ES6 变量声明,箭头函数,数组方法,解构赋值,JSON,类与继承,模块化练习
let和const变量声明
var 可以重复声明,变量提升,没有块作用域 {}
let, const 不可以重复声明,有块作用域
const 声明时必须赋值,值不可修改,声明的复合类型(对象和数组)指向内存地址
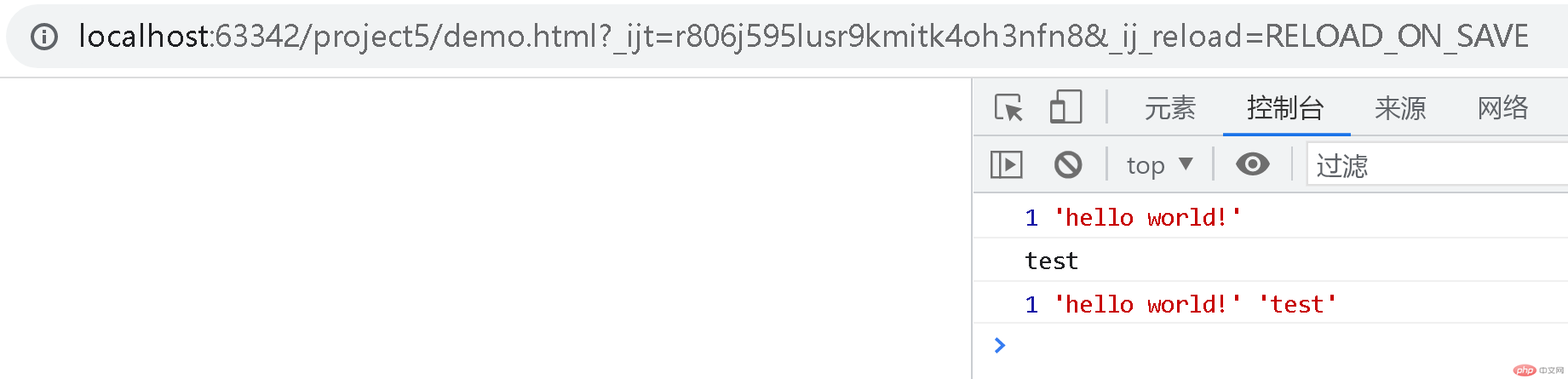
// let和const变量声明var a = 'a';let b = 'b';const c = ['c'];// 块作用域if (true) {// 无块作用域var a = 'aa';// 有块作用域let b = 'bb';const c = ['cc'];}// 复合类型指向指针地址c[0] = 'ccc';// aa b ['ccc']console.log(a, b, c);
箭头函数,数组 filter,map,reduce 方法
// 箭头函数,数组 filter,map,reduce 方法const evenPow2 = (...param) => param.filter(el => el % 2 === 0).map(el => Math.pow(el, 2)).reduce((p, n) => p + n, 0);// 计算一组值中偶数平方的和,输出 20console.log(evenPow2(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));// filter 数组去重const arr = ['a', 1, 'b', 'a', 'b', 1, 2];let arrUnique = arr.filter((value, i, arr) => arr.indexOf(value) === i);// ['a', 1, 'b', 2]console.log(arrUnique);// reduce 数组去重arrUnique = arr.reduce((prev, curr) => prev.includes(curr) ? prev : [...prev, curr], []);// ['a', 1, 'b', 2]console.log(arrUnique);
解构赋值
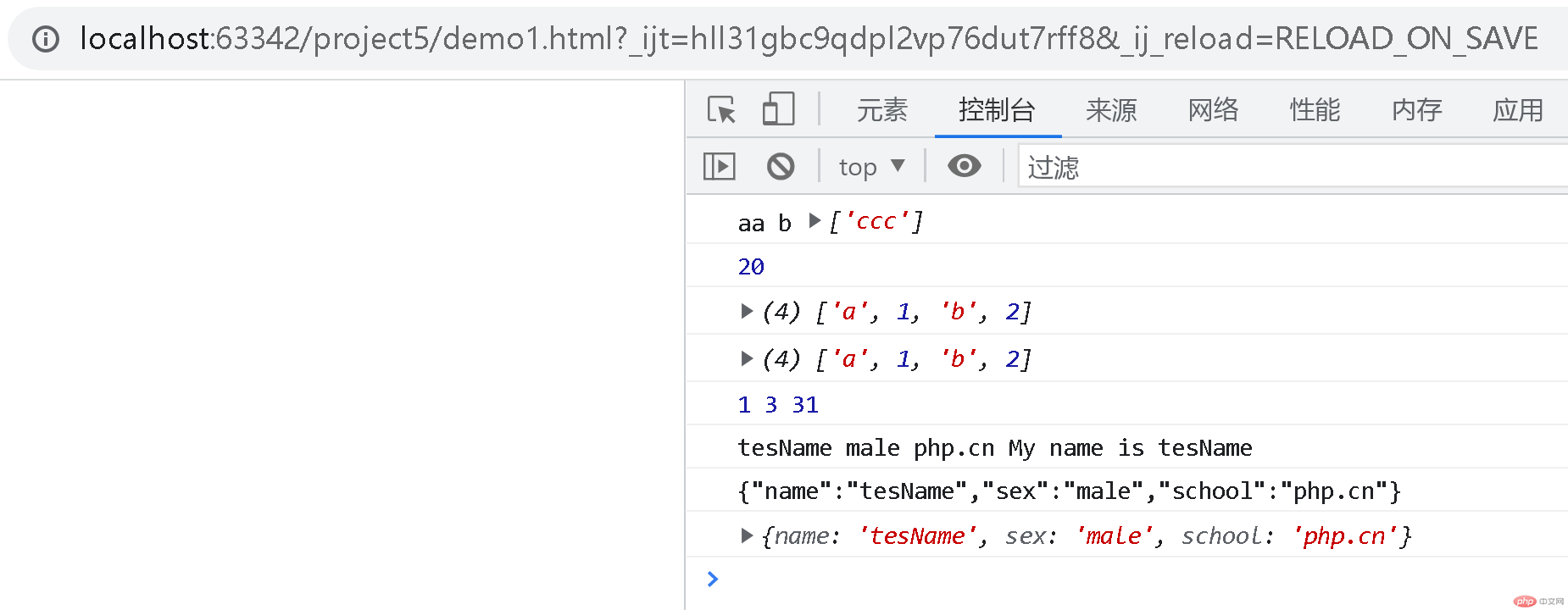
// 解构赋值const [{x,z}, [xy, yz, zx]] = [{x:1, y:2, z:3}, [12, 23, 31]];// 1 2 31console.log(x, z, zx);
类与继承和JSON串行化与反串行化
// 类与继承和JSON串行化与反串行化class Person {// 构造方法constructor(name, sex) {this.name = name;this.sex = sex;// this.say = () => `My name is ${this.name}`;}// say = function () {// return `My name is ${this.name}`;// }// say = () => `My name is ${this.name}`;say() {return `My name is ${this.name}`;}}class Student extends Person {constructor(name, sex, school) {// 父类构造函数,新建父类的 this 对象super(name, sex);this.school = school;}}const student1 = new Student('tesName', 'male', 'php.cn');// tesName male php.cn My name is tesNameconsole.log(student1.name, student1.sex, student1.school, student1.say());// 串行化const strStudent1 = JSON.stringify(student1);// 只能串行化 `字符串,数字,对象,数组,布尔,null` 因此 say() 函数被忽略// {"name":"tesName","sex":"male","school":"php.cn"}console.log(strStudent1);// 反串行化,返回 {name: 'tesName', sex: 'male', school: 'php.cn'}parseStudent1 = JSON.parse(strStudent1);console.log(parseStudent1);
module 模块化编程
demo2.js
const a = 1;const show = () => 'hello world!';const test = () => 'test';export {a as aVar, show, test as default};
demo.js
// 部分导入import {aVar as aTestVar, show} from "./demo2.js";// 1 'hello world!'console.log(aTestVar, show());// 缺省导入import testFunc from "./demo2.js";// 1 'hello world!' 'test'console.log(testFunc());// 全部导入import * as obj from "./demo2.js";// 1 'hello world!' 'test'console.log(obj.aVar, obj.show(), obj.default());
demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><script src="demo.js" type="module"></script></head><body></body></html>