C data type
In C language, data types refer to an extensive system for declaring variables or functions of different types. The type of a variable determines how much space the variable storage occupies and how the stored bit pattern is interpreted.
The types in C can be divided into the following categories:
| Serial number | Type and description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Basic types: They are arithmetic types, including two types: integer types and floating point types. |
| 2 | Enumeration types: They are also arithmetic types and are used to define only certain values that can be assigned to them in the program. A discrete integer-valued variable. |
| 3 | void Type: Type specifier void indicates that no value is available. |
| 4 | Derived types: They include: pointer types, array types, structure types, union types and function types. |
Array types and structure types are collectively called aggregate types. The type of a function refers to the type of the function's return value. In the rest of this chapter we will introduce the basic types, and several other types will be explained in the following chapters.
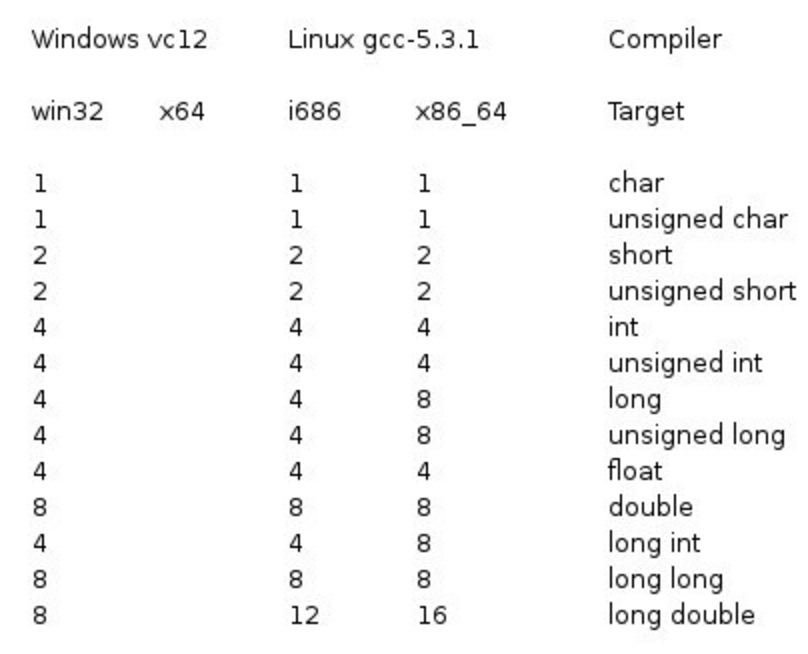
Integer types
The following table lists details about the storage size and value range of the standard integer types:
| Type | Storage size | Value range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| char | 1 Bytes | -128 to 127 or 0 to 255 | |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 255 | |
| signed char | 1 byte | -128 to 127 | |
| int | 2 or 4 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 or -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | |
| 2 or 4 bytes | 0 to 65,535 or 0 to 4,294,967,295 | ||
| 2 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 | ||
| 2 bytes | 0 to 65,535 | ||
| 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | ||
| 4 bytes | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| Type | Storage size | Value range | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | 4 bytes | 1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38 | 6 decimal places |
| double | 8 bytes | 2.3E-308 to 1.7E+308 | 15 decimal places |
| long double | 16 bytes | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 | 19 Decimal places |
#The header file float.h defines macros that allow you to use these values and other details about the binary representation of real numbers in your program. The following example will output the storage space occupied by the floating point type and its range value:
#include <stdio.h>#include <float.h>int main(){
printf("float 存储最大字节数 : %lu \n", sizeof(float));
printf("float 最小值: %E\n", FLT_MIN );
printf("float 最大值: %E\n", FLT_MAX );
printf("精度值: %d\n", FLT_DIG );
return 0;}When you compile and execute the above program on Linux, it will produce the following results:
float 存储最大字节数 : 4 float 最小值: 1.175494E-38float 最大值: 3.402823E+38精度值: 6
void type
The void type specifies no available value. It is usually used in the following three situations:
| Serial number | Type and description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Function returns null There are various functions in C that do not return a value or you can say they return null. The return type of a function that does not return a value is null. For example void exit (int status); |
| The function parameter is emptyThere are various This function does not accept any parameters. Functions without parameters can accept a void. For example int rand(void); | |
| The pointer points to void | The pointer of type void * Represents the address of the object, not the type. For example, the memory allocation function void *malloc( size_t size ); returns a pointer to void that can be converted to any data type. |