一. 优雅的获取表单元素
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>获取表单元素</title> <style> #login { margin-bottom: 2em; } .login { width: 15em; border: 1px solid #888; border-radius: 0.5em; box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #888; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 3em 1fr; gap: 0.5em 1em; } .login legend { padding: 0 0.5em; text-align: center; margin-bottom: 0.5em; font-weight: bolder; } .login button { grid-column: 2; } .login button:hover { cursor: pointer; background-color: lightcyan; } </style></head><body> <form action="login.php" method="post" id="login"> <fieldset class="login"> <legend>表单1</legend> <label for="email">邮箱:</label> <input type="email" name="email" id="email" value="admin@php.cn" autofocus /> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input type="password" name="password" id="password" value="123456" /> <button>提交</button> </fieldset> </form> <form action="login.php" method="post" id="login1"> <fieldset class="login"> <legend>表单2</legend> <label for="email">邮箱:</label> <input type="email" name="email" id="email" value="admin@php.cn" autofocus /> <label for="password">密码:</label> <input type="password" name="password" id="password" value="123456" /> <button>提交</button> </fieldset> </form> <script> // 使用document.forms可获取页面所有表单 // 通过form表单的id或索引[]获取指定的表单 console.log(document.forms); console.log(document.forms.login); console.log(document.forms[1]); // 获取表单内的元素,可通过元素的name值来获取:forms.表单id.元素name console.log(document.forms.login.email); console.log(document.forms.login.password); // 获取表单中元素的值 console.log(document.forms.login.email.value); </script></body></html>
示例图:

二. dom树的遍历与常用属性
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>遍历DOM树</title></head><body> <ol class="list"> <li class="item1">item</li> <li class="item2">item</li> <li class="item3">item</li> <li class="item4">item</li> <li class="item5">item</li> </ol> <script> // 获取整个list元素 let ol = document.querySelector(".list"); console.log(ol); //获取所有子节点元素:使用children获取到的结果是一个元素集合。 let child = ol.children; console.log(child); // 将元素集合转成数组 // Array.from() console.log(Array.from(ol.children)); // ...rest console.log([...ol.children]); // 遍历 //第一个, firstElementChild console.log([...ol.children][0]); [...ol.children][0].style.color = "blue"; ol.firstElementChild.style.background = "yellow"; // 下一个兄弟, 第2个, nextElementSibling ol.firstElementChild.nextElementSibling.style.background = "green"; // 最后一个, lastElementChild ol.lastElementChild.style.background = "yellow"; // 前一个兄弟, previousElementSibling ol.lastElementChild.previousElementSibling.style.background = "lightgreen"; // 父节点/元素节点, parentElment / parentNode ol.lastElementChild.parentNode.style.border = "1px solid red"; </script></body></html>
示例图:

三.dom元素的增删改操作
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>dom元素的增删改</title></head><body> <script> // 1. 创建元素 const ul = document.createElement("ul"); //给ul插入内联css ul.style.border = "1px solid"; //给ul插入指向样式 ul.className = "content"; // 2. 添加到页面中/html中: append document.body.append(ul); // 3. 为ul列表添加元素 for (let i = 0; i < 5; i++) { const li = document.createElement("li"); li.textContent = "item" + (i + 1); ul.append(li); } // 4.查看元素 console.log(ul); // outerHTML: 元素的html字符串表示 console.log(ul.outerHTML); // 5. 在节点之前插入: before const li = document.createElement("li"); li.textContent = "商品"; li.style.color = "red"; //在第4个元素前面插入新建的元素 //先获取第4个元素 const four = document.querySelector("ul li:nth-of-type(4)"); //插入 four.before(li); // 6. 在节点之后插入 : after // cloneNode(true): 克隆节点, true, 复制元素后代的内容 let cloneLi = li.cloneNode(true); //插入 four.after(cloneLi); // 7. 在父节点的标签为插入点,进行插入元素 // insertAdjacentElement('插入位置', 元素) // 插入位置有四个 // afterBegin: 开始标签之后,第一个子元素 // beforeBegin: 开始标签之前,是它的前一个兄弟元素 // afterEnd: 结束标签之后,它的下一个兄弟元素 // beforeEnd: 结束标签之前,它的最后一个子元素 const h3 = document.createElement("h3"); h3.textContent = "商品列表"; ul.insertAdjacentElement("beforeBegin", h3); const p = document.createElement("p"); p.textContent = "共计: 7 件"; ul.insertAdjacentElement("afterEnd", p); // 8. 替换元素 replaceChild // 1. 插入的元素 const a = document.createElement("a"); a.href = "https://php.cn"; a.textContent = "php.cn"; // 2. 执行替换第二个元素 const last = ul.lastElementChild; ul.replaceChild(a, last); // 9. 移除: removex //ul.lastElementChild.remove(last); </script></body></html>
示例图:

四.js操作元素内容的几个常用方法
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>js操作元素内容</title></head><body> <div class="box"> <style> h2 { color: red; } </style> <h2>通知</h2> <span style="display: none">试用期员工不参加</span> <p>今天下午17:00开会, 开发部, 运营部全体参加~~</p> </div> <script> const box = document.querySelector(".box"); // textContent: 返回元素以及后代元素中的所有文本内容,包括 <style>, display:none的内容 console.log(box.textContent); // innerText: 返回元素以及后代中的文本 console.log(box.innerText); // innerHTML: 返回内部的html字符串 console.log(box.innerHTML); // outerHTML: 返回当前节点的自身的html字符串 console.log(box.outerHTML); </script></body></html>
示例图:
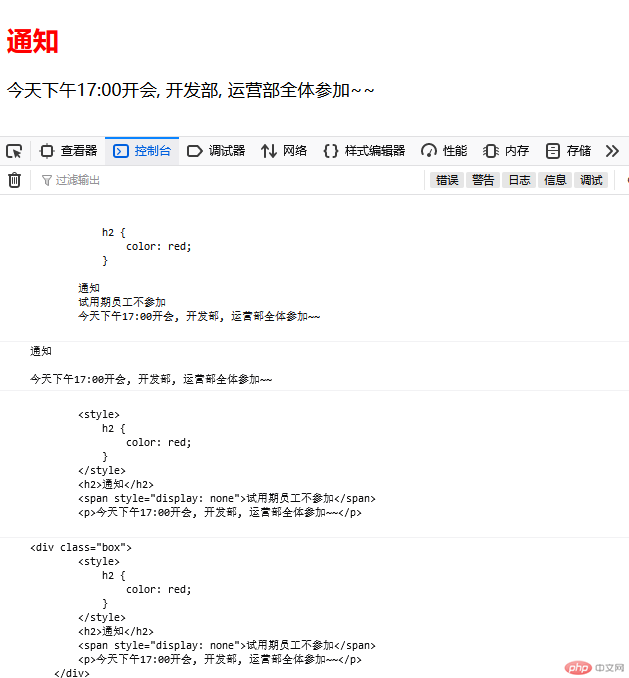
五.将留言板的实战案例进行仿写,加上一些样式
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>dom实战: 留言板</title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; box-sizing: border-box; } .content { width: 20em; height: 3em; border: 2px solid green; padding: 0 20px; border-radius: 20px; } ul { list-style: none; background-color: yellowgreen; width: 16.8em; margin: -1em 0 0 1em; border-radius: 20px; overflow: hidden; } li { height: 2.2em; line-height: 2.2em; border-bottom: 1px dashed rgb(253, 253, 253); padding-left: 1em; } input { margin: 2em 1em; } </style></head><body> <!-- onkeydown: 按下键时触发 --> <input class="content" type="text" onkeydown="addMsg(this)" placeholder="请输入留言内容" autofocus /> <ul class="list"></ul> <script> function addMsg(ele) { // 判断按键,如果是回车键则执行添加留言 if (event.key === "Enter") { // 1. 获取留言列表的容器 const ul = document.querySelector(".list"); // 2. 判断留言是否为空? if (ele.value.length === 0) { alert("留言内容不能为空"); ele.focus(); return false; } // 3. 添加一条新留言 const li = document.createElement("li"); // 添加删除留言功能 li.innerHTML = ele.value + "<button onclick='del(this.parentNode)'>删除</button>"; // 根据留言规则,最新的一条显示在最上面 ul.insertAdjacentElement("afterBegin", li); // 4. 清空留言的输入框,为下一次做准备 ele.value = null; // 5. 重置焦点到留言框中,方便用户更次输入 ele.focus(); } } // 删除功能 function del(ele) { return confirm("是否删除?") ? ele.remove() : false; } </script></body></html>
示例图:

六.dataset对象
元素属性有二类:
- 内置的预定义属性, 如 id, class,title,style等
- 用户自定义属性,主要用于js脚本控制, 以 “data-“”为前缀,如 data-key
<div class="btn-group"> <!-- onclick: 内置/预定义事件属性 --> <!-- data-index: 自定义属性 --> <button data-index="1" onclick="getIndex(this)">btn1</button> <button data-index="2" onclick="getIndex(this)">btn2</button> <button data-index="3" onclick="getIndex(this)">btn3</button></div><script> function getIndex(btn) { // 通过自定义属性data-index的值,知道我点的是哪一个? // dataset.prop, "data-"一定要省略掉 console.log("点击了第 ", btn.dataset.index, " 个按钮"); }</script><!-- 自定义属性还可以将一些数据保存到标签中 --><!-- data-emial, data-work-unit --><div class="user" data-email="88888@qq.com" data-work-unit="php中文网">老师</div><script> const user = document.querySelector(".user"); console.log(user.dataset.email); console.log(user.dataset.workUnit);</script>
七.获取元素的计算样式
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>获取元素的计算样式</title> <style> .box { width: 150px; height: 100px; } </style></head><body> <div class="box" style="color: green; background-color: lightblue">Hello World!</div> <script> const div = document.querySelector("div"); // 行内样式,style console.log(div.style.color); console.log(div.style.backgroundColor); // 计算样式: 内部<style>或外部 如 style.css console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div).width); console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div).height); console.log(window.getComputedStyle(div).backgroundColor); </script></body></html>
示例图:

八.classList 对象常用方法
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>js操作class属性: classList对象</title> <style> .red { color: red; } .bgc { background-color: yellow; } .blue { color: blue; } .bd { border: 5px solid #000; } </style></head><body> <h2>hello</h2> <script> const h2 = document.querySelector("h2"); // add: 添加class,可以叠加 h2.classList.add("red"); // color: red; h2.classList.add("bgc"); //background-color: yellow; // remove: 移除class //h2.classList.remove("bgc"); // replace: 替换class //h2.classList.replace("red", "blue"); // toggle: 切换 class // 如果已存在 bd, 则执行remove 移除操作, 否则执行 add 添加操作 h2.classList.toggle("bd"); </script></body></html>
示例图:

九.事件的添加与派发
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title>事件的添加与删除</title></head><body> <button>元素对象</button> <button>元素事件监听器</button> <button>事件派发/点击广告赚钱</button> <script> // 1.先获取元素,然后通过元素.onclick(){}进行添加 const btn1 = document.querySelector("button:first-of-type"); btn1.onclick = function() { console.log(event); }; // 删除事件:null // btn1.onclick = null; // 2.事件监听器 const btn2 = document.querySelector("button:nth-of-type(2)"); function show() { console.log(event); } // 事件回调方法不能移除,必须是命名函数才可以 btn2.addEventListener("click", show, false); // 移除事件 //btn2.removeEventListener("click", show, false); //3.事件派发 const btn3 = document.querySelector("button:nth-of-type(3)"); // 先添加一个事件,然后自动去的触发它 let i = 0; btn3.addEventListener( "click", () => { console.log("恭喜你,又赚了 : " + i + "元"); i += 0.8; }, false ); // 创建一个自定义事件 const myclick = new Event("click"); setInterval(() => btn3.dispatchEvent(myclick), 2000); </script></body></html>








