Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >Python-Tutorial >Bereitstellen eines zustandslosen Containers in der Cloud
Bereitstellen eines zustandslosen Containers in der Cloud
- DDDOriginal
- 2024-10-08 06:10:30834Durchsuche
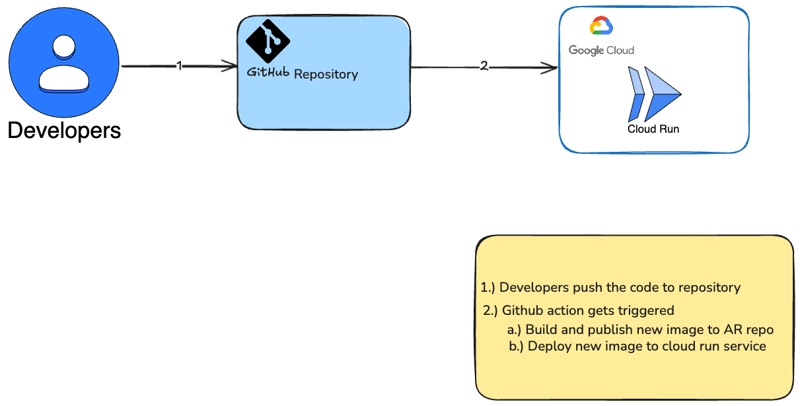
I will demonstrate how to deploy a simple container on cloud run.
Cloud Run is a fully managed platform that enables you to run your code directly on top of Google’s scalable infrastructure. Cloud Run is simple, automated, and designed to make you more productive.
- Create a simple hello world application using fastapi library (python)
- Containerize the application
- Configure the workflow with GCP
- Deploy the container onto cloud run service via github workflow
I followed official fastapi doc to spin up a hello world app
Create a requirements.txt file
fastapi[standard] pydantic>=2.7.0,<3.0.0
- Create an app directory and enter it
- Create an empty file init.py
- Create a main.py file with:
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Union[str, None] = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
Create a Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9 WORKDIR /code COPY ./requirements.txt /code/requirements.txt RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade -r /code/requirements.txt COPY ./app /code/app CMD ["fastapi", "run", "app/main.py", "--port", "80"]
GitHub Action
In order for the GitHub actions process to pick up the YAML file, there’s specific location for it to live. Each repository using actions requires a directory structure called /.github/workflows
*Configure this workflow with GCP more info *
# This workflow build and push a Docker container to Google Artifact Registry # and deploy it on Cloud Run when a commit is pushed to the $default-branch # branch. # # To configure this workflow: # # 1. Enable the following Google Cloud APIs: # # - Artifact Registry (artifactregistry.googleapis.com) # - Cloud Run (run.googleapis.com) # - IAM Credentials API (iamcredentials.googleapis.com) # # You can learn more about enabling APIs at # https://support.google.com/googleapi/answer/6158841. # # 2. Create and configure a Workload Identity Provider for GitHub: # https://github.com/google-github-actions/auth#preferred-direct-workload-identity-federation. # # Depending on how you authenticate, you will need to grant an IAM principal # permissions on Google Cloud: # # - Artifact Registry Administrator (roles/artifactregistry.admin) # - Cloud Run Developer (roles/run.developer) # # You can learn more about setting IAM permissions at # https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/manage-access-other-resources # # 3. Change the values in the "env" block to match your values.
Create a file google-cloudrun-docker.yml
name: 'Build and Deploy to Cloud Run'
on:
push:
branches:
- '$default-branch'
env:
PROJECT_ID: 'my-project' # TODO: update to your Google Cloud project ID
REGION: 'us-central1' # TODO: update to your region
SERVICE: 'my-service' # TODO: update to your service name
WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER: 'projects/123456789/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/my-pool/providers/my-provider' # TODO: update to your workload identity provider
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: 'ubuntu-latest'
permissions:
contents: 'read'
id-token: 'write'
steps:
- name: 'Checkout'
uses: 'actions/checkout@692973e3d937129bcbf40652eb9f2f61becf3332' # actions/checkout@v4
# Configure Workload Identity Federation and generate an access token.
#
# See https://github.com/google-github-actions/auth for more options,
# including authenticating via a JSON credentials file.
- id: 'auth'
name: 'Authenticate to Google Cloud'
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@f112390a2df9932162083945e46d439060d66ec2' # google-github-actions/auth@v2
with:
workload_identity_provider: '${{ env.WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_PROVIDER }}'
# BEGIN - Docker auth and build
#
# If you already have a container image, you can omit these steps.
- name: 'Docker Auth'
uses: 'docker/login-action@9780b0c442fbb1117ed29e0efdff1e18412f7567' # docker/login-action@v3
with:
username: 'oauth2accesstoken'
password: '${{ steps.auth.outputs.auth_token }}'
registry: '${{ env.REGION }}-docker.pkg.dev'
- name: 'Build and Push Container'
run: |-
DOCKER_TAG="$${{ env.REGION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.PROJECT_ID }}/${{ env.SERVICE }}:${{ github.sha }}"
docker build --tag "${DOCKER_TAG}" .
docker push "${DOCKER_TAG}"
- name: 'Deploy to Cloud Run'
# END - Docker auth and build
uses: 'google-github-actions/deploy-cloudrun@33553064113a37d688aa6937bacbdc481580be17' # google-github-actions/deploy-cloudrun@v2
with:
service: '${{ env.SERVICE }}'
region: '${{ env.REGION }}'
# NOTE: If using a pre-built image, update the image name below:
image: '${{ env.REGION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.PROJECT_ID }}/${{ env.SERVICE }}:${{ github.sha }}'
# If required, use the Cloud Run URL output in later steps
- name: 'Show output'
run: |2-
echo ${{ steps.deploy.outputs.url }}
Directory Structure
You should now have a directory structure like:
├── app
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── main.py
├── Dockerfile
└── requirements.txt
└── requirements.txt
├── .github
│ ├── workflows
├── google-cloudrun-docker.yml
> 1. Create a new repo in gitHUb > 2. Push your exisisting code to new repository on default branch
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonBereitstellen eines zustandslosen Containers in der Cloud. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

