Heim >Web-Frontend >js-Tutorial >js的2种继承方式详解_javascript技巧
js的2种继承方式详解_javascript技巧
- WBOYOriginal
- 2016-05-16 16:57:13877Durchsuche
js中继承可以分为两种:对象冒充和原型链方式
一、对象冒充包括三种:临时属性方式、call()及apply()方式
1.临时属性方式
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
this.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
}
function F2E(name,id){
this.temp = Person;
this.temp(name);
delete this.temp;
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
var simon = new F2E('Simon',9527);
simon.say();
simon.showId();
2.call()/apply()方式
实质上是改变了this指针的指向
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
this.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
}
function F2E(name,id){
Person.call(this,name); //apply()方式改成Person.apply(this,new Array(name));
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
var simon = new F2E('Simon',9527);
simon.say();
simon.showId();
缺点:先来看这么一张内存分配图:
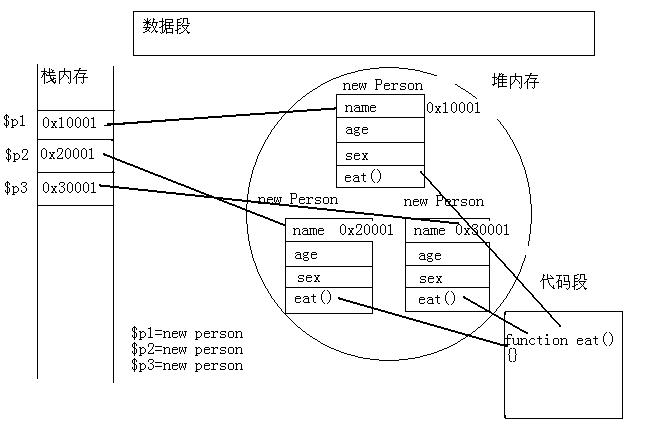 |
在OO概念中,new实例化后,对象就在堆内存中形成了自己的空间,值得注意的是,这个代码段。而成员方法就是存在这个代码段的,并且方法是共用的。问题就在这里,通过对象冒充方式继承时,所有的成员方法都是指向this的,也就是说new之后,每个实例将都会拥有这个成员方法,并不是共用的,这就造成了大量的内存浪费。并且通过对象冒充的方式,无法继承通过prototype方式定义的变量和方法,如以下代码将会出错:
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
this.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
}
Person.prototype.age = 20;
Person.prototype.sayAge = function(){alert('My age is '+this.age)};
function F2E(name,id){
Person.apply(this,new Array(name));
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
var simon = new F2E('Simon',9527);
simon.sayAge(); //提示TypeError: simon.sayAge is not a function
二、原型链方式
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(){
this.name = 'Simon';
}
Person.prototype.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
function F2E(id){
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
F2E.prototype = new Person();
var simon = new F2E(9527);
simon.say();
simon.showId();
alert(simon.hasOwnProperty('id')); //检查是否为自身属性
接下来按照上面的例子来理解以下js原型链概念:
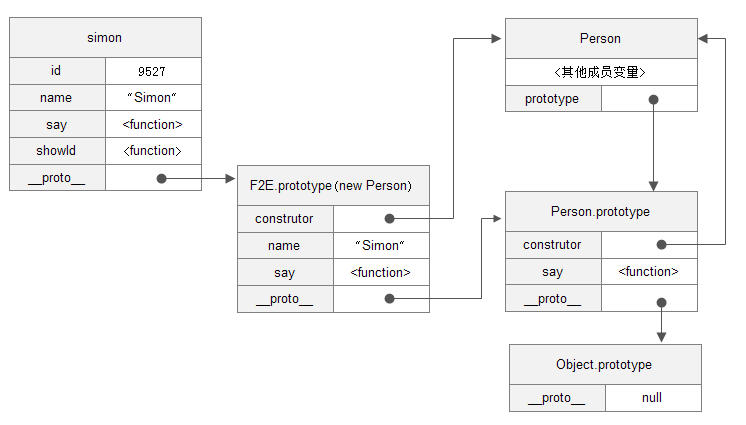 |
原型链可以理解成:js中每个对象均有一个隐藏的__proto__属性,一个实例化对象的__proto__属性指向其类的prototype方法,而这个prototype方法又可以被赋值成另一个实例化对象,这个对象的__proto__又需要指向其类,由此形成一条链,也就是前面代码中的
复制代码 代码如下:
F2E.prototype = new Person()
这句是关键。js对象在读取某个属性时,会先查找自身属性,没有则再去依次查找原型链上对象的属性。也就是说原型链的方法是可以共用的,这样就解决了对象冒充浪费内存的缺点。
下面再来说缺点:
缺点显而易见,原型链方式继承,就是实例化子类时不能将参数传给父类,也就是为什么这个例子中function Person()没有参数,而是直接写成了this.name=”Simon”的原因。下面的代码将不能达到预期的效果:
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
function F2E(name,id){
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
F2E.prototype = new Person();
var simon = new F2E("Simon",9527);
simon.say();
simon.showId();
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
function F2E(name,id){
this.id = id;
this.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
}
F2E.prototype = new Person(); //此处无法进行传值,this.name或者name都不行,直接写F2E.prototype = new Person('wood')是可以的,但是这样的话simon.say()就变成了My name is wood
var simon = new F2E("Simon",9527);
simon.say(); //弹出 My name is undefined
simon.showId();
最后,总结一下自认为较好的继承实现方式,成员变量采用对象冒充方式,成员方法采用原型链方式,代码如下:
复制代码 代码如下:
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.say = function(){
alert('My name is '+this.name);
}
function F2E(name,id){
Person.call(this,name);
this.id = id;
}
F2E.prototype = new Person();
//此处注意一个细节,showId不能写在F2E.prototype = new Person();前面
F2E.prototype.showId = function(){
alert('Good morning,Sir,My work number is '+this.id);
}
var simon = new F2E("Simon",9527);
simon.say();
simon.showId();
Stellungnahme:
Der Inhalt dieses Artikels wird freiwillig von Internetnutzern beigesteuert und das Urheberrecht liegt beim ursprünglichen Autor. Diese Website übernimmt keine entsprechende rechtliche Verantwortung. Wenn Sie Inhalte finden, bei denen der Verdacht eines Plagiats oder einer Rechtsverletzung besteht, wenden Sie sich bitte an admin@php.cn
Vorheriger Artikel:jquerymobile局部渲染的各种刷新方法小结_jqueryNächster Artikel:Seajs的学习笔记_Seajs
In Verbindung stehende Artikel
Mehr sehen- Eine eingehende Analyse der Bootstrap-Listengruppenkomponente
- Detaillierte Erläuterung des JavaScript-Funktions-Curryings
- Vollständiges Beispiel für die Generierung von JS-Passwörtern und die Erkennung der Stärke (mit Download des Demo-Quellcodes)
- Angularjs integriert WeChat UI (weui)
- Wie man mit JavaScript schnell zwischen traditionellem Chinesisch und vereinfachtem Chinesisch wechselt und wie Websites den Wechsel zwischen vereinfachtem und traditionellem Chinesisch unterstützen – Javascript-Kenntnisse

