![]() 值传递与引用传递 代码
值传递与引用传递 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>值传递与引用传递</title></head><body> <script> // 1 赋值 // 1.1 值传递:原始类型,string,number,bool let a = 1; let b = a; console.log("a = %d, b = %d", a, b); a = 2; //更新a, 不影响b console.log("a = %d, b = %d", a, b); //1.2 引用传递:引用类型,object,array let obj1 = {a:1, b:2}; console.log(obj1); let obj2 = obj1; console.log(obj2); //更新obj1 obj1.a = 10; console.log(obj1); //obj2同步更新 console.log(obj2); // 2.传参 const f1 = x => (x = 10); let m = 5; console.log("m = %d", m); f1(m); // 入参:调用函数是传入的参数,简称:“入参” // 函数中对参数的更新,并不会影响到入参 console.log("m = %d", m); const f2 = x => (x.a = 10); let o = {a: 1, b: 2}; console.log(o); f2(o); //看上去函数对于o.a的更新生效,实际上仍是值传递 console.log(o); // 对与引用类型,只有全新赋值才算是更新,修改属性不算的 const obj = {x: 1, y: 2}; obj.x = 20; // 赋值一个全新对像,才是更新 // obj = {} const f3 = x => ( x = {} ); f3(o); console.log(o); // 深拷贝:值传递 // 浅拷贝:引用传递 </script></body></html>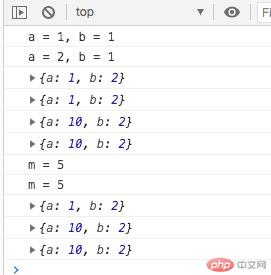
![]() 模板字面量与标签函数 代码
模板字面量与标签函数 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>模板字面量与标签函数</title></head><body> <script> // 1. 模板字面量:将表达式嵌入到字符串 let a = 1, b = 2; let res = a + " + " + b + " = " + (a + b); console.log(res); // 模板字面量使用反引号:“`” res = `${a} + ${b} = ${a + b}`; console.log(res); // 模板字面量的组成: // 1. 字符串字面量: "+, =" // 2. 变量或表达式:a, b, (a+b) // 模板字面量创建多行字符串可以保留格式 let menu = ['首页', '视频', '文章']; let htmlStr = `<ul> <li><a href="">${menu[0]}</a></li> <li><a href="">${menu[1]}</a></li> <li><a href="">${menu[2]}</a></li></ul>`; console.log(htmlStr); document.body.insertAdjacentHTML("beforeEnd",htmlStr); // 2.标签函数: 自定义模板字面量的行为 let hello = name => alert(name); // hello("天蓬老师"); // hello `天蓬老师`; // 使用自定义函数来处理模板字面量,它的参数约定 // 1. 第一个参数:模板字面量中的字符串字面量组成的数组 // 2. 从第二个参数开始,将模板字面量中的变量依次传入 let sum = (strs, a, b) => { console.log(strs); console.log(a,b); } sum([' + ', ' = ',''], a, b); sum `${a} + ${b} = `; //rest sum = (strs, ...args) => { console.log(strs); console.log(args); } sum `${a} + ${b} = `; </script></body></html>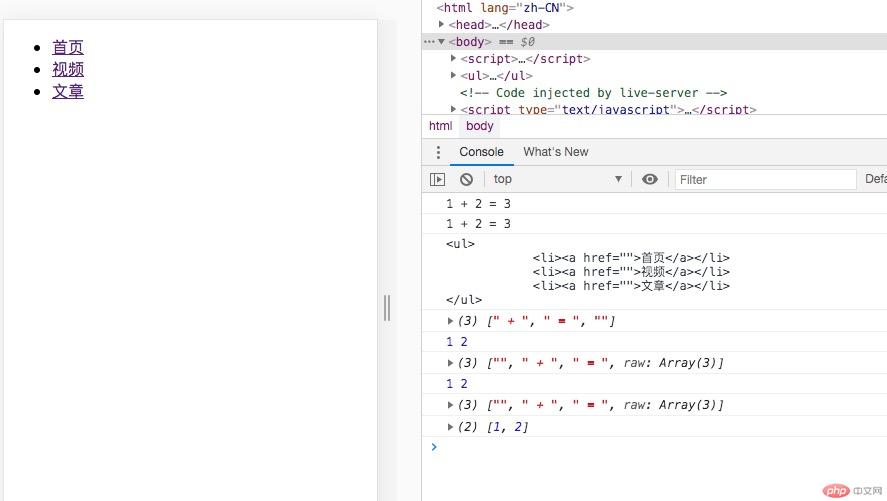
![]() 解构赋值 代码
解构赋值 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>解构赋值</title></head><body> <script> //解构赋值: 快速从集合数据(数组/对象)解构出独立变量 //1.数组 let [a,b,c] = [1,2,3]; console.log(a,b,c); [a,b] = [1,2,3]; console.log(a,b); [a,b,c,d = "xxxx"] = [1,2,3]; console.log(a,b,c,d); [a,b,...c] = [1,2,3,4,5]; console.log(a,b,c); [,,a,,] = [1,2,3,4,5]; console.log(a); let x = 1, y = 2, t; console.log("x = %d, y = %d", x, y); // t = x; // x = y; // y = t; [y,x] = [x,y]; console.log("x = %d, y = %d", x, y); // 2.对象解构 let {id, name} = {id: 10, name: "手机"} console.log(id, name); //属性名与变量名必须一一对应,顺序无所谓 ({name, id} = { id: 10, name: "手机"}); console.log(id, name); let email = "admin@php.cn"; let { role, email: userEmail } = {role: "user", email: "user@php.cn"}; console.log(userEmail); console.log(email); //3. 参数解构 // 数组传参 let sum = ([a,b]) => a + b; console.log(sum([10, 20])); // 对象传参 let getUser = ({name,email}) => [name,email]; console.log(getUser({email:"tp@php.cn", name: "天蓬老师"})); </script></body></html>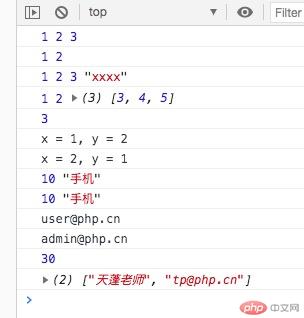
![]() 对象字面量的简化 代码
对象字面量的简化 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>对象字面量的简化</title></head><body> <script> let user = { userName: "天蓬老师", userEmail: "tp@php.cn", getInfo: function (){ return `${this.userName} (${this.userEmail})`; } }; console.log(user.getInfo()); let {userName, userEmail} = user; console.log(userName, userEmail); user = { // userName: userName, userName, // userEmail: userEmail, // 当属性与同一作用域中的变量同名时,可以直接使用属性来引用变量值 userEmail, // 方法也能简化:删除冒号和 function 关健字 getInfo(){ return `${this.userName} (${this.userEmail})`; }, // 当前箭头函数中的this指向了全局window test: ()=> console.log(this), } console.log("简化后: ", user.getInfo()); console.log(user.test()); // 箭头函数中的this总是指向定义它时的作用域(静态作用域/词法作用域),而并非调用时的作用域 // user对象不能创建作用域,this 指向了user的作用域/作用域链: window // 全局没有userName, userEmail,所以输出 undefined </script></body></html>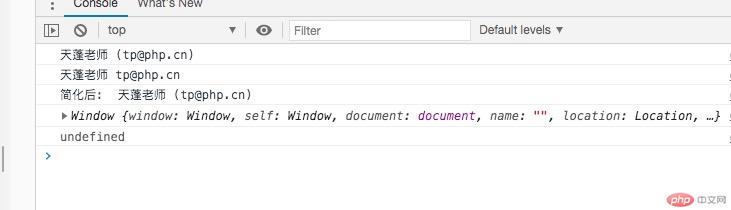
![]() bind,call,apply 代码
bind,call,apply 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>bind,call,apply</title></head><body> <button>Click</button> <script> function hello(name) { this.name = name; console.log(this.name); } const obj = { name: "admin" }; //经典调用 console.log(hello("朱老师")); //bind()不会立即执行, 只返回一个函数声明 let f = hello.bind(obj,"天蓬老师"); console.log(f()); // call/apply 立即执行 f = hello.call(obj, "灭绝老师"); console.log(f); f = hello.apply(obj, ["西门老师"]); console.log(f); // bind()应用案例:动态改变this document.querySelector("button").addEventListener( "click", function(){ console.log(this.name); console.log(this); document.body.appendChild(document.createElement("p")).innerHTML = "欢迎:" + this.name; }.bind({name:"猫科动物"}) ); </script></body></html>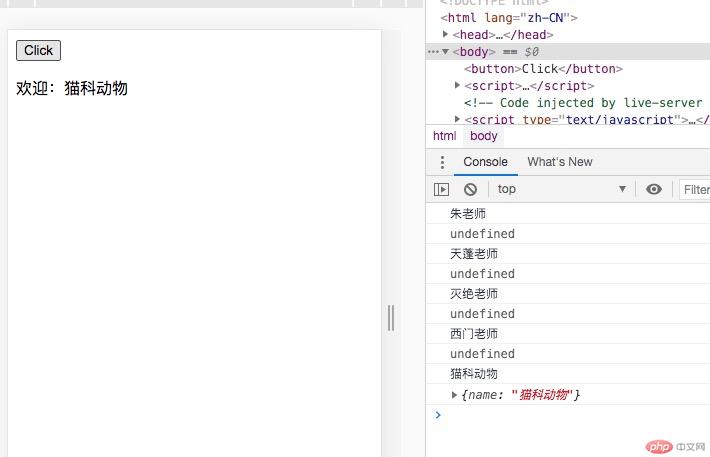
![]() 访问器属性 代码
访问器属性 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>访问器属性</title></head><body> <script> const product = { data: [ { name: "电脑", price: 5000, num: 5 }, { name: "手机", price: 4000, num: 10 }, { name: "相机", price: 8000, num: 3 }, ], getAmounts() { return this.data.reduce( (t, c) => ( t += c.price * c.num), 0 ); }, // 访问器属性 // 将方法伪造成一个属性 get total() { return this.data.reduce( (t, c) => ( t += c.price * c.num), 0 ); }, set setPrice(price) { this.data[1].price = price; }, } console.log("总金额 :", product.getAmounts()); console.log("总金额 :", product.total); product.setPrice = 9988; console.log(product.data[1].price); </script></body></html>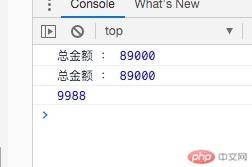
![]() 访问器属性的优先级 代码
访问器属性的优先级 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>访问器属性的优先级</title></head><body> <script> let user = { // name: "朱老师", data: { name: "朱老师"}, get name() { // return "灭绝小师妹"; return this.data.name; }, set name(value){ // this.name = value; this.data.name = value; } } // 访问器属性优级高于同名的普通属性 user.name = "天蓬老师"; console.log(user.name); </script></body></html>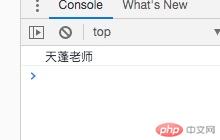
![]() 流程控制-分支 代码
流程控制-分支 代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>流程控制-分支</title></head><body> <script> let score = 64; // // 单分支 // if (score >= 60) { // console.log('及格'); // } //双分支 if (score >= 60) { console.log('及格'); //默认分支 } else { console.log('补考'); } //多分支 score = -1; if (score >= 60 && score < 80) { console.log('合格'); } else if (score >= 80 && score <= 100) { console.log('学霸'); }else if(score > 100 || score < 0){ console.log("非法数据"); } else { console.log('补考'); } // switch( true ) { case score >= 60 && score < 80 : console.log('合格'); break; case score >= 80 && score <= 100 : console.log('学霸'); break; case score > 100 || score < 0 : console.log("非法数据"); break; default: console.log('补考'); } // switch 用在单值判断 let response = "Success"; switch(response.toLowerCase()) { case 'fail': console.log("请求失败"); break; case 'success': console.log("请求成功"); break; default: console.log("未知错误"); } //三元运算符 // 条件? true : false // //双分支 // if (score >= 60) { // console.log('及格'); // //默认分支 // } else { // console.log('补考'); // } score = 80; console.log( score >= 60 ? "及格" : "补考"); </script></body></html>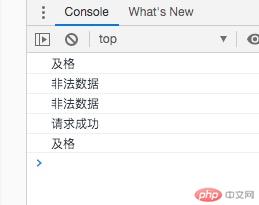
![]() 总结:
总结:
![]() 值传递与引用传递:
值传递与引用传递:
值传递(原始类型)如:深拷贝
引用传递(object,array)如:浅拷贝
![]() 模板字面量:
模板字面量:
将表达式嵌入到字符串
模板字面量使用反引号:“`”
格式${a} 其中a为变量
使用自定义函数来处理模板字面量,它的参数约定
第一个参数:模板字面量中的字符串字面量组成的数组
从第二个参数开始,将模板字面量中的变量依次传入
![]() 解构赋值:
解构赋值:
快速从集合数据(数组/对象)解构出独立变量
对象解构中:属性名与变量名必须一一对应,顺序无所谓
![]() 参数解构:
参数解构:
数组传参 和 对象传参
![]() 对象字面量的简化:
对象字面量的简化:
当属性与同一作用域中的变量同名时,可以直接使用属性来引用变量值
方法也能简化:删除冒号和 function 关健字
箭头函数中的this总是指向定义它时的作用域(静态作用域/词法作用域),而并非调用时的作用域
user对象不能创建作用域,this 指向了user的作用域/作用域链: window
全局没有userName, userEmail,所以输出 undefined
![]() bind,call,apply:
bind,call,apply:
bind()不会立即执行, 只返回一个函数声明
call/apply 立即执行
![]() 访问器属性:
访问器属性:
get set
访问器属性优级高于同名的普通属性
![]() 流程控制-分支
流程控制-分支
单分支
双分支
多分支
switch 用在单值判断
三元运算符 条件? true : false

