Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >C#.Net-Tutorial >C#-Stack
C#-Stack
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-09-03 15:30:28893Durchsuche
Die Sammlung von Objekten, die durch „Last In“ und „First Out“ dargestellt wird, wird Stapel genannt und ist eine Sammlung, die mit dem Hinzufügen von Elementen zum Stapel entsprechend den Anforderungen des Programms zunimmt. Daher handelt es sich um eine dynamische Sammlung Elemente desselben Typs und unterschiedlicher Typen können im Stapel gespeichert werden. Der Vorgang des Hinzufügens eines Elements zum Stapel wird als Schieben des Elements auf den Stapel bezeichnet, und der Vorgang des Entfernens eines Elements vom Stapel wird als Herausnehmen des Elements vom Stapel bezeichnet und dieser Stapel fällt unter Systeme. Sammlungs-Namespace.
Syntax:
Die Syntax von C# Stack lautet wie folgt:
Stack stack_name = new Stack();
Wobei stack_name der Name des Stacks ist.l
Funktionen von Stack in C#
- Immer wenn wir Zugriff auf die Elemente des Stapels in der Reihenfolge „Last In“ und „First Out“ benötigen, erstellen wir eine Sammlung von Objekten namens Stack.
- Der Vorgang des Hinzufügens eines Elements zum Stapel wird als Schieben der Elemente auf den Stapel bezeichnet, und der Vorgang des Entfernens eines Elements aus dem Stapel wird als Herausnehmen eines Elements aus dem Stapel bezeichnet.
- Stapel ist eine dynamische Sammlung von Elementen, da die Größe des Stapels mit dem Hinzufügen von Elementen zum Stapel zunimmt.
- Die Anzahl der Elemente, die ein Stapel aufnehmen kann, wird als Kapazität des Stapels bezeichnet. Da die Größe des Stapels durch das Hinzufügen von Elementen zum Stapel zunimmt, erhöht sich auch die Kapazität des Stapels durch Neuzuweisung.
- Es können doppelte Elemente im Stapel zulässig sein.
- Null wird vom Stapel als gültiger Wert für Typ und Referenzen akzeptiert.
In Stack in C# gibt es mehrere Konstruktoren. Sie sind:
- Stack(): Eine neue Instanz der Stack-Klasse wird initialisiert, die leer ist und deren Anfangskapazität die Standardeinstellung ist.
- Stack(ICollection): Eine neue Instanz der Stack-Klasse wird initialisiert, die aus Elementen besteht, die aus einer als Parameter angegebenen Sammlung entnommen werden und deren Anfangskapazität der Anzahl der entnommenen Elemente entspricht aus der als Parameter angegebenen Sammlung.
- Stack(Int32): Eine neue Instanz der Stack-Klasse wird initialisiert, die leer ist und deren Anfangskapazität entweder die als Parameter angegebene Anfangskapazität oder die Standardanfangskapazität ist.
Methoden im C#-Stack
In Stack in C# gibt es mehrere Methoden. Sie sind:
- Clear(): Die Objekte des Stapels werden mit der Clear()-Methode entfernt.
- Push(Object): Ein als Parameter angegebenes Objekt wird mithilfe der Push(Object)-Methode oben in den Stapel eingefügt.
- Contains(Object): Die Methode Contains(Object) wird verwendet, um zu bestimmen, ob ein Element im Stapel vorhanden ist.
- Peek(): Das oben im Stapel angegebene Objekt wird zurückgegeben, aber nicht mit der Peek()-Methode entfernt.
- Pop(): Das oben im Stapel angegebene Objekt wird zurückgegeben und mit der Pop()-Methode entfernt.
Beispiele
Im Folgenden finden Sie Beispiele für den C#-Stack:
Beispiel #1
Betrachten Sie das folgende Beispielprogramm, um die Push()-Methode, die Pop()-Methode, die Peek()-Methode, die Contains()-Methode und die Clear()-Methode zu demonstrieren:
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections;
//a class called program is defined
class program
{
//main method is called
public static void Main()
{
//a new stack is created
Stack mystk = new Stack();
//Adding the elements to the newly created stack
mystk.Push("India");
mystk.Push("USA");
mystk.Push("Canada");
mystk.Push("Germany");
//displaying the elements of the stack using foreach loop
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack are : ");
foreach(varele in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(ele);
}
//using contains() method to check if an element is present in the stack or not
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Contains("Germany"));
// The count of the elements in the stack is displayed
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack are : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
// displaying the top most element of the stack using Peek() method
Console.WriteLine("The topmost element in the stack is : " + mystk.Peek());
//Using pop() method to remove the top element in the stack
Console.WriteLine("the element of the stack that is going to be removed" + " is: {0}",mystk.Pop());
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack after using pop() method are : ");
foreach(var el in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(el);
}
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack after using pop() method is : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
//using Clear() method to remove all the elements in the stack
mystk.Clear();
Console.Write("The count of elements in the Stack after using Clear() method is : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Count);
}
}
Ausgabe:
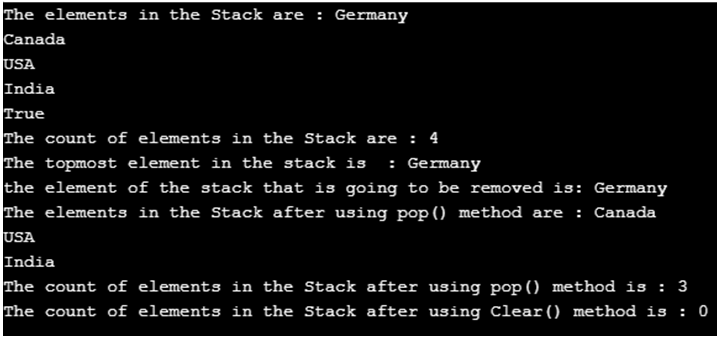
Im obigen Programm ist eine Klasse namens Programm definiert. Dann wird die Hauptmethode aufgerufen. Dann wird ein neuer Stapel erstellt. Anschließend werden die Elemente mithilfe der Push()-Methode zum neu erstellten Stapel hinzugefügt. Anschließend werden die Elemente des neu erstellten Stapels mithilfe einer foreach-Schleife angezeigt. Dann wird die Methode „contains()“ verwendet, um zu prüfen, ob ein Element im Stapel vorhanden ist oder nicht. Anschließend wird die Anzahl der Elemente im Stapel mithilfe der Methode count() angezeigt. Anschließend wird mit der Peek()-Methode das oberste Element des Stapels angezeigt. Anschließend wird das oberste Element des Stapels mit der Methode Pop() entfernt. Anschließend werden nach Verwendung der Pop()-Methode erneut die Anzahl der Elemente und die Elemente des Stapels angezeigt. Dann wird die Clear()-Methode verwendet, um alle Elemente des Stapels zu entfernen. Anschließend werden nach Verwendung der Clear()-Methode wiederum die Anzahl der Elemente und die Elemente des Stapels angezeigt. Die Ausgabe des Programms ist im Schnappschuss oben dargestellt.
- Clone(): A shallow copy of the stack is created using the Clone() method.
- Equals(Object): The Equals(Object) method is used to determine if the object specified as the parameter is equal to the current object.
- Synchronized(Stack): A synchronized wrapper for the stack is returned using the Synchronized(Stack) method.
- CopyTo(Array,Int32): The stack is copied into an array which is one dimensional with the index of the array specified as a parameter.
- ToArray(): The stack is copied to a new array using ToArray() method.
- GetType(): The type of the current instance is obtained using GetType() method.
- ToString(): A string representing the current object is returned using ToString() method.
- GetEnumerator(): An IEnumerator for the stack is returned using GetEnumerator() method.
- GetHashCode(): The GetHashCode() method is the hash function by default.
- MemberwiseClone(): A shallow copy of the current object is created using MemberwiseClone() method.
Example #2
Consider the example program below to demonstrate Clone() method, Equals() method, Synchronized() method, CopyTo() method, ToArray() method, GetType() method and GetEnumerator() method:
Code:
using System;
using System.Collections;
//a class called program is defined
class program
{
// Main Method is called
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// creating a new stack
Stack mystk = new Stack();
mystk.Push("India");
mystk.Push("USA");
mystk.Push("Canada");
mystk.Push("Germany");
Console.Write("The elements in the Stack are : ");
foreach(varele in mystk)
{
Console.WriteLine(ele);
}
// a clone of the newly created stack is created
Stack mystk1 = (Stack)mystk.Clone();
// the top most element of the clone of the newly created stack is removed using pop() method
mystk1.Pop();
Console.Write("The elements in the clone of the Stack after using pop() method are : ");
//the elements of the clone of the newly created stack is displayed
foreach(Object ob in mystk1)
Console.WriteLine(ob);
//checking if the elements of the clone of the newly created stack and the newly created stack are equal or not
Console.Write("The elements in the clone of the Stack and the stack are equal or not : ");
Console.WriteLine(mystk.Equals(mystk1));
//Checking if the clone of the newly created stack and the newly created stack is synchronised or not
Console.WriteLine("The Clone of the newly created stack is {0}.", mystk1.IsSynchronized ? "Synchronized" : "Not Synchronized");
Console.WriteLine("The newly created stack is {0}.", mystk.IsSynchronized ? "Synchronized" : "Not Synchronized");
//a new array of strings is created and the newly created stack is assigned to this array
string[] arra = new string[mystk.Count];
// The elements of the newly created stack is copied to the array
mystk.CopyTo(arra, 0);
// the elements of the array are displayed
Console.Write("The elements of the array copied from the newly created stack are : ");
foreach(string st in arra)
{
Console.WriteLine(st);
}
//converting the elements of the newly created stack to array using toarray() method
Object[] ar1 = mystk.ToArray();
Console.Write("The elements of the array copied from the newly created stack by using ToArray() method are :");
//the elements of the array are displayed
foreach(Object st1 in ar1)
{
Console.WriteLine(st1);
}
Console.WriteLine("The type of newly created stack before using "+
"ToStringMethod is: "+mystk.GetType());
Console.WriteLine("The type of newly created stack after using "+
"ToString Method is: "+mystk.ToString().GetType());
Console.Write("The elements of the newly created stack after using GetEnumerator() method are : ");
//Getenumerator() method is used to obtain the enumerator of thestack
IEnumeratorenume = mystk.GetEnumerator();
while (enume.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine(enume.Current);
}
}
}
Output:
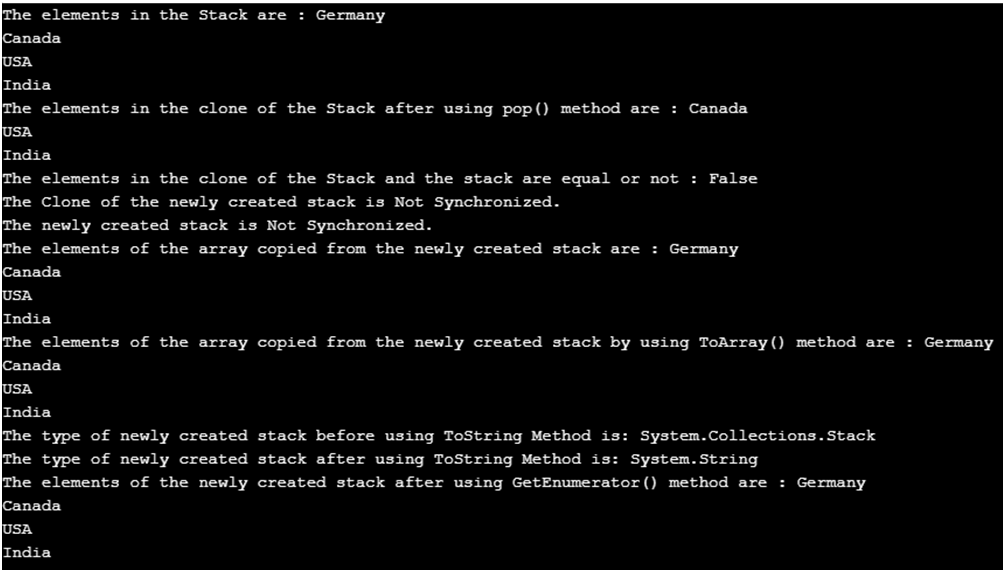
In the above program, a class called program is defined. Then the main method is called. Then a new stack is created. Then the clone of the newly created stack is created by using the clone() method. Then the topmost element of the clone of the newly created stack is removed using the pop() method. Then the elements of the clone of the newly created method are displayed. Then Equals() method is used to check if the newly created stack and the clone of the newly created stack are equal or not. Then the synchronized() method is used to check if the newly created stack and the clone of the newly created stack are synchronized or not. Then Copyto() method is used to copy the newly created stack to an array and the elements of the array are displayed. Then ToArray() method is used to copy the newly created stack to another array and then the elements of the array are displayed. Then GetType() method is used to obtain the type of the newly created stack. Then ToString() method is used to convert the type stack to string. Then GetEnumerator() method is used to obtain the IEnumerator of the stack. The output of the program is shown in the snapshot above.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonC#-Stack. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- .Net Core-Grafikverifizierungscode
- Laden der .NET Core-Konfigurationsdatei und DI-Injektion von Konfigurationsdaten
- Dokumentation zum .NET Core CLI-Tool dotnet-publish
- asp.net verwendet .net-Steuerelemente, um Dropdown-Navigationsmenüs zu erstellen
- So erhalten Sie den Namen des Controllers in Asp.net MVC

