Introduction
A graph is a data structure with a number of vertices(nodes) and edges(connections) between them.
A tree is an example of a graph. Every tree is a graph but not every graph is a tree, for example, graphs that have cycles are not trees. A tree will have one root and one unique path between two nodes whilst a graph can have many roots and multiple paths between vertices.
Basic Terminology
Vertex: A node in a graph.
Edge: The connection between two vertices.
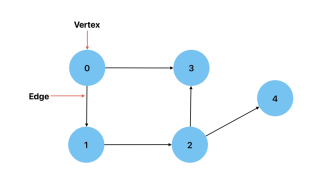
Directed: When the connection between two vertices has a direction. This implies that there is only one way to get from one vertex to another. An example could be graph showing the cities(vertices) and the routes(edges) between them.
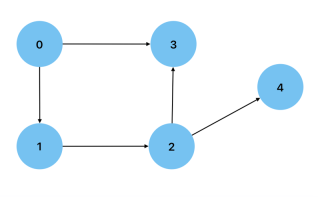
Undirected: When the connection between two vertices on a graph goes both ways. An example could be a graph showing people(vertices) connected by their friendships.
Degree: The number of edges connected to a vertex. The vertices of a directed graph can have an indegree or an outdegree, which is the number of edges pointing towards and away from the vertex respectively.
Weighted: A graph in which the edges have values as weights. An example could be a road map, where the distances between nodes are represented as weights.
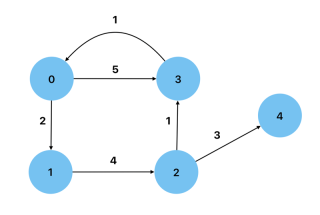
Cyclic: A graph that has a path from at least one vertex back to itself.
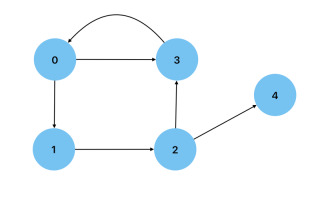
Acyclic: A graph that has no cycles, that is to say, no node has a path back to itself. A Directed Acyclic Graph is a type of graph that can be used to show data processing flows.
Dense: When a graph has close to the maximum possible number of edges
Sparse: When a graph has close to the minimum possible number of edges.
Self-loop: When an edge has one vertex linking to itself.
Multi-edge: When a graph has multiple edges between two vertices.
Simple: When a graph has no self-loops nor multi-edges.
To get the maximum number of edges in a simple directed graph: n*(n-1) where n is the number of nodes.
To get the maximum number of edges in a simple undirected graph: n*(n-1)/2 where n is the number of nodes.
Implementing graphs in JavaScript
To implement a graph, we can start by specifying the vertices and edges of a graph, below is an example of how to do this given the following graph:
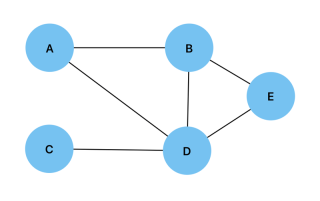
const vertices = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]; const edges = [ ["A", "B"], ["A", "D"], ["B", "D"], ["B", "E"], ["C", "D"], ["D", "E"], ];
Then we can create a function to find what is adjacent to a given vertex:
const findAdjacentNodes = function (node) {
const adjacentNodes = [];
for (let edge of edges) {
const nodeIndex = edge.indexOf(node);
if (nodeIndex > -1) {
let adjacentNode = nodeIndex === 0 ? edge[1] : edge[0];
adjacentNodes.push(adjacentNode);
}
}
return adjacentNodes;
};
And another function to check if two vertices are connected:
const isConnected = function (node1, node2) {
const adjacentNodes = new Set(findAdjacentNodes(node1));
return adjacentNodes.has(node2);
};
Adjacency List
An adjacency list is a representation of a graph where all of the vertices that are connected to a node are stored as a list. Below is a graph and a visual representation of its corresponding adjacency list.


An adjacency list can be implemented in JavaScript by creating two classes, a Node class and a Graph class. The Node class will consist of a constructor and a connect() method to join two vertices. It will also have the isConnected() and getAdjacentNodes() methods which work in exactly the same manner as shown above.
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.edgesList = [];
}
connect(node) {
this.edgesList.push(node);
node.edgesList.push(this);
}
getAdjNodes() {
return this.edgesList.map((edge) => edge.value);
}
isConnected(node) {
return this.edgesList.map((edge) =>
edge.value).indexOf(node.value) > -1;
}
}
The Graph class consists of a constructor and the addToGraph() method which adds a new vertex to the graph.
class Graph {
constructor(nodes) {
this.nodes = [...nodes];
}
addToGraph(node) {
this.nodes.push(node);
}
}
Adjacency Matrix
A 2-D array where each array represents a vertex and each index represents a possible connection between vertices. An adjacency matrix is filled with 0s and 1s, with 1 representing a connection. The value at adjacencyMatrix[node1][node2] will show whether or not there is a connection between the two specified vertices. Below is is a graph and its visual representation as an adjacency matrix.


To implement this adjacency matrix in JavaScript, we start by creating two classes, the first being the Node class:
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
We then create the Graph class which will contain the constructor for creating the 2-D array initialized with zeros.
class Graph {
constructor(nodes) {
this.nodes = [...nodes];
this.adjacencyMatrix = Array.from({ length: nodes.length },
() => Array(nodes.length).fill(0));
}
}
We will then add the addNode() method which will be used to add new vertices to the graph.
addNode(node) {
this.nodes.push(node);
this.adjacencyMatrix.forEach((row) => row.push(0));
this.adjacencyMatrix.push(new Array(this.nodes.length).fill(0));
}
Next is the connect() method which will add an edge between two vertices.
connect(node1, node2) {
const index1 = this.nodes.indexOf(node1);
const index2 = this.nodes.indexOf(node2);
if (index1 > -1 && index2 > -1) {
this.adjacencyMatrix[index1][index2] = 1;
this.adjacencyMatrix[index2][index1] = 1;
}
}
We will also create the isConnected() method which can be used to check if two vertices are connected.
isConnected(node1, node2) {
const index1 = this.nodes.indexOf(node1);
const index2 = this.nodes.indexOf(node2);
if (index1 > -1 && index2 > -1) {
return this.adjacencyMatrix[index1][index2] === 1;
}
return false;
}
Lastly we will add the printAdjacencyMatrix() method to the Graph class.
printAdjacencyMatrix() {
console.log(this.adjacencyMatrix);
}
Breadth First Search
Similar to a Breadth First Search in a tree, the vertices adjacent to the current vertex are visited before visiting any subsequent children. A queue is the data structure of choice when performing a Breadth First Search on a graph.
Below is a graph of international airports and their connections and we will use a Breadth First Search to find the shortest route(path) between two airports(vertices).
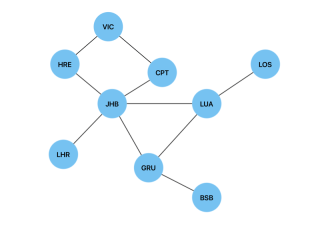
In order to implement this search algorithm in JavaScript, we will use the same Node and Graph classes we implemented the adjacency list above. We will create a breadthFirstTraversal() method and add it to the Graph class in order to traverse between two given vertices. This method will have the visitedNodes object, which will be used to store the visited vertices and their predecessors. It is initiated as null to show that the first vertex in our search has no predecessors.
breathFirstTraversal(start, end) {
const queue = [start];
const visitedNodes = {};
visitedNodes[start.value] = null;
while (queue.length > 0) {
const node = queue.shift();
if (node.value === end.value) {
return this.reconstructedPath(visitedNodes, end);
}
for (const adjacency of node.edgesList) {
if (!visitedNodes.hasOwnProperty(adjacency.value)) {
visitedNodes[adjacency.value] = node;
queue.push(adjacency);
}
}
}
}
Once the end vertex is found, we will use the reconstructedPath() method in the Graph class in order to return the shortest path between two vertices. Each vertex is added iteratively to the shortestPath array, which in turn must be reversed in order to come up with the correct order for the shortest path.
reconstructedPath(visitedNodes, endNode) {
let currNode = endNode;
const shortestPath = [];
while (currNode !== null) {
shortestPath.push(currNode.value);
currNode = visitedNodes[currNode.value];
}
return shortestPath.reverse();
}
In the case of the graph of international airports, breathFirstTraversal(JHB, LOS) will return JHB -> LUA -> LOS as the shortest path. In the case of a weighted graph, we would use Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest path.
Depth First Search
Similar to a depth first search in a tree, this algorithm will fully explore every descendant of a vertex, before backtracking to the root. A stack is the data structure of choice for depth first traversals in a graph.
A depth first search can be used to detect a cycle in a graph. We will use the same graph of international airports to illustrate this in JavaScript.

Similar to the Breadth First Search algorithm above, this implementation of a Depth First Search algorithm in JavaScript will use the previously created Node and Graph classes. We will create a helper function called depthFirstTraversal() and add it to the Graph class.
depthFirstTraversal(start, visitedNodes = {}, parent = null) {
visitedNodes[start.value] = true;
for (const adjacency of start.edgesList) {
if (!visitedNodes[adjacency.value]) {
if (this.depthFirstTraversal(adjacency, visitedNodes, start)) {
return true;
}
} else if (adjacency !== parent) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
This will perform the Depth First Traversal of the graph, using the parent parameter to keep track of the previous vertex and prevent the detection of a cycle when revisiting the parent vertex. Visited vertices will be marked as true in the visitedNodes object. This method will then use recursion to visit previously unvisited vertices. If the vertex has already been visited, we check it against the parent parameter. A cycle has been found if the vertex has already been visited and it is not the parent.
We will also create the wrapper function hasCycle() in the Graph class. This function is used to detect a cycle in a disconnected graph. It will initialize the visitedNodes object and loop through all of the vertices in the graph.
hasCycle() {
const visitedNodes = {};
for (const node of this.nodes) {
if (!visitedNodes[node.value]) {
if (this.depthFirstTraversal(node, visitedNodes)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
In the case of the graph of international airports, the code will return true.
Depth First Traversal of a graph is also useful for pathfinding(not necessarily shortest path) and for solving mazes.
Kesimpulan
Pemahaman yang kukuh tentang graf sebagai struktur data dan algoritma yang berkaitan dengannya amat diperlukan apabila melanjutkan kajian tentang struktur dan algoritma data. Walaupun tidak mesra pemula seperti siaran sebelumnya dalam siri ini, panduan ini sepatutnya berguna untuk memperdalam pemahaman anda tentang struktur data dan algoritma.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonDatenstrukturen und Algorithmen: Diagramme. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
 Python gegen JavaScript: Community, Bibliotheken und RessourcenApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python gegen JavaScript: Community, Bibliotheken und RessourcenApr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AMPython und JavaScript haben ihre eigenen Vor- und Nachteile in Bezug auf Gemeinschaft, Bibliotheken und Ressourcen. 1) Die Python-Community ist freundlich und für Anfänger geeignet, aber die Front-End-Entwicklungsressourcen sind nicht so reich wie JavaScript. 2) Python ist leistungsstark in Bibliotheken für Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen, während JavaScript in Bibliotheken und Front-End-Entwicklungsbibliotheken und Frameworks besser ist. 3) Beide haben reichhaltige Lernressourcen, aber Python eignet sich zum Beginn der offiziellen Dokumente, während JavaScript mit Mdnwebdocs besser ist. Die Wahl sollte auf Projektbedürfnissen und persönlichen Interessen beruhen.
 Von C/C nach JavaScript: Wie alles funktioniertApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Von C/C nach JavaScript: Wie alles funktioniertApr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AMDie Verschiebung von C/C zu JavaScript erfordert die Anpassung an dynamische Typisierung, Müllsammlung und asynchrone Programmierung. 1) C/C ist eine statisch typisierte Sprache, die eine manuelle Speicherverwaltung erfordert, während JavaScript dynamisch eingegeben und die Müllsammlung automatisch verarbeitet wird. 2) C/C muss in den Maschinencode kompiliert werden, während JavaScript eine interpretierte Sprache ist. 3) JavaScript führt Konzepte wie Verschlüsse, Prototypketten und Versprechen ein, die die Flexibilität und asynchrone Programmierfunktionen verbessern.
 JavaScript -Engines: Implementierungen vergleichenApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript -Engines: Implementierungen vergleichenApr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMUnterschiedliche JavaScript -Motoren haben unterschiedliche Auswirkungen beim Analysieren und Ausführen von JavaScript -Code, da sich die Implementierungsprinzipien und Optimierungsstrategien jeder Engine unterscheiden. 1. Lexikalanalyse: Quellcode in die lexikalische Einheit umwandeln. 2. Grammatikanalyse: Erzeugen Sie einen abstrakten Syntaxbaum. 3. Optimierung und Kompilierung: Generieren Sie den Maschinencode über den JIT -Compiler. 4. Führen Sie aus: Führen Sie den Maschinencode aus. V8 Engine optimiert durch sofortige Kompilierung und versteckte Klasse.
 Jenseits des Browsers: JavaScript in der realen WeltApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Jenseits des Browsers: JavaScript in der realen WeltApr 12, 2025 am 12:06 AMZu den Anwendungen von JavaScript in der realen Welt gehören die serverseitige Programmierung, die Entwicklung mobiler Anwendungen und das Internet der Dinge. Die serverseitige Programmierung wird über node.js realisiert, die für die hohe gleichzeitige Anfrageverarbeitung geeignet sind. 2. Die Entwicklung der mobilen Anwendungen erfolgt durch reaktnative und unterstützt die plattformübergreifende Bereitstellung. 3.. Wird für die Steuerung von IoT-Geräten über die Johnny-Five-Bibliothek verwendet, geeignet für Hardware-Interaktion.
 Erstellen einer SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mietern mit Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Erstellen einer SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mietern mit Next.js (Backend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AMIch habe eine funktionale SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mandanten (eine EdTech-App) mit Ihrem täglichen Tech-Tool erstellt und Sie können dasselbe tun. Was ist eine SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mietern? Mit Multi-Tenant-SaaS-Anwendungen können Sie mehrere Kunden aus einem Sing bedienen
 So erstellen Sie eine SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mietern mit Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
So erstellen Sie eine SaaS-Anwendung mit mehreren Mietern mit Next.js (Frontend Integration)Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AMDieser Artikel zeigt die Frontend -Integration mit einem Backend, das durch die Genehmigung gesichert ist und eine funktionale edtech SaaS -Anwendung unter Verwendung von Next.js. erstellt. Die Frontend erfasst Benutzerberechtigungen zur Steuerung der UI-Sichtbarkeit und stellt sicher, dass API-Anfragen die Rollenbasis einhalten
 JavaScript: Erforschung der Vielseitigkeit einer WebspracheApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Erforschung der Vielseitigkeit einer WebspracheApr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript ist die Kernsprache der modernen Webentwicklung und wird für seine Vielfalt und Flexibilität häufig verwendet. 1) Front-End-Entwicklung: Erstellen Sie dynamische Webseiten und einseitige Anwendungen durch DOM-Operationen und moderne Rahmenbedingungen (wie React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Serverseitige Entwicklung: Node.js verwendet ein nicht blockierendes E/A-Modell, um hohe Parallelitäts- und Echtzeitanwendungen zu verarbeiten. 3) Entwicklung von Mobil- und Desktop-Anwendungen: Die plattformübergreifende Entwicklung wird durch reaktnative und elektronen zur Verbesserung der Entwicklungseffizienz realisiert.
 Die Entwicklung von JavaScript: Aktuelle Trends und ZukunftsaussichtenApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
Die Entwicklung von JavaScript: Aktuelle Trends und ZukunftsaussichtenApr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AMZu den neuesten Trends im JavaScript gehören der Aufstieg von Typenkripten, die Popularität moderner Frameworks und Bibliotheken und die Anwendung der WebAssembly. Zukunftsaussichten umfassen leistungsfähigere Typsysteme, die Entwicklung des serverseitigen JavaScript, die Erweiterung der künstlichen Intelligenz und des maschinellen Lernens sowie das Potenzial von IoT und Edge Computing.


Heiße KI -Werkzeuge

Undresser.AI Undress
KI-gestützte App zum Erstellen realistischer Aktfotos

AI Clothes Remover
Online-KI-Tool zum Entfernen von Kleidung aus Fotos.

Undress AI Tool
Ausziehbilder kostenlos

Clothoff.io
KI-Kleiderentferner

AI Hentai Generator
Erstellen Sie kostenlos Ai Hentai.

Heißer Artikel

Heiße Werkzeuge

EditPlus chinesische Crack-Version
Geringe Größe, Syntaxhervorhebung, unterstützt keine Code-Eingabeaufforderungsfunktion

VSCode Windows 64-Bit-Download
Ein kostenloser und leistungsstarker IDE-Editor von Microsoft

MinGW – Minimalistisches GNU für Windows
Dieses Projekt wird derzeit auf osdn.net/projects/mingw migriert. Sie können uns dort weiterhin folgen. MinGW: Eine native Windows-Portierung der GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), frei verteilbare Importbibliotheken und Header-Dateien zum Erstellen nativer Windows-Anwendungen, einschließlich Erweiterungen der MSVC-Laufzeit zur Unterstützung der C99-Funktionalität. Die gesamte MinGW-Software kann auf 64-Bit-Windows-Plattformen ausgeführt werden.

SublimeText3 Linux neue Version
SublimeText3 Linux neueste Version

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) ist eine PHP/MySQL-Webanwendung, die sehr anfällig ist. Seine Hauptziele bestehen darin, Sicherheitsexperten dabei zu helfen, ihre Fähigkeiten und Tools in einem rechtlichen Umfeld zu testen, Webentwicklern dabei zu helfen, den Prozess der Sicherung von Webanwendungen besser zu verstehen, und Lehrern/Schülern dabei zu helfen, in einer Unterrichtsumgebung Webanwendungen zu lehren/lernen Sicherheit. Das Ziel von DVWA besteht darin, einige der häufigsten Web-Schwachstellen über eine einfache und unkomplizierte Benutzeroberfläche mit unterschiedlichen Schwierigkeitsgraden zu üben. Bitte beachten Sie, dass diese Software





