereichs sowie die Breite und Höhe des Bereichs durch den Mittelpunkt, die Breite und Höhe des vergrößerten Bereich und den Vergrößerungsfaktor.
scaleGlassRectangle = {
x: centerPoint.x - originalRectangle.width * scale / 2,
y: centerPoint.y - originalRectangle.height * scale / 2,
width: originalRectangle.width * scale,
height: originalRectangle.height * scale}Zeichnen Sie ein Bild
Hier verwenden wir die Methode context.drawImage(img,sx,sy,swidth,sheight,x,y,width,height); sich selbst als Bild, nehmen Sie dann das Bild des vergrößerten Bereichs auf und zeichnen Sie es in den Vergrößerungsglasbereich.
context.drawImage(canvas,
originalRectangle.x, originalRectangle.y,
originalRectangle.width, originalRectangle.height,
scaleGlassRectangle.x, scaleGlassRectangle.y,
scaleGlassRectangle.width, scaleGlassRectangle.height);Zeichnen Sie die vergrößerte Kante
createRadialGradient wird zum Zeichnen von Verlaufsbildern verwendet
context.beginPath();
var gradient = context.createRadialGradient(
centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius - 5,
centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius);
gradient.addColorStop(0, 'rgba(0,0,0,0.2)');
gradient.addColorStop(0.80, 'silver');
gradient.addColorStop(0.90, 'silver');
gradient.addColorStop(1.0, 'rgba(150,150,150,0.9)');
context.strokeStyle = gradient;
context.lineWidth = 5;
context.arc(centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
context.stroke();Mausereignisse hinzufügen
Mausbewegungsereignisse zur Leinwand hinzufügen
canvas.onmousemove = function (e) {
......
}Koordinaten umwandeln
Die durch Mausereignisse erhaltenen Koordinaten sind im Allgemeinen Bildschirm- oder Fensterkoordinaten, und wir müssen sie in Leinwandkoordinaten umwandeln. getBoundingClientRect wird verwendet, um die linke, obere, rechte und untere Position eines Elements auf der Seite relativ zum Browserfenster zu ermitteln.
function windowToCanvas(x, y) {
var bbox = canvas.getBoundingClientRect();
return {x: x - bbox.left, y: y - bbox.top}}Mausstil ändern
我们可以通过 css 来修改鼠标样式
#canvas {
display: block;
border: 1px solid red;
margin: 0 auto;
cursor: crosshair;}图表放大镜
我们可能基于 canvas 绘制一些图表或者图像,如果两个元素的坐标离得比较近,就会给元素的选择带来一些影响,例如我们画两条线,一个线的坐标是(200.5, 400) -> (200.5, 200),另一个线的坐标为 (201.5, 400) -> (201.5, 20),那么这两条线几乎就会重叠在一起,如下图所示:

使用图表放大镜的效果
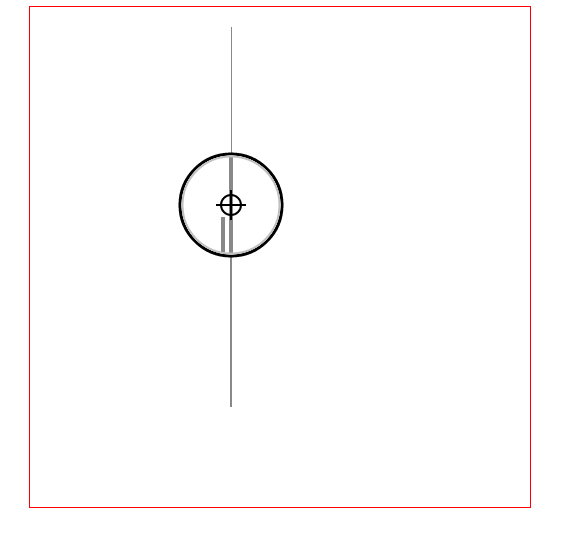
在线演示 源码
原理
类似于地图中的图例,放大镜使用较为精确的图例,如下图所示:
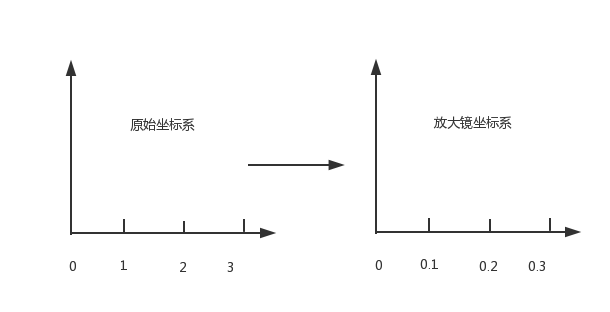
在放大镜坐标系统中,原始的区域会变大,如下图所示
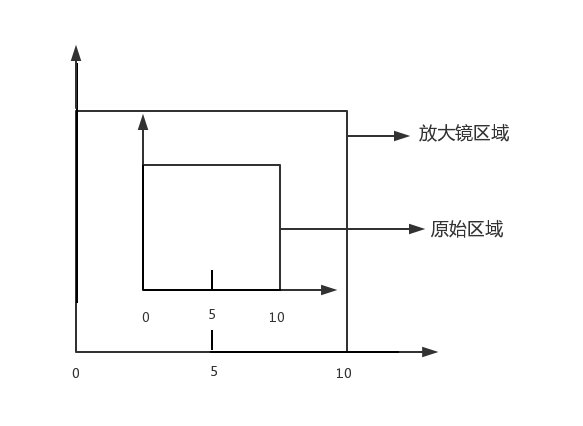
绘制原始线段
首先创建一个线段对象
function Line(xStart, yStart, xEnd, yEnd, index, color) {
// 起点x坐标
this.xStart = xStart;
// 起点y坐标
this.yStart = yStart;
// 终点x坐标
this.xEnd = xEnd;
// 终点y坐标
this.yEnd = yEnd;
// 用来标记是哪条线段
this.index = index;
// 线段颜色
this.color = color;}初始化线段
// 原始线段var chartLines = new Array();// 处于放大镜中的原始线段var glassLines;// 放大后的线段var scaleGlassLines;// 位于放大镜中的线段数量var glassLineSize;function initLines() {
var line;
line = new Line(200.5, 400, 200.5, 200, 0, "#888");
chartLines.push(line);
line = new Line(201.5, 400, 201.5, 20, 1, "#888");
chartLines.push(line);
glassLineSize = chartLines.length;
glassLines = new Array(glassLineSize);
for (var i = 0; i < glassLineSize; i++) {
line = new Line(0, 0, 0, 0, i);
glassLines[i] = line;
}
scaleGlassLines = new Array(glassLineSize);
for (var i = 0; i < glassLineSize; i++) {
line = new Line(0, 0, 0, 0, i);
scaleGlassLines[i] = line;
}}绘制线段
function drawLines() {
var line;
context.lineWidth = 1;
for (var i = 0; i < chartLines.length; i++) {
line = chartLines[i];
context.beginPath();
context.strokeStyle = line.color;
context.moveTo(line.xStart, line.yStart);
context.lineTo(line.xEnd, line.yEnd);
context.stroke();
}}计算原始区域和放大镜区域
function calGlassRectangle(point) {
originalRectangle.x = point.x - originalRadius;
originalRectangle.y = point.y - originalRadius;
originalRectangle.width = originalRadius * 2;
originalRectangle.height = originalRadius * 2;
scaleGlassRectangle.width = originalRectangle.width * scale;
scaleGlassRectangle.height = originalRectangle.height * scale;
scaleGlassRectangle.x = originalRectangle.x + originalRectangle.width / 2 - scaleGlassRectangle.width / 2;
scaleGlassRectangle.y = originalRectangle.y + originalRectangle.height / 2 - scaleGlassRectangle.height / 2;
// 将值装换为整数
scaleGlassRectangle.width = parseInt(scaleGlassRectangle.width);
scaleGlassRectangle.height = parseInt(scaleGlassRectangle.height);
scaleGlassRectangle.x = parseInt(scaleGlassRectangle.x);
scaleGlassRectangle.y = parseInt(scaleGlassRectangle.y);}计算线段在新坐标系统的位置
由原理图我们知道,放大镜中使用坐标系的图例要比原始坐标系更加精确,比如原始坐标系使用 1:100,那么放大镜坐标系使用 1:10,因此我们需要重新计算线段在放大镜坐标系中的位置。同时为了简便,我们将线段的原始坐标进行了转化,减去原始区域起始的x值和y值,即将原始区域左上角的点看做为(0,0)。
function calScaleLines() {
var xStart = originalRectangle.x;
var xEnd = originalRectangle.x + originalRectangle.width;
var yStart = originalRectangle.y;
var yEnd = originalRectangle.y + originalRectangle.height;
var line, gLine, sgLine;
var glassLineIndex = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < chartLines.length; i++) {
line = chartLines[i];
// 判断线段是否在放大镜中
if (line.xStart < xStart || line.xEnd > xEnd) {
continue;
}
if (line.yEnd > yEnd || line.yStart < yStart) {
continue;
}
gLine = glassLines[glassLineIndex];
sgLine = scaleGlassLines[glassLineIndex];
if (line.yEnd > yEnd) {
gLine.yEnd = yEnd;
}
if (line.yStart < yStart) {
gLine.yStart = yStart;
}
gLine.xStart = line.xStart - xStart;
gLine.yStart = line.yStart - yStart;
gLine.xEnd = line.xEnd - xStart;
gLine.yEnd = line.yEnd - yStart;
sgLine.xStart = parseInt(gLine.xStart * scale);
sgLine.yStart = parseInt(gLine.yStart * scale);
sgLine.xEnd = parseInt(gLine.xEnd * scale);
sgLine.yEnd = parseInt(gLine.yEnd * scale);
sgLine.color = line.color;
glassLineIndex++;
}
glassLineSize = glassLineIndex;}绘制放大镜中心点
绘制放大镜中心的瞄准器
function drawAnchor() {
context.beginPath();
context.lineWidth = 2;
context.fillStyle = "#fff";
context.strokeStyle = "#000";
context.arc(parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y), 10, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
var radius = 15;
context.moveTo(parseInt(centerPoint.x - radius), parseInt(centerPoint.y));
context.lineTo(parseInt(centerPoint.x + radius), parseInt(centerPoint.y));
context.moveTo(parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y - radius));
context.lineTo(parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y + radius));
//context.fill();
context.stroke();}绘制放大镜
function drawMagnifyingGlass() {
calScaleLines();
context.save();
context.beginPath();
context.arc(centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
context.clip();
context.beginPath();
context.fillStyle = "#fff";
context.arc(centerPoint.x, centerPoint.y, originalRadius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
context.fill();
context.lineWidth = 4;
for (var i = 0; i < glassLineSize; i++) {
context.beginPath();
context.strokeStyle = scaleGlassLines[i].color;
context.moveTo(scaleGlassRectangle.x + scaleGlassLines[i].xStart, scaleGlassRectangle.y + scaleGlassLines[i].yStart);
context.lineTo(scaleGlassRectangle.x + scaleGlassLines[i].xEnd, scaleGlassRectangle.y + scaleGlassLines[i].yEnd);
context.stroke();
}
context.restore();
context.beginPath();
var gradient = context.createRadialGradient( parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y), originalRadius - 5,
parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y), originalRadius);
gradient.addColorStop(0.50, 'silver');
gradient.addColorStop(0.90, 'silver');
gradient.addColorStop(1, 'black');
context.strokeStyle = gradient;
context.lineWidth = 5;
context.arc(parseInt(centerPoint.x), parseInt(centerPoint.y), originalRadius, 0, Math.PI * 2, false);
context.stroke();
drawAnchor();}添加事件
鼠标拖动
鼠标移动到放大镜上,然后按下鼠标左键,可以拖动放大镜,不按鼠标左键或者不在放大镜区域都不可以拖动放大镜。
为了实现上面的效果,我们要实现3种事件 mousedown, mousemove, 'mouseup', 当鼠标按下时,检测是否在放大镜区域,如果在,设置放大镜可以移动。鼠标移动时更新放大镜中兴点的坐标。鼠标松开时,设置放大镜不可以被移动。
canvas.onmousedown = function (e) {
var point = windowToCanvas(e.clientX, e.clientY);
var x1, x2, y1, y2, dis;
x1 = point.x;
y1 = point.y;
x2 = centerPoint.x;
y2 = centerPoint.y;
dis = Math.pow(x2 - x1, 2) + Math.pow(y2 - y1, 2);
if (dis < Math.pow(originalRadius, 2)) {
lastPoint.x = point.x;
lastPoint.y = point.y;
moveGlass = true;
}}canvas.onmousemove = function (e) {
if (moveGlass) {
var xDis, yDis;
var point = windowToCanvas(e.clientX, e.clientY);
xDis = point.x - lastPoint.x;
yDis = point.y - lastPoint.y;
centerPoint.x += xDis;
centerPoint.y += yDis;
lastPoint.x = point.x;
lastPoint.y = point.y;
draw();
}}canvas.onmouseup = function (e) {
moveGlass = false;}鼠标双击
当移动到对应的线段上时,鼠标双击可以选择该线段,将该线段的颜色变为红色。
canvas.ondblclick = function (e) {
var xStart, xEnd, yStart, yEnd;
var clickPoint = {};
clickPoint.x = scaleGlassRectangle.x + scaleGlassRectangle.width / 2;
clickPoint.y = scaleGlassRectangle.y + scaleGlassRectangle.height / 2;
var index = -1;
for (var i = 0; i < scaleGlassLines.length; i++) {
var scaleLine = scaleGlassLines[i];
xStart = scaleGlassRectangle.x + scaleLine.xStart - 3;
xEnd = scaleGlassRectangle.x + scaleLine.xStart + 3;
yStart = scaleGlassRectangle.y + scaleLine.yStart;
yEnd = scaleGlassRectangle.y + scaleLine.yEnd;
if (clickPoint.x > xStart && clickPoint.x < xEnd && clickPoint.y < yStart && clickPoint.y > yEnd) {
scaleLine.color = "#f00";
index = scaleLine.index;
break;
}
}
for (var i = 0; i < chartLines.length; i++) {
var line = chartLines[i];
if (line.index == index) {
line.color = "#f00";
} else {
line.color = "#888";
}
}
draw();}键盘事件
因为线段离得比较近,所以使用鼠标移动很难精确的选中线段,这里使用键盘的w, a, s, d 来进行精确移动
document.onkeyup = function (e) {
if (e.key == 'w') {
centerPoint.y = intAdd(centerPoint.y, -0.2);
}
if (e.key == 'a') {
centerPoint.x = intAdd(centerPoint.x, -0.2);
}
if (e.key == 's') {
centerPoint.y = intAdd(centerPoint.y, 0.2);
}
if (e.key == 'd') {
centerPoint.x = intAdd(centerPoint.x, 0.2);
}
draw();}** 参考资料 **
HTML5-MagnifyingGlass
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Das Vollbild-Bildlauf-Plug-in AlloyTouch erstellt in 30 Sekunden eine flüssige H5-Seite
- Tatsächlicher HTML5-Kampf und Analyse von Touch-Ereignissen (Touchstart, Touchmove und Touchend)
- Ausführliche Erläuterung der Beispiele für Bildzeichnungen in HTML5 Canvas 9
- Reguläre Ausdrücke und neue HTML5-Elemente
- So kombinieren Sie NodeJS und HTML5, um mehrere Dateien per Drag-and-Drop auf den Server hochzuladen

