Heim >Backend-Entwicklung >PHP-Tutorial >2D-Arrays in PHP
2D-Arrays in PHP
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOriginal
- 2024-08-29 12:43:14865Durchsuche
Ein Array ist eine Sammlung von Elementen eines beliebigen Datentyps. Es gibt viele Datentypen in PHP wie String, Ganzzahl, Boolescher Wert, Array, Objekt, Ressource usw. Ein 2D-Array ist eine Mischung dieser Datentypen, hauptsächlich des Arrays. Es gibt drei verschiedene Arten von 2D-Arrays in PHP:
WERBUNG Beliebter Kurs in dieser Kategorie PHP-ENTWICKLER - Spezialisierung | 8-Kurs-Reihe | 3 ProbetestsStarten Sie Ihren kostenlosen Softwareentwicklungskurs
Webentwicklung, Programmiersprachen, Softwaretests und andere
- Numerisches Array
- Assoziatives Array
- Mehrdimensionales Array
Arten von 2D-Arrays in PHP
Diese drei Arrays werden im Folgenden erklärt:
1. Das numerische Array
Das Array mit einem numerischen Index.
Syntax:
array(value1, value2, value3, …);
Beispiel:
$input = array(10,20,30,40,50);
2. Das assoziative Array
Das Array mit String- oder Zahlenindex. Die Elemente dieses Arrays werden in Form eines Schlüssel-Wert-Paares gespeichert.
Syntax:
array('key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2', 'key3' => 'value3',…);
Beispiel:
$input = array(0 =>Emma, 1=>Alice, 2=>'John');
3. Das mehrdimensionale Array
Das Array-Array ist ein mehrdimensionales Array oder ein 2D-Array oder ein verschachteltes Array. Dieses Format ist immer ein Array oder Array. Und wird daher als verschachteltes Array bezeichnet.
Syntax:
array ( array (elements...), array (elements...), ... )
Beispiel:
$input = array( array( "red", "green", "blue" ), array( "yellow", "black", "white" ) );
Im obigen Beispiel ist das Eingabearray ein Beispiel für ein zweidimensionales Array. Hier enthält das Hauptarray zwei Elemente, wobei jedes Element selbst ein Array aus drei Elementen ist.
Wie definiere ich 2D-Arrays?
Wir haben gelernt, dass im 2D-Array das Wertelement ein Array ist, das darüber hinaus Unterarrays haben kann. Die in einem Array genannten Dimensionen liegen in Form von Zeilen und Spalten vor. Wenn Sie das tabellarische Format des Arrays im Hinterkopf behalten, ist es einfacher zu lernen, wie diese Arrays definiert werden. Das heißt, wenn es sich um ein zweidimensionales Array handelt, werden zwei Indizes verwendet, und wenn es sich um ein dreidimensionales Array handelt, werden drei Indizes verwendet und so weiter.
Wie erstelle ich 2D-Arrays?
Da wir wissen, wie man ein 2D-Array definiert, können wir es jetzt erstellen. Hier ist der Index nicht definiert und ist standardmäßig eine Zahl, die immer mit 0 beginnt.
$input=array( array( "red", "green", "blue" ), array( "yellow", "black", "white" ) );
Das Array kann auch in Form des assoziativen Arrays definiert werden.
(in key =>value form)
Der Index oder der Schlüssel ist eine Zeichenfolge wie Farben, Früchte und Autos. Die Wertelemente liegen in Form eines Arrays vor, das jeweils 3 Elemente enthält.
$input = array(
'colors'=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
'fruits'=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
'cars'=>array ("BMW", "Skoda", "Mercedes")
);
Wie greife ich auf Elemente von 2D-Arrays zu?
Um auf diese Array-Werte zuzugreifen, können Sie eckige Klammern verwenden. Je tiefer Sie in weitere Ebenen des 2D-Arrays vordringen, desto häufiger wird der Satz eckiger Klammern mit jeder Ebene verwendet.
Beispiel #1
Code:
$input = array (
'colors' =>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
'fruits' =>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
'cars' =>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
Denken Sie daran, dass der erste Satz eckiger Klammern den Schlüssel enthält, der in diesem Fall Farben, Früchte und Autos sind. Gefolgt von einem weiteren Satz eckiger Klammern, um zur nächsten Ebene zu gelangen. Der Zugriff kann mit Zahlen wie 0,1,2 erfolgen.
Wenn wir also auf das Element „Grapes“ im obigen Array zugreifen möchten,
echo $input['fruits'][2];
Ähnlich die folgenden Beispiele
Wenn wir auf das Element „Mercedes“ im Array zugreifen wollen, dann
echo $input['cars'][2];
Wenn wir auf das Element „Rot“ im Array zugreifen wollen, dann
echo $input['colors'][0];
Da der Index in einem Array immer mit 0 beginnt.
Beispiel #2
Code:
$input = array (
array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
array ("Yellow", "Orange", "Purple"),
);
Wenn wir auf das Element „Orange“ im obigen Array zugreifen möchten, verwenden wir die folgende Zeile
echo $input[0][1];
gibt „Grün“
echo $input[1][2];
gibt „Lila“
echo $input[0][0];
gibt „Rot“
Wie füge ich Elemente von 2D-Arrays in PHP ein?
Da wir wissen, wie man Array-Elemente definiert, erstellt und darauf zugreift, lernen wir jetzt, wie man Elemente in das Array einfügt. Es gibt in PHP definierte Array-Funktionen für die Arbeit mit mehrdimensionalen Arrays, wie die Funktion array_push() zum Einfügen, die Funktion array_shift() zum Entfernen usw.
$input = array (
'colors'=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
'fruits'=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
'cars'=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
Mit der Funktion print_r() drucken wir zunächst das Array so, wie es ist.
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
"colors"=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
"fruits"=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
"cars"=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
// print the multidimensional array
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Ausgabe:

Um nun ein Element zum Unterarray „Früchte“ hinzuzufügen, verwenden wir
array_push() function
Syntax:
array_push(array, value1,value2...)
Wo,
- Das Array ist das $input-Array
- Wert1 ist das Element, das dem Array hinzugefügt werden soll
- Wert2 und Wert3 sind optional
Beispiel #1
Code:
$input = array (
"colors"=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
"fruits"=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
"cars"=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
array_push($input['colors'], "Black");
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Ausgabe:

Im folgenden Programm haben wir einfach den Schlüssel „colors“ entfernt und festgestellt, dass er mit einem 0-Schlüssel an das letzte Teil des angegebenen Arrays angehängt wird, wie im Ausgabebild gezeigt.
Example #2
Code:
// create multidimensional array
$input = array (
"colors"=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
"fruits"=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
"cars"=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
// adding a value to array
array_push($input, "Black");
// print the multidimensional array
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Output:
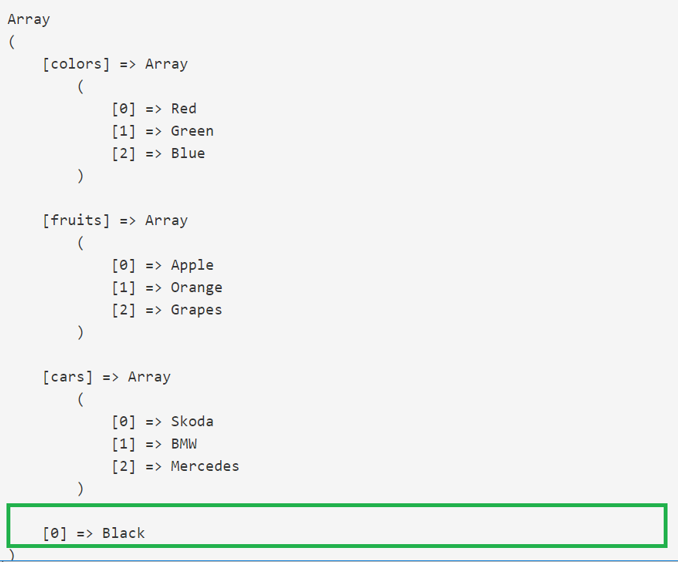
Example #3
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
array ("Yellow", "Orange", "Purple")
);
//add a color to the array
array_push($input, "Black");
// print the multidimensional array
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Output:

How to Update Elements of 2D Arrays in PHP?
To update an element of the 2D array just get the key from the array and replace the value of that key in a particular array.
$input['cars']['Mercedes'] = 'Duster';
Example #1
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
"colors"=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
"fruits"=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
"cars"=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
//update the Mercedes with Duster
$input["cars"][2] = "Duster";
// print the multidimensional array
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Output:

Example #2
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
array ("Yellow", "Orange", "Purple")
);
//update the Mercedes with Duster
$input[0][1] = "White";
// print the multidimensional array
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
print_r($input);
echo "<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">";
Output:

How to Delete Elements of 2D Arrays?
To delete an element of the 2D array we will use array_shift() function.
array_shift removes and returns the first element value of the array.
Syntax:
array_shift(array)
where
-array is the $input array
Example #1
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
"colors"=>array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
"fruits"=>array ("Apple", "Orange", "Grapes"),
"cars"=>array ("Skoda", "BMW", "Mercedes")
);
//print the removed element
print_r(array_shift($input));
Output:

Example #2
Code:
//create multidimensional array
$input = array (
array ("Red", "Green", "Blue"),
array ("Yellow", "Orange", "Purple")
);
//print the removed element
print_r(array_shift($input));
Output:

Two dimensional in Associative Array
In the following example, we have created a 2-d array containing the information of books like the author of the book, type of book, and published in the year. Also, we will learn how to traverse or loop through this array. Looping through the multidimensional array we will use a nested foreach loop. Meaning one foreach loop inside another foreach loop. The same can also be done using for loop.
$input = array( "The_Alchemist" => array ( "author" => "Paulo Coelho", "type" => "Fiction", "published_year" => 1988 ), "Managing_Oneself" => array ( "author" => "Peter Drucker", "type" => "Non-fiction", "published_year" => 1999 ), "Measuring_the_World" => array( "author" => "Daniel Kehlmann", "type" => "Fiction", "published_year" => 2005 ) );
Just printing the above array without any loop will give us the following output:
Code:
// create multidimensional array $input = array( "The_Alchemist" => array ( "author" => "Paulo Coelho", "type" => "Fiction", "published_year" => 1988 ), "Managing_Oneself" => array ( "author" => "Peter Drucker", "type" => "Non-fiction", "published_year" => 1999 ), "Measuring_the_World" => array( "author" => "Daniel Kehlmann", "type" => "Fiction", "published_year" => 2005 ) ); // print the plain multidimensional array echo ""; print_r($input); echo "";
Output:

Now we will print the multidimensional array using a foreach loop.
Code:
// create multidimensional array
$input = array(
"The_Alchemist" => array (
"author" => "Paulo Coelho",
"type" => "Fiction",
"published_year" => 1988
),
"Managing_Oneself" => array (
"author" => "Peter Drucker",
"type" => "Non-fiction",
"published_year" => 1999
),
"Measuring_the_World" => array(
"author" => "Daniel Kehlmann",
"type" => "Fiction",
"published_year" => 2005
)
);
//foreach to loop the outer array
foreach($input as $book) {
echo "
";
// foreach to loop the inner array
foreach($book as $key=>$value)
{
echo $key." ". $value. "
";
}
}
Output:

Conclusion
I hope this article is helpful to learn the concepts of the topic on a 2D array in PHP. This topic covers all the concepts required for the understanding related to the 2D array in PHP. This topic is made simpler with the help of examples with the output snapshots to refer to. According to the article, if all the programs are practiced well will surely help you to grasp the concepts easily. I hope the topic is made more informative for gaining more knowledge.
Das obige ist der detaillierte Inhalt von2D-Arrays in PHP. Für weitere Informationen folgen Sie bitte anderen verwandten Artikeln auf der PHP chinesischen Website!
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- So verwenden Sie cURL zum Implementieren von Get- und Post-Anfragen in PHP
- Alle Ausdruckssymbole in regulären Ausdrücken (Zusammenfassung)

