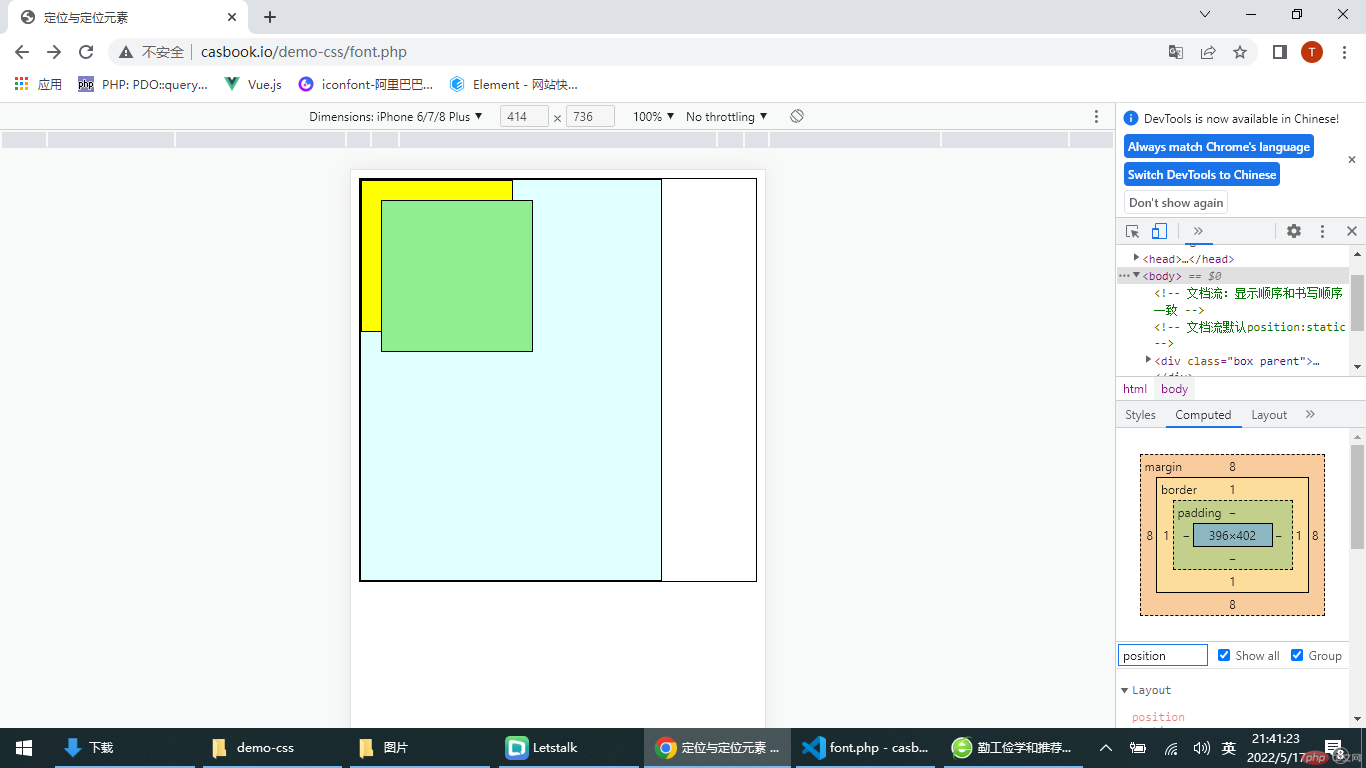
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>定位与定位元素</title></head><body> <!-- 文档流:显示顺序和书写顺序一致 --> <!-- 文档流默认position:static --> <div class="box parent"> <div class="box child first"></div> <div class="box child"></div> </div></body></html><style> body{ border: 1px solid #000; } .box { border: 1px solid #000; } .box.parent{ width: 300px; height: 400px; background-color: lightcyan; } .box.child{ width:150px; height: 150px; background-color: yellow; } .box.child.first{ width:150px; height: 150px; background-color: lightgreen; /* 1 相对定位 */ position:relative; /* 相对于自身在文档流中的位置,元素仍然在文档流中国,原占空间不释放, 只有相对原位置进行了偏移 */ top:30px; left:30px; /* 2 绝对定位 */ /* 相对于他的包含快,看他的元素结构了 能充当绝对定位包含快的元素,必须是定位元素 不能是static就可以了 如果绝对定位元素向上一直找不到可定位的父级,那就相对于Body/html*/ position:absolute; } .box.parent{ /* 设定定位参考父级,包含快 */ position: relative; } /* 相对定位:相对自身,在文档流中 绝对定位:相对包含快,不在文档流中 */ /* 3 固定定位 */ /* 永远不动了,是绝对定位的一个子集,就是绝对定位 ,只是包含快是固定,永远是Body/html */ .box.child.first{ position: fixed; }</style>


