Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >Python-Online-Code-Ausführungsassistent
Python-Online-Code-Ausführungsassistent
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2016-08-04 08:55:433881Durchsuche
Mit dem Python-Code-Ausführungsassistenten können Sie Python-Code online eingeben und den Code dann über ein Python-Skript ausführen, das lokal ausgeführt wird. Das Prinzip ist wie folgt:
Geben Sie den Code auf der Webseite ein:

Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche „Ausführen“ und der Code wird an den Python-Code-Ausführungsassistenten gesendet, der auf dem lokalen Computer ausgeführt wird
Der Python-Code-Ausführungsassistent speichert den Code als temporäre Datei und ruft dann den Python-Interpreter auf, um den Code auszuführenDie Webseite zeigt die Ergebnisse der Codeausführung an:
 Herunterladen
Herunterladen
Rechtsklick und das Ziel speichern als: learning.py
Alternative Download-Adresse: learning.py
Vollständiger Code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
r'''
learning.py
A Python 3 tutorial from http://www.liaoxuefeng.com
Usage:
python3 learning.py
'''
import sys
def check_version():
v = sys.version_info
if v.major == 3 and v.minor >= 4:
return True
print('Your current python is %d.%d. Please use Python 3.4.' % (v.major, v.minor))
return False
if not check_version():
exit(1)
import os, io, json, subprocess, tempfile
from urllib import parse
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
EXEC = sys.executable
PORT = 39093
HOST = 'local.liaoxuefeng.com:%d' % PORT
TEMP = tempfile.mkdtemp(suffix='_py', prefix='learn_python_')
INDEX = 0
def main():
httpd = make_server('127.0.0.1', PORT, application)
print('Ready for Python code on port %d...' % PORT)
httpd.serve_forever()
def get_name():
global INDEX
INDEX = INDEX + 1
return 'test_%d' % INDEX
def write_py(name, code):
fpath = os.path.join(TEMP, '%s.py' % name)
with open(fpath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(code)
print('Code wrote to: %s' % fpath)
return fpath
def decode(s):
try:
return s.decode('utf-8')
except UnicodeDecodeError:
return s.decode('gbk')
def application(environ, start_response):
host = environ.get('HTTP_HOST')
method = environ.get('REQUEST_METHOD')
path = environ.get('PATH_INFO')
if method == 'GET' and path == '/':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return [b'<html><head><title>Learning Python</title></head><body><form method="post" action="/run"><textarea name="code" style="width:90%;height: 600px"></textarea><p><button type="submit">Run</button></p></form></body></html>']
if method == 'GET' and path == '/env':
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
L = [b'<html><head><title>ENV</title></head><body>']
for k, v in environ.items():
p = '<p>%s = %s' % (k, str(v))
L.append(p.encode('utf-8'))
L.append(b'</html>')
return L
if host != HOST or method != 'POST' or path != '/run' or not environ.get('CONTENT_TYPE', '').lower().startswith('application/x-www-form-urlencoded'):
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'{"error":"bad_request"}']
s = environ['wsgi.input'].read(int(environ['CONTENT_LENGTH']))
qs = parse.parse_qs(s.decode('utf-8'))
if not 'code' in qs:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'{"error":"invalid_params"}']
name = qs['name'][0] if 'name' in qs else get_name()
code = qs['code'][0]
headers = [('Content-Type', 'application/json')]
origin = environ.get('HTTP_ORIGIN', '')
if origin.find('.liaoxuefeng.com') == -1:
start_response('400 Bad Request', [('Content-Type', 'application/json')])
return [b'{"error":"invalid_origin"}']
headers.append(('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', origin))
start_response('200 OK', headers)
r = dict()
try:
fpath = write_py(name, code)
print('Execute: %s %s' % (EXEC, fpath))
r['output'] = decode(subprocess.check_output([EXEC, fpath], stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, timeout=5))
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Exception', output=decode(e.output))
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired as e:
r = dict(error='Timeout', output='执行超时')
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
r = dict(error='Error', output='执行错误')
print('Execute done.')
return [json.dumps(r).encode('utf-8')]
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Ausführen
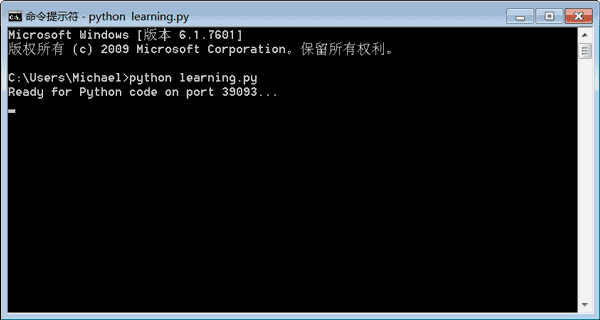
Führen Sie den Befehl in dem Verzeichnis aus, in dem learning.py gespeichert ist:
Wenn Sie Bereit für Python-Code auf Port 39093 sehen, bedeutet dies, dass der Vorgang erfolgreich war. Schließen Sie das Befehlszeilenfenster nicht, sondern minimieren Sie es und führen Sie es im Hintergrund aus:
 Probieren Sie den Effekt aus
Probieren Sie den Effekt aus
Erfordert einen Browser, der HTML5 unterstützt:
IE >= 9
Firefox
Chrom
Sarafi

