Heim >Java >javaLernprogramm >Mehrdimensionales Array in Java
Mehrdimensionales Array in Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-08-30 15:27:381234Durchsuche
Eine vollständige Anleitung zum mehrdimensionalen Array in Java. Ein Array ist eine homogene mehrdimensionale Datenstruktur, die eine Sammlung von Elementen mit einem ähnlichen Datentyp ist. Sie werden im zusammenhängenden Speicherort abgelegt. Im Array wird das erste Element im Index 0 gespeichert; das zweite Element wird in Index 1 gespeichert und so weiter. Arrays können eindimensional oder mehrdimensional sein. In diesem Dokument werden wir uns mit mehrdimensionalen Arrays in Java befassen. Ein mehrdimensionales Array ist ein Array von Arrays, das mehr als eine Zeile und Spalte enthalten kann. Sehen wir uns nun in den folgenden Abschnitten die Syntax und Implementierung eines mehrdimensionalen Arrays an.
WERBUNG Beliebter Kurs in dieser Kategorie JAVA MASTERY - Spezialisierung | 78 Kursreihe | 15 ProbetestsSyntax:
data_type[dimension 1][dimension 2][]…[dimension n] array_name= new data_type[size 1][size 2]…[size n]
- Datentyp: Datentyp des Arrays, Beispiel: int, char, float usw.
- Dimension: die Dimension des Arrays, Beispiel: 1D, 2D usw.
- Array-Name: Name des Arrays.
- Größe1, Größe2, …, GrößeN: Größen der Dimension.
Typen mehrdimensionaler Arrays in Java
Die häufigsten mehrdimensionalen Arrays in Java sind:
- Zweidimensionales Array oder 2D-Array.
- Dreidimensionales Array oder 3D-Array.
1. Zweidimensionales Array
2D-Arrays werden häufig in Plattform-Videospielen wie Super Mario verwendet, um Gelände oder Bildschirm darzustellen. Sie können auch zum Zeichnen von Schachbrettern, zur Darstellung von Strukturen wie einer Tabellenkalkulation usw. verwendet werden.
Code:
int[][] array1 = new int[2][2];//Two dimensional Integer Array with 2 rows and 2 columns
Beispiel:
9 10
7 66
Dies ist ein 2D-Array mit zwei Zeilen und zwei Spalten.
2. Dreidimensionales Array
Dreidimensionale Arrays werden in Echtzeitanwendungen nicht häufig verwendet. Daher werden zweidimensionale Arrays auch in Programmierbeispielen bevorzugt.
Code:
int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Three dimensional Array
Beispiel:
6 8 66
66 65 47
46 89 98
Wie deklariere ich ein mehrdimensionales Array in Java?
Das mehrdimensionale Array in Java ist leicht zu verstehen, wenn normale Arrays bekannt sind. Mehrdimensionale Arrays können wie unten gezeigt deklariert werden:
Sehen wir uns zunächst die Deklaration von 2D-Arrays an:
- int[][] array1 = new int[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales Ganzzahl-Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- String[][] array1 = new String[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales String-Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- char[][] array1 = new char[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales char-Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- boolean[][] array1 = new boolean[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales boolesches Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- double[][] array1 = neues double[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales Doppelarray mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- float[][] array1 = new float[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales Float-Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- long[][] array1 = new long[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales langes Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- short[][] array1 = new short[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales kurzes Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
- byte[][] array1 = neues Byte[2][2]; //Zweidimensionales Byte-Array mit 2 Zeilen und 2 Spalten.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass beim Programmieren in Java die richtige Deklaration erstellt wird.
Beispiel #1
Code:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional 2D array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
public static void main(String args[]){
//2D array a is declared and initialized
int a[][]={{2,2,3},{8,4,5},{9,4,5}};
//Print the array elements
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Ausgabe:

Die Deklaration des dreidimensionalen Arrays kann besprochen werden.
- int[][][] array2 = new int[12][24][36]; //Dreidimensionales Array
Diese Arrays können beliebige Datentypen haben. Nachfolgend finden Sie einige der dreidimensionalen Arrays mit unterschiedlichen Datentypen.
- int [][][] IntArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Ganzzahlen.
- byte[][][] ByteArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Bytes.
- short[][][] ShortArray; // Deklaration einer dreidimensionalen Anordnung von Shorts.
- long[][][] LongArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Longs.
- float[][][] FloatArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Floats.
- double[][][] DoubleArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Doubles.
- boolean[][][] BooleanArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Booleschen Werten.
- char[][][] CharArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Zeichen.
- String[][][] StringArray; // Deklaration eines dreidimensionalen Arrays von Strings.
Beispiel #2
Code:
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
//3D array arr
int[][][] arr = { { { 1 , -9 , 3 } ,{ 2 , 7 , 4 } } , { { -45 , -5 , 6 , 75 } , { 88 } , { 29 , 30 } } };
// for..each loop to iterate through the elements of the 3d array arr
for (int[][] ar: arr) {
for (int[] a: ar) {
for(int finalarray: a) {
System.out.println(finalarray);
}
}
}
}
}
Ausgabe:

Wie initialisiere ich das mehrdimensionale Array in Java?
Mehrdimensionale Arrays können auf verschiedene Arten initialisiert werden:
1. Declare and Create a Java Multidimensional Array
- int[][][] a= new int[3][5][4];
In a more traditional way, Initializing Array elements can be as follows.
- a[0][1][0] = 15; // Initializing Array elements at position [0][1][0]
- a[1][2][0] = 45; // Initializing Array elements at position [1][2][0]
- a[2][1][1] = 65; // Initializing Array elements at position [2][1][1]
2. Directly Specify the Elements
int[][][] a = { { { 11 , 23 , 30 }, { 5 ,65 , 70 } , { 0 , 80 , 10 } ,{ 10 , 12 , 450 } } ,{ { 33 , 2 , 4 } , {11, 66, 6}, {55, 11, 22}, {11, 57, 43} } };
In this case, even though the size of rows and columns are not mentioned, the java compiler is able to identify the size of rows and columns by counting the number of elements.
3. Nested For Loop
In the case of storing a large number of elements, Nested For Loop can be used as shown below:
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for(k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
a[i][j][k] = i + j + k;} } }
4. Assigning Values to One Row
int a= new int[3][2][4]; a[0][2][1]= 33; a[0][1][2]= 73; a[0][1][1]= 88;
A three-dimensional array of size 3 levels * 2 rows * 4 columns is created, but values are assigned to some positions only. Since none of the other elements does have any value assigned, default values will be assigned.
Operations on Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Array in Java can perform several operations.
Example #1
Let Us See the Matrix Addition of Two Arrays.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to demonstrate the multidimensional array
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
public static void main(String args[])
{
int row, col, c, d;
//input the number of rows and columns
Scanner <u>in</u> = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of rows of matrix");
row = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter the number of columns of matrix");
col = in.nextInt();
//initialization of two matrices and sum matrix
int firstmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int secondmat[][] = new int[row][col];
int summat[][] = new int[row][col];
//adding elements to first matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the first matrix");
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
firstmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//adding elements to second matrix
System.out.println("Enter the elements to be added to the second matrix");
for (c = 0 ; c < row ; c++)
for (d = 0 ; d < col ; d++)
secondmat[c][d] = in.nextInt();
//sum of the two matrices
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
summat[c][d] = firstmat[c][d] + secondmat[c][d];
System.out.println("Sum of the two given matrices is:");
//printing the sum matrix
for (c = 0; c < row; c++)
{
for (d = 0; d < col; d++)
System.out.print(summat[c][d]+"\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

If subtraction needs to be performed, replace ‘+’ with ‘-‘ in the code.
Example #2
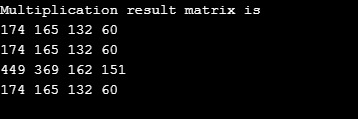
Let us see how Matrix Multiplication Works.
Code:
import java.util.*;
//Java Program to perform matrix multiplication
public class MultidimensionalArray {
//main method
static int N = 4;
// multiply matrices a and b, and then stores the result in c
static void mul(int a[][],
int b[][], int c[][])
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j]; //multiply a and b matrices
}
}
}
//main method
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int a[][] = { {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2},
{9, 7, 2, 3}};
int b[][] = {{ 9, 7, 2, 3}, {9, 7, 2, 3},
{9, 7, 2, 3},
{4, 13, 32, 2}};
// Store the result in c
int c[][] = new int[N][N] ;
int i, j;
mul(a, b, c); //calling the mul method
System.out.println("Multiplication result matrix" + " is ");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
Arrays are homogenous data structures that can store similar types of elements. It can be of single-dimensional or multidimensional. In this document, multidimensional arrays are discussed with explaining the syntax structure, initialization, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Multidimensional Array in Java. Here we discuss 2 types of the multidimensional array in java, how to declare, how to initialize and operation in it. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Multidimensional Array in C
- 2D Arrays in Java
- 2D Arrays in C#
- Multidimensional Array in PHP
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt vonMehrdimensionales Array in Java. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!

