1.盒模型
(1)em与rem的区别
em:根据元素的上下文或者当前元素的字号大小(font-size:16px)进行绑定的,以确定em值的大小,是可以动态修改的,例如body和html标签,一般默认为16px,也就是16px为1em。
rem:根据元素的根元素的字号大小进行绑定,就不是根据上下文绑定了,一般确定了就不会更改。
内边距和外边距(margin,padding)
margin:也就是外边距,不影响盒子本身的大小,但是会影响盒子在页面中占据的空间大小。
padding : 内边距,在盒子外面增加距离,会影响盒子的大小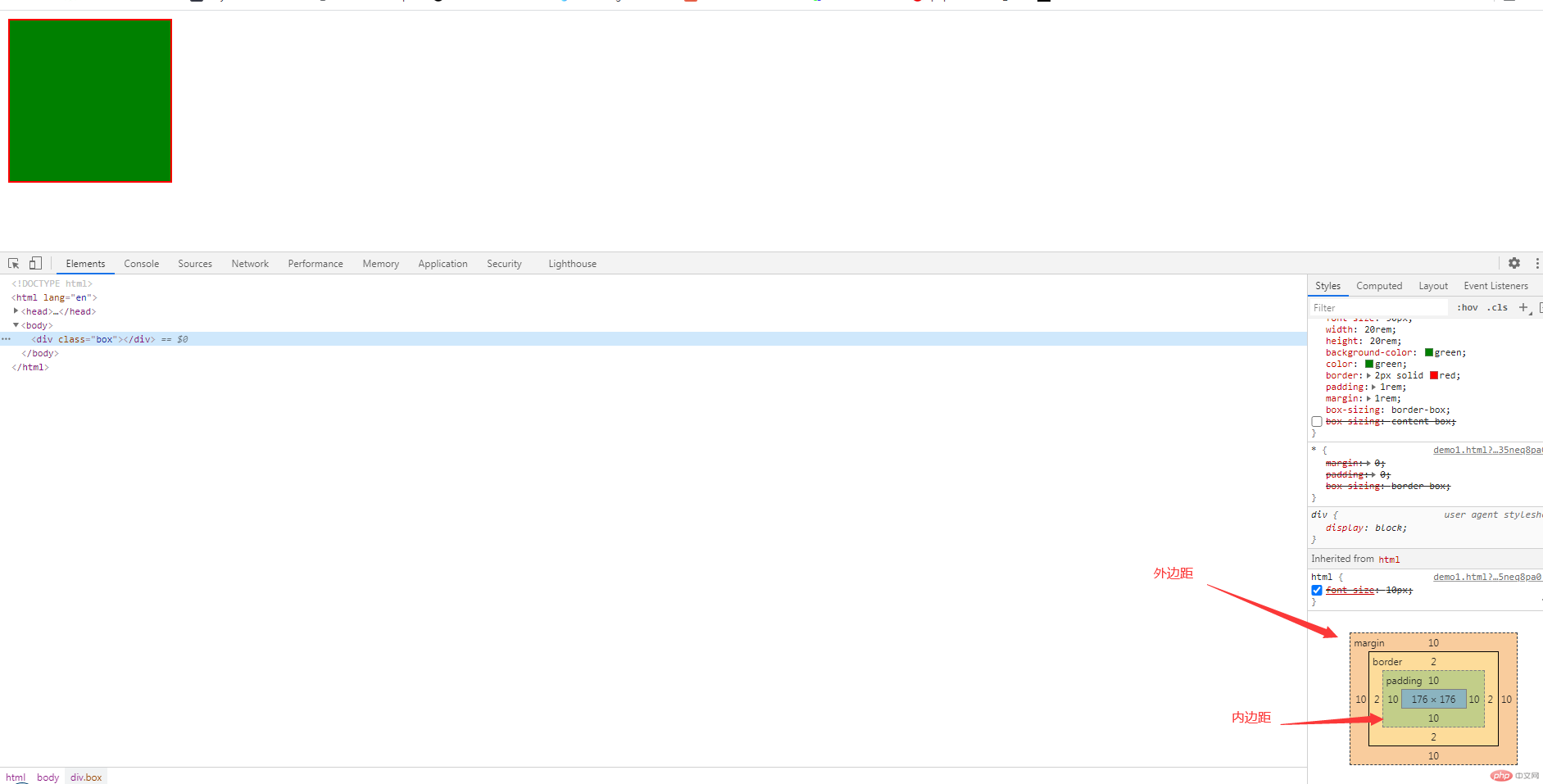
css初始化
通常写style的时候都要做一个初始化,来做一个ie盒子(box-sizing : border-box)的转换和内外边距的清零。
如果要查看内容区的盒子大小,可以使用box-sizing: content-box;转换成w3c标准盒子。
* {margin: 0;padding : 0;box-sizing : border-box;}
示例
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>vh / vm</title><style>* {margin: 0;padding : 0;box-sizing : border-box;}/*视口 : 可视窗口,手机端为了显示pc页面,默认为980px*/.box {width: 50vw;height: 25vh;background-color: red;margin : 20px auto;}</style></head><body><div class="box"></div></body></html>

2.相对定位与绝对定位
默认的是静态定位:position:static;也就是没有定位。
- 相对定位:position:relative;相对于它在文档流的原始位置进行定位
- 绝对定位:position:absolute;定位元素是脱离文档流的,它的定位位置可以通过设置定位父级的方式进行定位,父级定位没有设置父级的话默认是html,父级定位就必须是定位元素,一般用相对定位转换为定位元素。
- 固定定位:position: fixed;永远相对于html进行定位
定位元素:只要有非static的定位属性,就是定位元素。
相对定位需要设置定位偏移量,才有效果,只要是定位元素,定位偏移量就有效果,所以相对定位是定位元素定位偏移量:top left right bottom
演示实例
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>html {border: 1px solid brown;}/* .box {width: 10em;height: 10em;background-color: #63a35c;!*相对定位*!!*position: relative;*!!*定位元素: 只要这个元素上有非static的定位属性,就是定位元素*!!*定位偏移量*!!*只要是定位元素,定位偏移量有效*!!*相对于它在文档流中的原始位置进行定位*!!*绝对定位脱离了文档流*!!*文档流: 显示顺序于书写顺序一致*!position: absolute;top: 5em;left: 3em;}*/.parent {width: 20em;height: 20em;border: 1px solid red;top: 1em;left: 1em;/*转为定位元素,作为绝对元素的定位父级*/position: relative;}/*固定定位*/.box {position: fixed;}</style></head><body><div class="parent"><div class="box"></div></div><!--<h2>hello</h2>--></body></html>

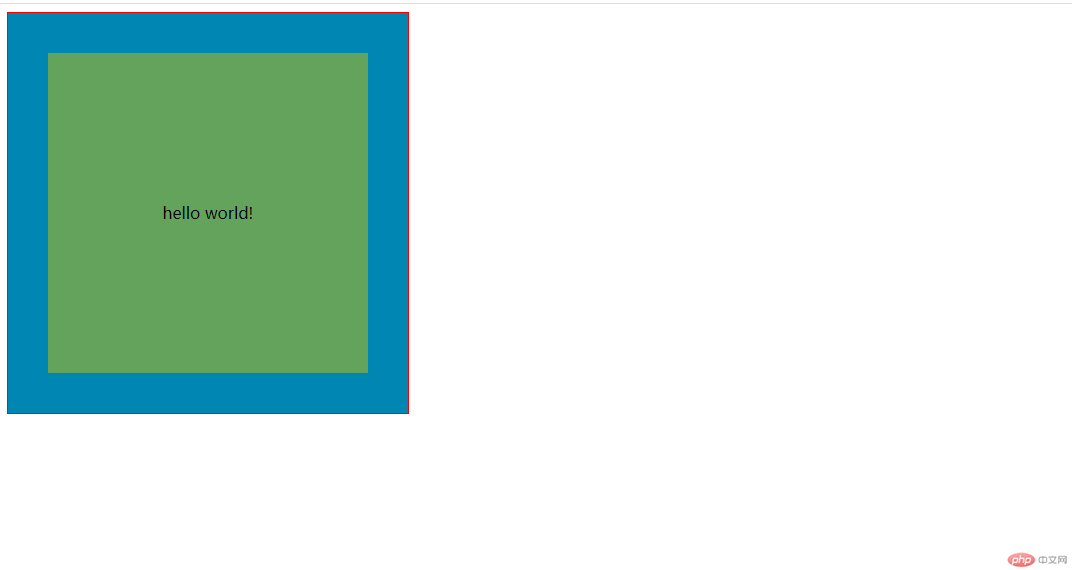
3.块级元素如何居中
1.水平居中
text-align : center;
2.垂直居中
line-height:标签的高度
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>绝对定位的应用 :块级居中</title><style>.box {width: 20em;height: 20em;background-color: #63a35c;}/*行内元素*/.box {/*!*水平居中*!*/text-align : center;/*!*垂直居中*!*/line-height: 20em;}.parent {border: 1px solid red;background-color: #0086b3;width: 25em;height: 25em;position: relative;}.box {/*布局的前提:页面宽度受限,高度是不受限的*/}/*使用绝对定位一步搞定块元素的垂直水平居中*/.box {/*约定定位*/position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;right: 0;bottom: 0;/*定位空间*/margin: auto;}</style></head><body><div class="parent"><div class="box">hello world!</div></div></body></html>


