Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >C#.Net-Tutorial >C#-Funktionen
C#-Funktionen
- PHPzOriginal
- 2024-09-03 15:13:531227Durchsuche
C#-Funktionen sind die wesentlichen Teile des C#-Programms, die aus mehreren Elementen bestehen können, wie z. B. dem Funktionsnamen, der als Referenz der Funktion verwendet wird, Rückgabetypen der in den Funktionen verarbeiteten Daten, dem logischen Hauptteil der Funktion, Parameter, die als Argumente für die Funktion übergeben werden können, und der Zugriffsspezifizierer zum Definieren der Zugänglichkeit der Funktion innerhalb des Programms. Die verschiedenen Funktionen, die in ein C#-Programm integriert werden können, sind eine Kombination von Funktionen mit oder ohne Parameter, die je nach Anforderung die Rückgabewerte haben können oder nicht.
Es gibt mehrere Komponenten in Funktionen –
- Wir haben einen eindeutigen Namen namens Funktionsname, um einen Funktionsaufruf durchzuführen.
- Wir werden den Rückgabetyp verwenden, um den Datentyp des Rückgabewerts anzugeben.
- Der Anweisungsblock, der die ausführbaren Anweisungen enthält, heißt Body.
- Wir können die Funktionen während des Funktionsaufrufs als Liste von Parameterargumenten übergeben.
- Um die Zugänglichkeit einer Funktion in der Anwendung anzugeben, können wir den Access-Spezifizierer verwenden.
Andere C#-Funktion
- Ohne Parameter (Argumente) und Rückgabetyp.
- Mit Parametern (Argumenten), aber ohne Rückgabetyp.
- Verwendung von Parametern (Argumenten) und mit dem Rückgabetyp.
- Ohne Parameter (Argumente) und mit dem Rückgabewert.
C#-Funktionssyntax
<access-specifier><return-type>FunctionName(<parameters>)
{
// function body
// return statement
}
Rückgabeanweisungen, Parameter und Zugriffsspezifizierer sind in der obigen Syntax optional.
|
Syntax(Funktion) | ||||||||||
| Mit Parametern und mit Rückgabewerte |
Deklaration: int display ( int );
Funktionsaufruf: Anzeige (Wert);
Funktionsdefinition: int display(int value) { Aussagen; Rückgabewert; |
||||||||||
| Mit Parametern und ohne Rückgabewerte |
Deklaration: void display ( int );
Aufruf: Anzeige (Wert);
Funktionsdefinition: Leere Anzeige (int-Wert) { Aussagen; |
||||||||||
| Ohne Parameter und ohne Rückgabewerte |
Erklärung: void display ();
Aufruf: display ();
Definition: void display () { Aussagen; |
||||||||||
| Ohne Parameter und mit Rückgabewerte |
Deklaration: int display ( );
Aufruf: Anzeige ( );
Definition: int display ( ) { Aussagen; Rückgabewert; |
If a function’s return value is “void,” it cannot return any values to the calling function.
Note: If the return value of the function, such as “int, double, float, string, etc.” is other than void, then it can return values to the calling function.1. Using Without Parameters and Without Return Type
We specified the function with no parameter and no return type, a function that does not return any values here, as void type as a return type value. In this program, any values should not be passed to the function call Display(), and also, there are no values that are returned from this function call to the main function.
Let’s see the example with a function build without a return type and parameter,
Example:
Code:
using System;
namespace FunctionSamples
{
class Program_A
{
// User defined function without return type and parameter
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("Non Parameterized Function"); // No return statement
}
static void Main(string[] args) // Main Program
{
Program_A program = new Program_A (); // to create a new Object
program.Display(); // Call the Function
}
}
}
Output:

2. Using With Parameters (Arguments) and Without Return Type
In this program, a string is passed as a parameter to the function. This function’s return type is “void,” and no values can be returned. The value of the string is manipulated and displayed inside the function itself.
Example:
Code:
using System;
namespace FunctionSample
{
class Program_B
{
public void Display(string value) // User defined function without return type
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + value); // No return statement
}
static void Main(string[] args) // Main function
{
Program_B program = new Program_B(); // Creating Objec
program.Display("Welcome to C# Functions"); // Calling Function
}
}
}
Output:

3. Using With Parameters (Arguments) and with Return Type
In this program, a string is passed as a parameter to the function. The return type of this function is “string,” and the return value of the string can be returned from the function. The value of the string is manipulated and displayed inside the function itself.
Example
Code:
using System;
namespace FunctionsSample
{
class Program_C
{
// User defined function
public string Show(string message)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inside the Show Function Call");
return message;
}
// Main function
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program_C program = new Program_C();
string message = program.Show("C# Functions");
Console.WriteLine("Hello "+message);
}
}
}
Output:

4. Using Without Parameters (Arguments) and with Return Value
In this program, arguments or parameters will not be passed to the function “calculate” but to the main function; the values are returned from this calculate () function call. The variables a and b values are calculated in the function called “calculate,” and in the main function, the sum of these values is returned as a result.
Example:
Code:
using System;
namespace FunctionsSample
{
class Program_D
{
public void calculate()
{
int a = 50, b = 80, sum;
sum = a + b;
Console.WriteLine("Calculating the given to values: " +sum);
}
static void Main(string[] args) // Main function
{
Program_D addition =new Program_D();
addition.calculate();
}
}
}
Output:
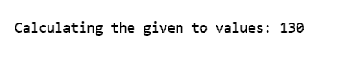
C# Passing Parameters to Methods
When creating a method with arguments/parameters in c#, we must pass arguments/parameters to that specified method when calling our application’s function. We have several ways to pass parameters to the method; let’s see the parameters/arguments.
| Parameters | Description |
| Value Parameters | Value parameters are called the “input parameters.” Instead of the original parameters, the input parameters will pass a copy of the actual value; due to that, there will not be any cause or changes made to the parameter during the called method, and it will not affect on original values while the control passes to the caller function. |
| Reference Parameters | Reference parameters are called the “input/output parameters.” The reference parameter will pass the reference memory of the original parameters. Thus, the changes/alteration made to the parameters in called method, while the control returns to the caller function, affects the actual values. |
|
Output Parameters |
It is an “output parameter” like the reference type parameters. The only difference is there is no need to initialize it before passing the data. |
Conclusion – C# Functions
In this article, we well-read the usage of the functions/ methods available in C# and learned the different C# functions. I hope this article has helped you understand the several functional aspects of C#.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonC#-Funktionen. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- .Net Core-Grafikverifizierungscode
- Laden der .NET Core-Konfigurationsdatei und DI-Injektion von Konfigurationsdaten
- Dokumentation zum .NET Core CLI-Tool dotnet-publish
- asp.net verwendet .net-Steuerelemente, um Dropdown-Navigationsmenüs zu erstellen
- So erhalten Sie den Namen des Controllers in Asp.net MVC

