C judgment
The judgment structure requires the programmer to specify one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested, as well as statements to be executed when the condition is true (required) and statements to be executed when the condition is false (optional) selected).
The C language assumes that any nonzero and nonempty value is true, and zero or null Assumed false.
The following is the general form of a typical judgment structure in most programming languages:
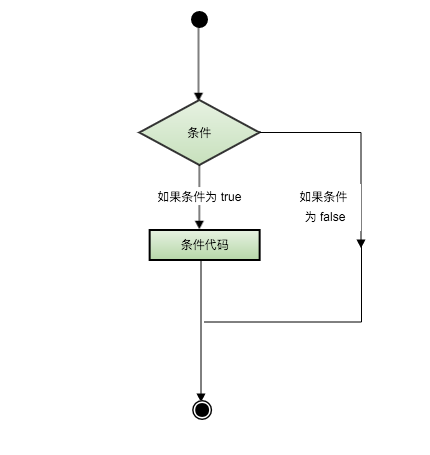
Judgment statement
C language provides The following types of judgment statements are provided. Click on the links to see the details of each statement.
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| if statement | A if statement Consists of a Boolean expression followed by one or more statements. |
| if...else statement | A if statement can be followed by an optional else statement ,else The statement is executed when the Boolean expression is false. |
| Nested if statements | You can use an if or else if statement inside another if or else if statement. |
| switch statement | A switch statement allows testing of a variable equal to multiple values. |
| Nested switch statements | You can use a switch statement inside another switch statement. |
? : Operator
We have already explained the conditional operator in the previous chapter? :, yes Used to replace the if...else statement. Its general form is as follows:
Exp1 ? Exp2 : Exp3;
where Exp1, Exp2 and Exp3 are expressions. Note the use and placement of colons.
? The value of the expression is determined by Exp1. If Exp1 is true, Exp2 is evaluated and the result is the value of the entire ? expression. If Exp1 is false, Exp3 is evaluated and the result is the value of the entire ? expression.








