一.选择器优先级
| 选择器 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| id选择器 | 语法是 #+di名称{} id选择器与元素属性选择器不同的是,id选择器选择id的时候需要在前面加上#号 |
| class选择器 | 语法是 .+类名称{} class选择器的前缀名是英文句号.可以给不同的属性改变样式只要是类名一致就行 |
| 标签/元素选择器 | 语法是 元素名称+{}元素选择器是找到或选择到相同类型的元素去改变内部样式,如果不是同类元素则不会改变基本样式 |
1.标签/元素选择器
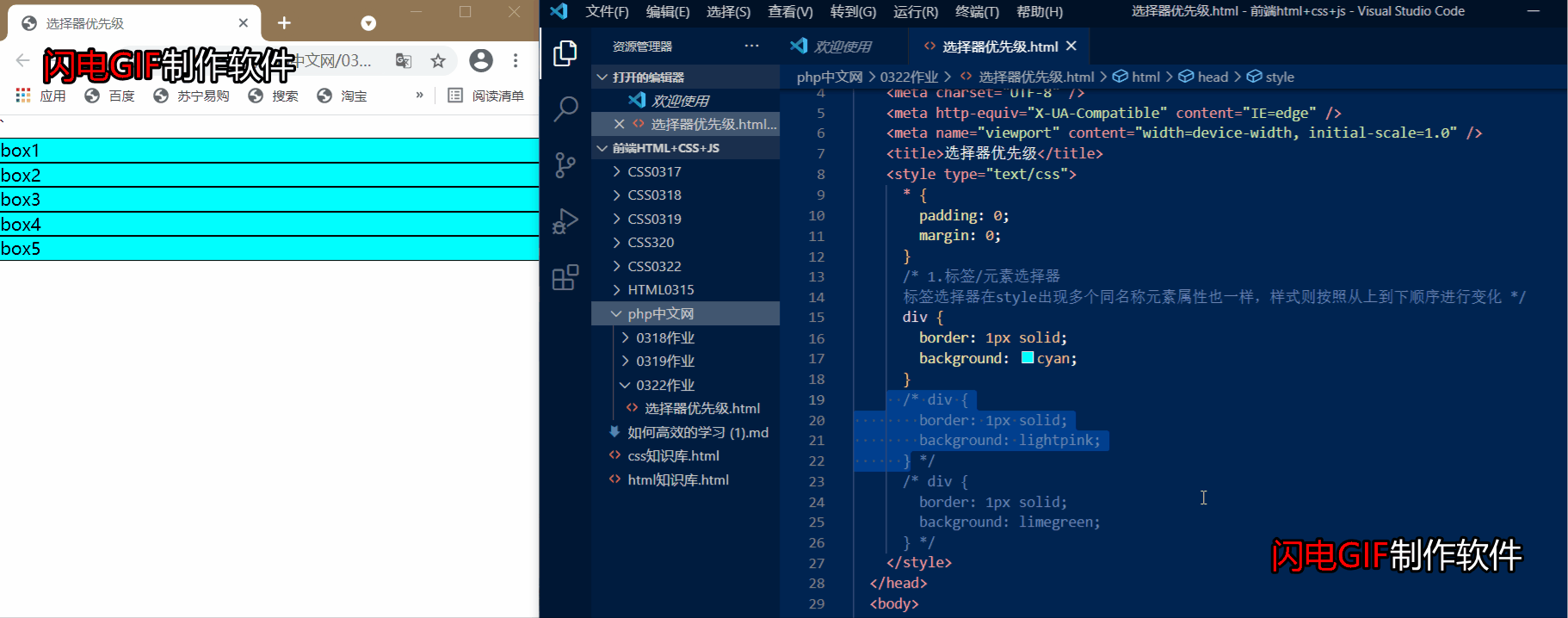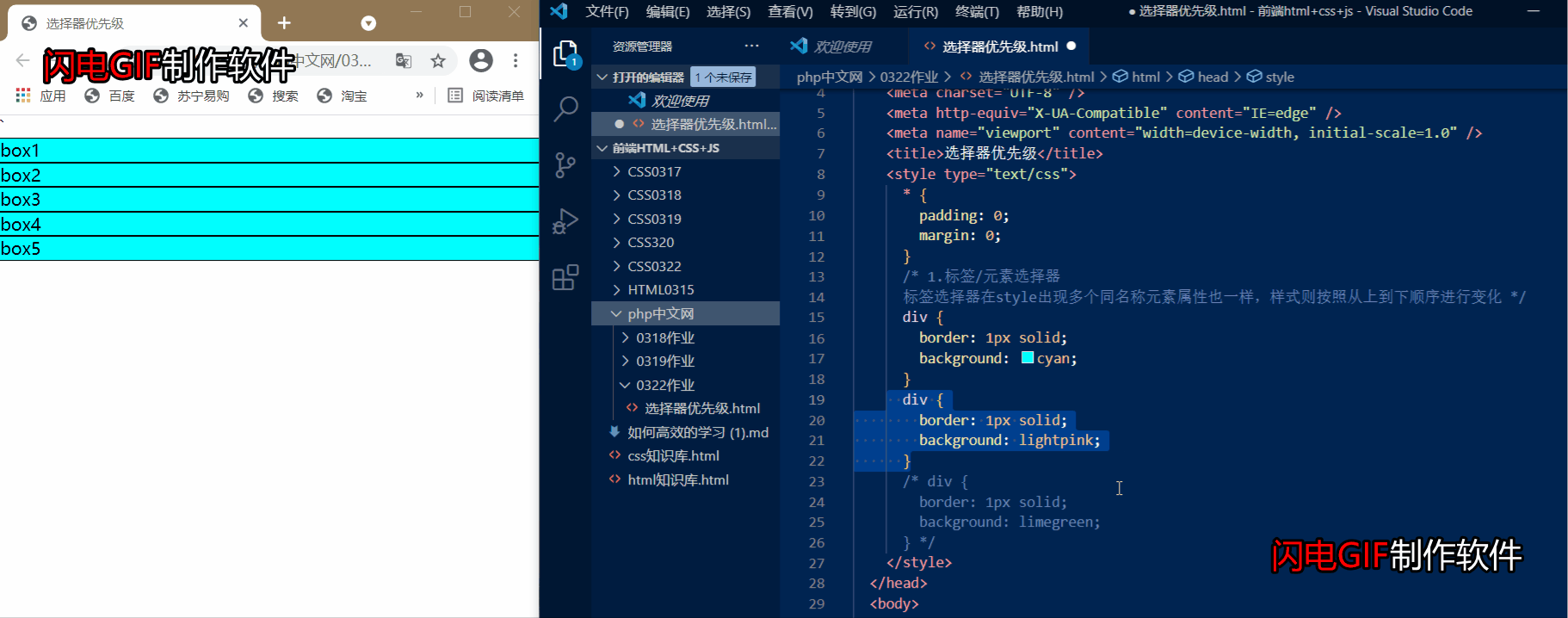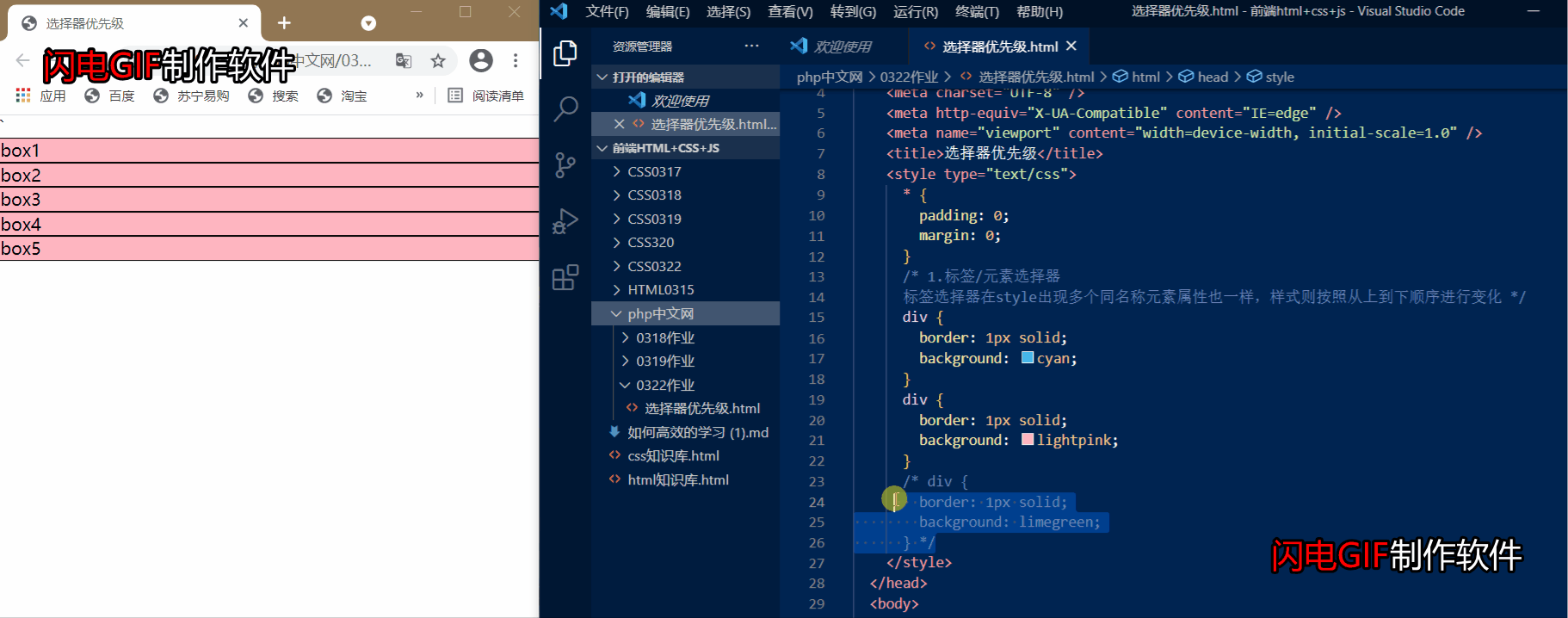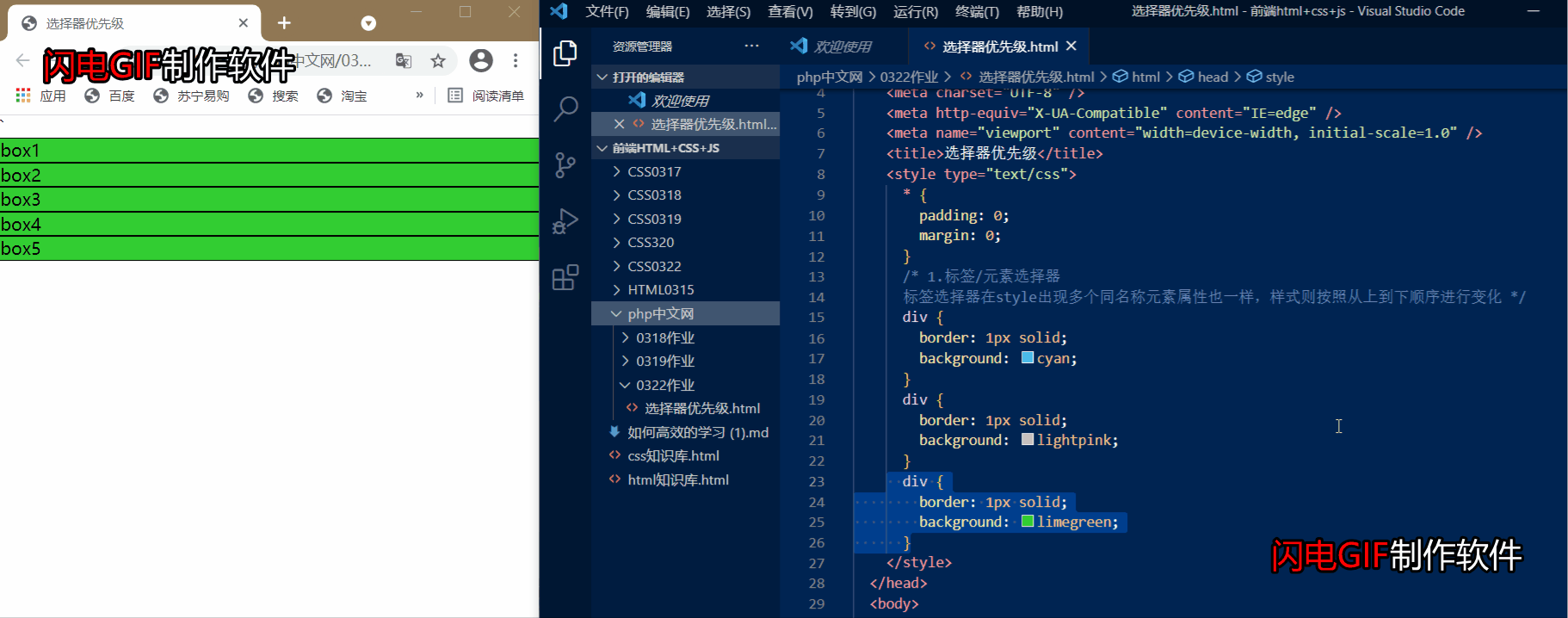
元素标签优先级: 标签选择器在style出现多个同名称元素属性也一样,样式则按照从上到下顺序进行变化
2.class和id选择器
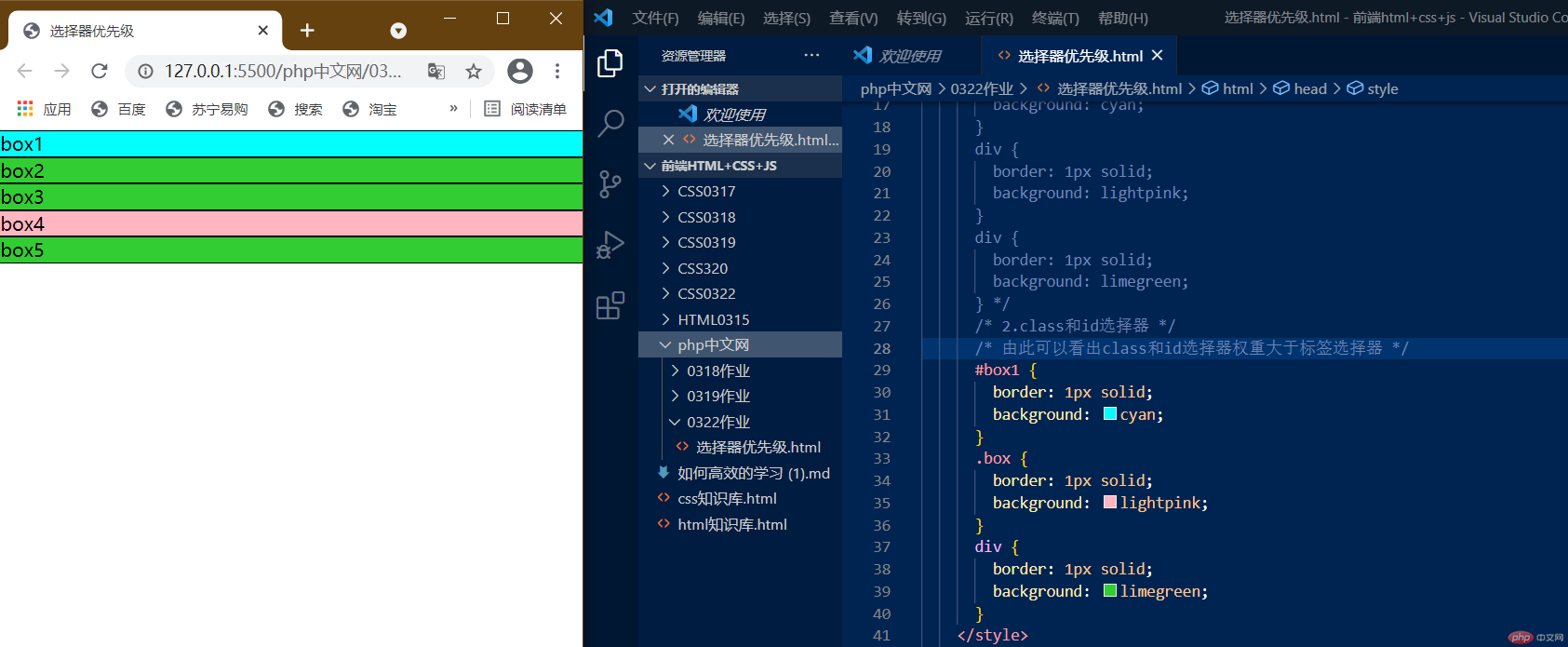
由此可以看出class和id选择器权重大于标签选择器,那么class和id选择器谁大谁小呢?请看下图
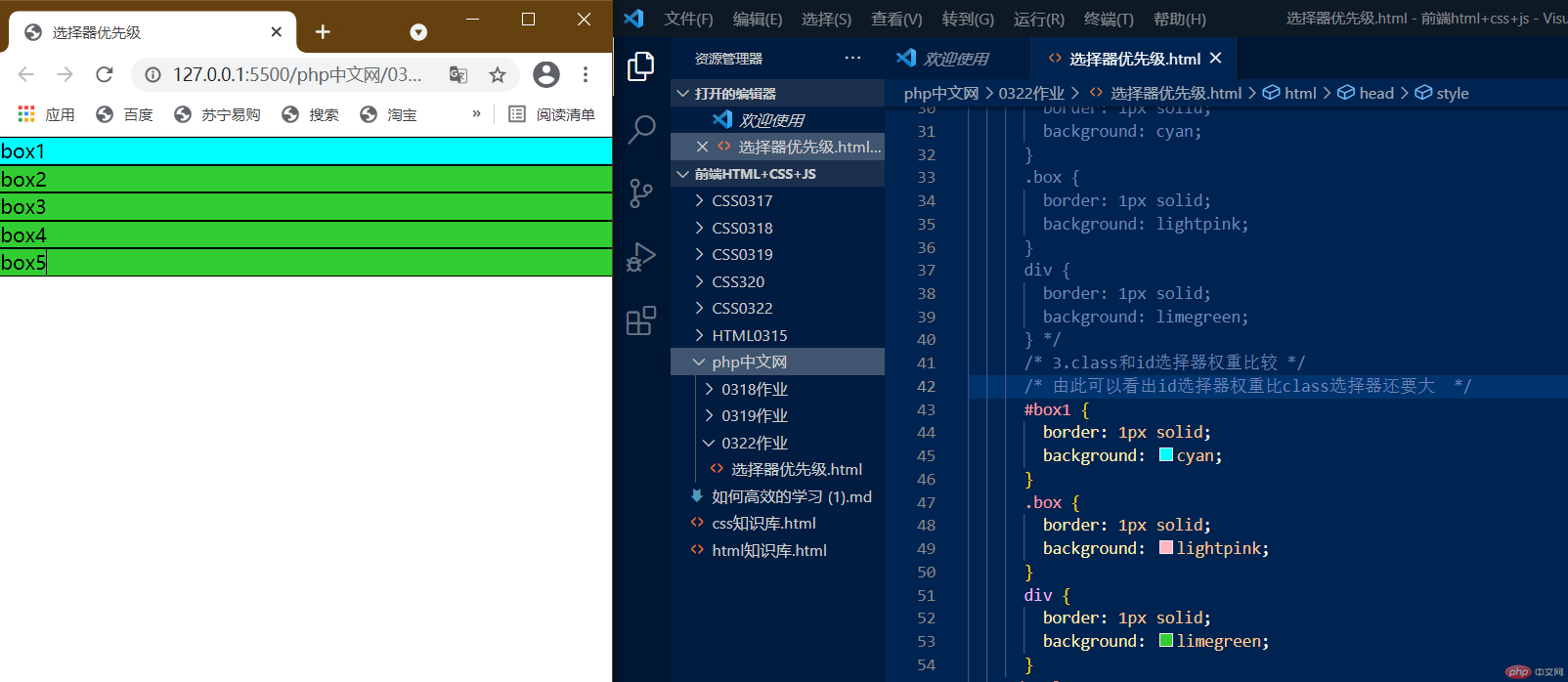
由此可以看出id选择器权重比class选择器还要大,因此我们可以得出一个结论:id选择器>class选择器>标签/元素选择器
3.代码块
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>选择器优先级</title><style type="text/css">* {padding: 0;margin: 0;}/* 1.标签/元素选择器标签选择器在style出现多个同名称元素属性也一样,样式则按照从上到下顺序进行变化 *//* div {border: 1px solid;background: cyan;}div {border: 1px solid;background: lightpink;}div {border: 1px solid;background: limegreen;} *//* 2.class和id选择器 *//* 由此可以看出class和id选择器权重大于标签选择器 *//* #box1 {border: 1px solid;background: cyan;}.box {border: 1px solid;background: lightpink;}div {border: 1px solid;background: limegreen;} *//* 3.class和id选择器权重比较 *//* 由此可以看出id选择器权重比class选择器还要大 */#box1 {border: 1px solid;background: cyan;}.box {border: 1px solid;background: lightpink;}div {border: 1px solid;background: limegreen;}</style></head><body><div id="box1" class="box">box1</div><div>box2</div><div>box3</div><div>box4</div><div>box5</div></body></html>
二.前端组件样式模块化原理与实现
| 样式表 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| link外部样式表 | 外部样式表link是标签是在head内部使用,引入css样式 rel是必须要输入的属性 内容是stylesheet表示引入的是一个css样式表文件,type填text/css说明是标准固定的css文件,href属性表示的是css文件路径 引入html外部的css文件 |
| @impord外部样式表 | url()内部输入css文件路径 |
| style=””内部样式表 | 内部样式表 style type=”text/css”是写在 head中 |
| style=””行内样式表 | 行内样式表 style 不同的是是写在body 行元素中 |
1.行内样式表
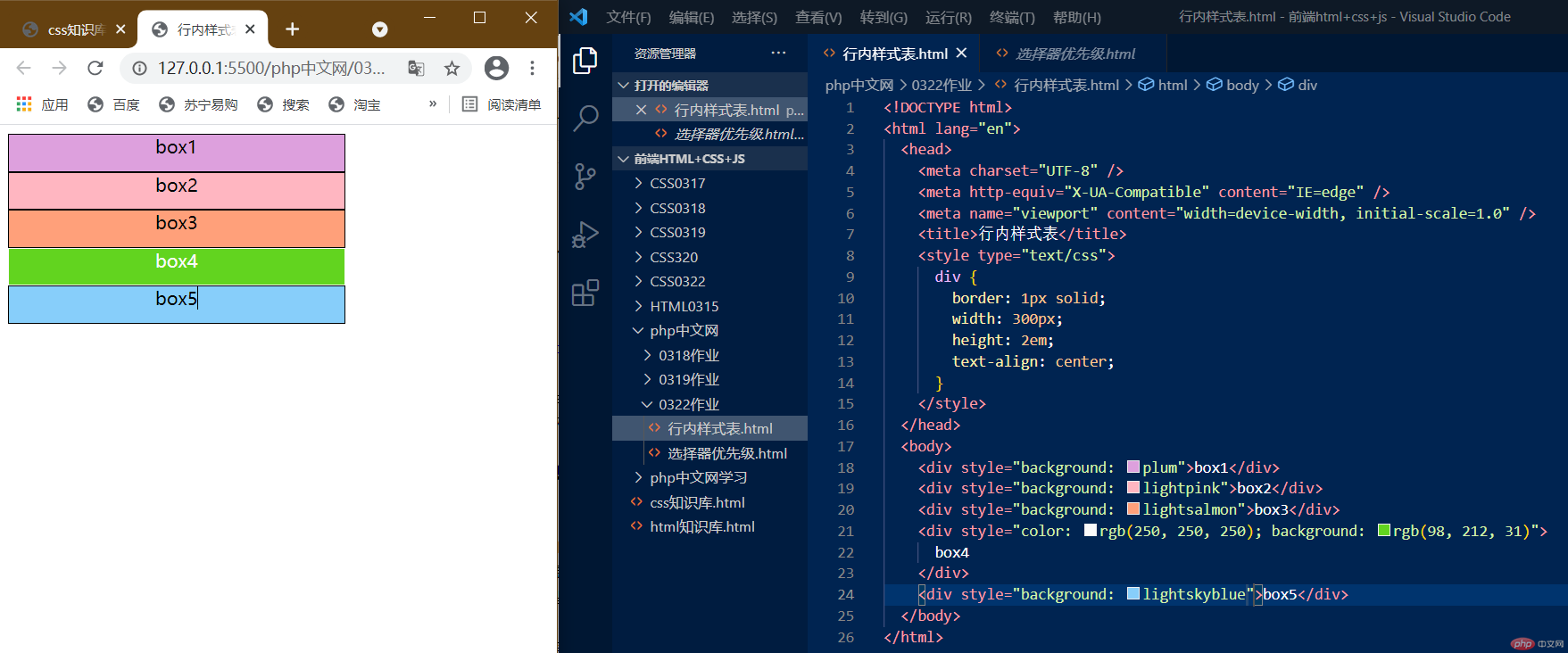
行内样式表我们把style写在body标签中去改变每一行的样式
<body><!-- 行内样式表我们把style写在body标签元素中去改变每一行的样式 --><div style="background: plum">box1</div><div style="background: lightpink">box2</div><div style="background: lightsalmon">box3</div><div style="color: rgb(250, 250, 250); background: rgb(98, 212, 31)">box4</div><div style="background: lightskyblue">box5</div></body>
2.内部样式表
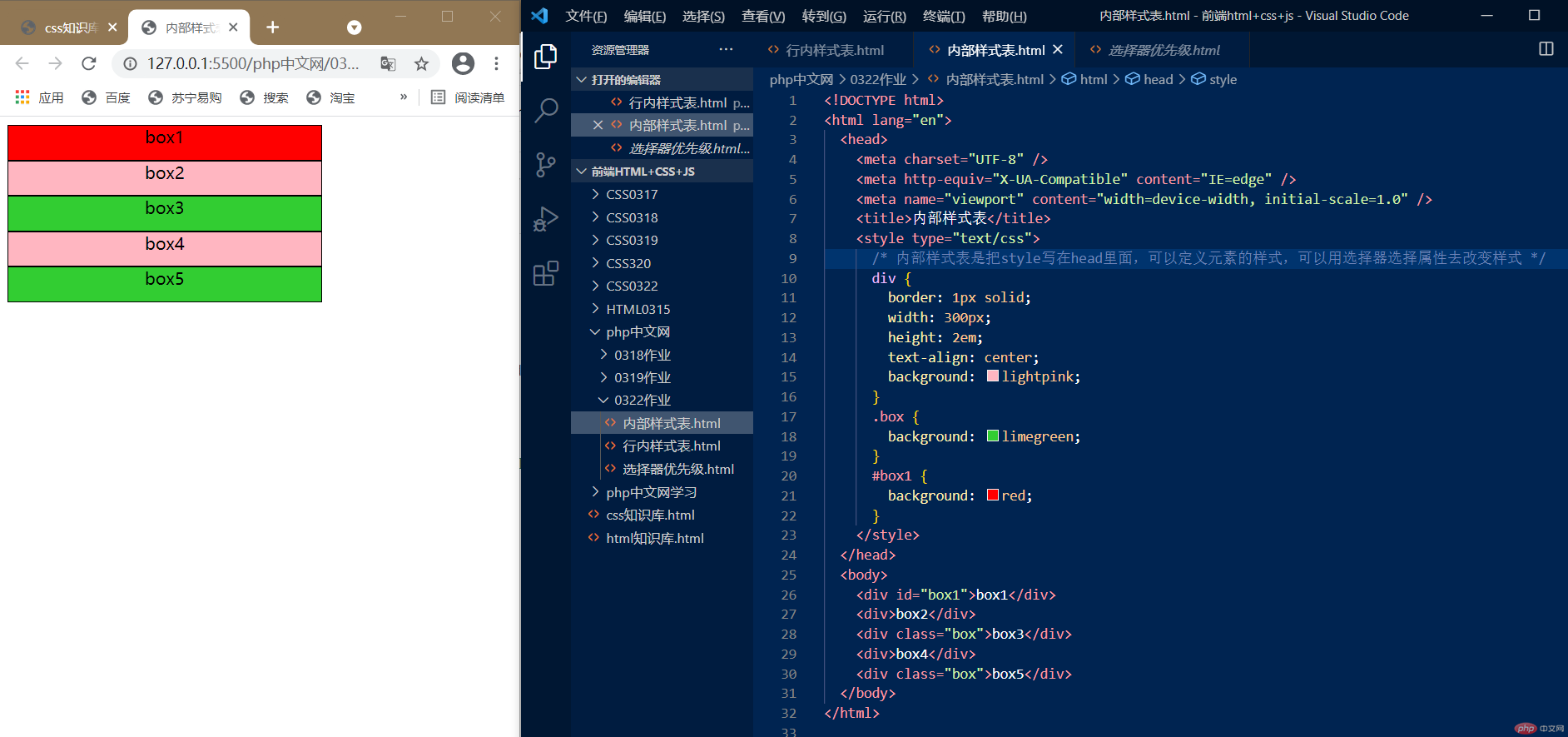
内部样式表是把style写在head里面,可以定义元素的样式,可以用选择器选择属性去改变样式,我用了元素选择器,id选择器,class选择器
<head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>内部样式表</title><style type="text/css">/* 内部样式表是把style写在head里面,可以定义元素的样式,可以用选择器选择属性去改变样式 */div {border: 1px solid;width: 300px;height: 2em;text-align: center;background: lightpink;}.box {background: limegreen;}#box1 {background: red;}</style></head>
3.外部样式表(模块化)
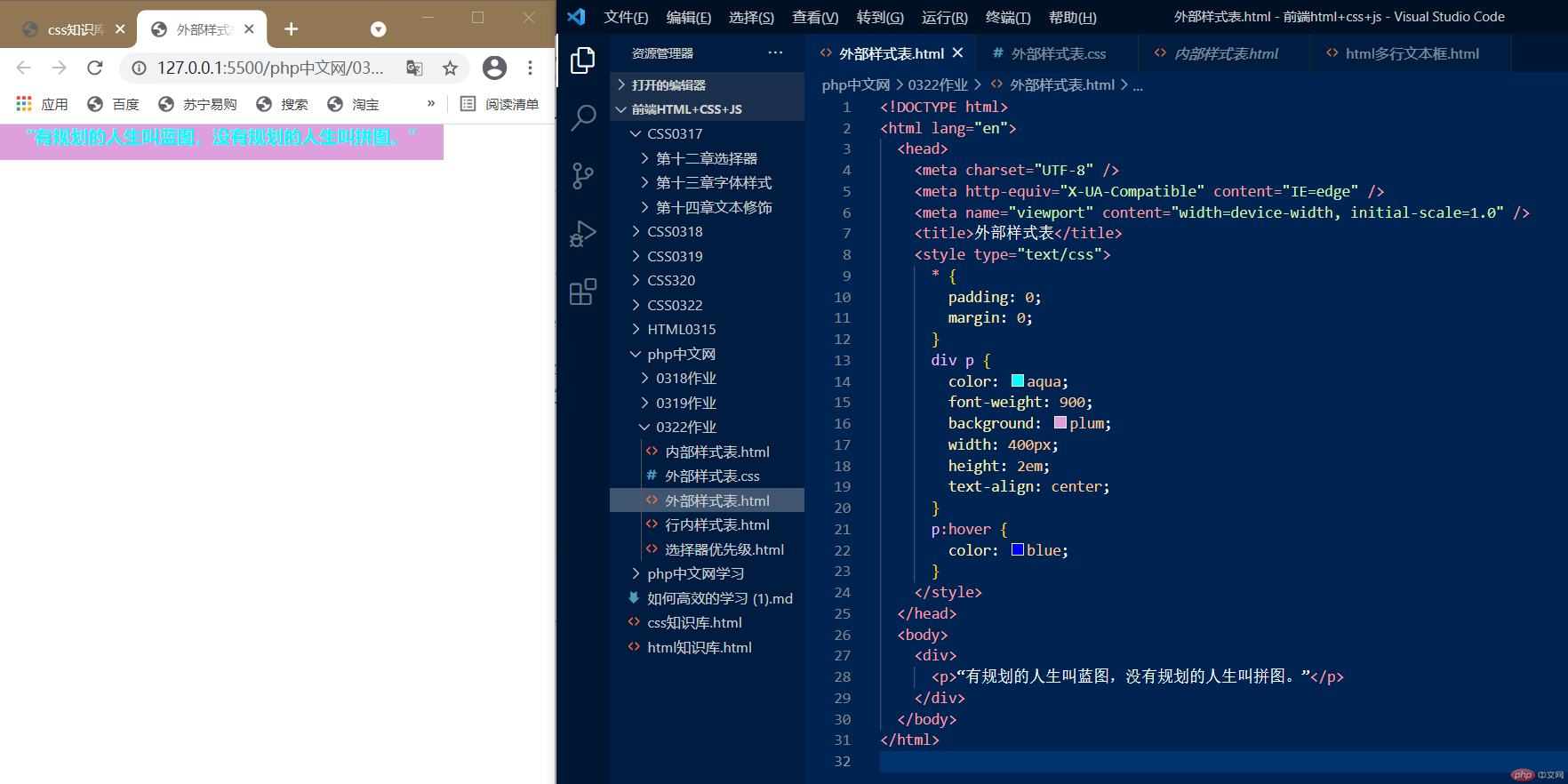
这里采用的是内部样式表,可以看到在一段文字中,加入了太多样式会觉得看起代码来很复杂,接下来我们用外部样式表看看如何去简化我们的代码
①创建一个css文件
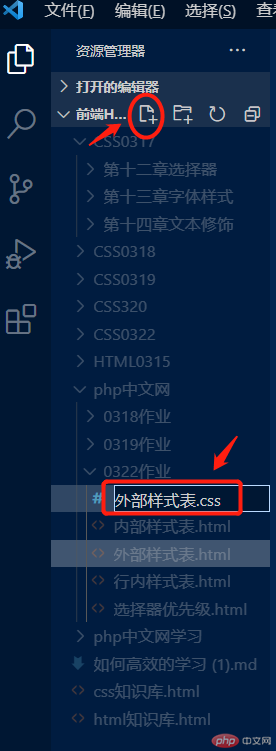
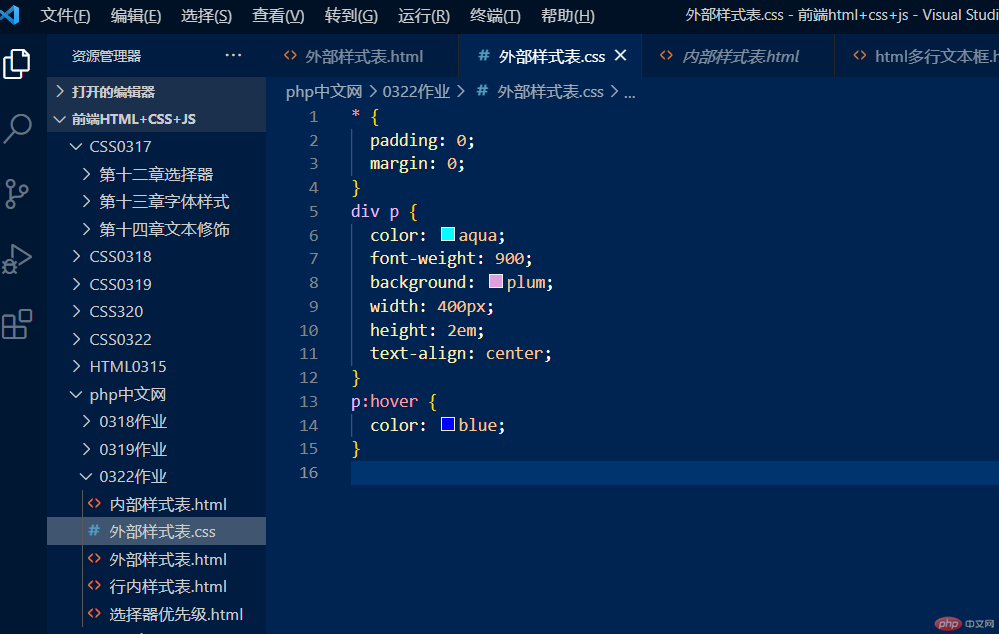
②把写好的样式放到css文件中
③html引入外部css文件
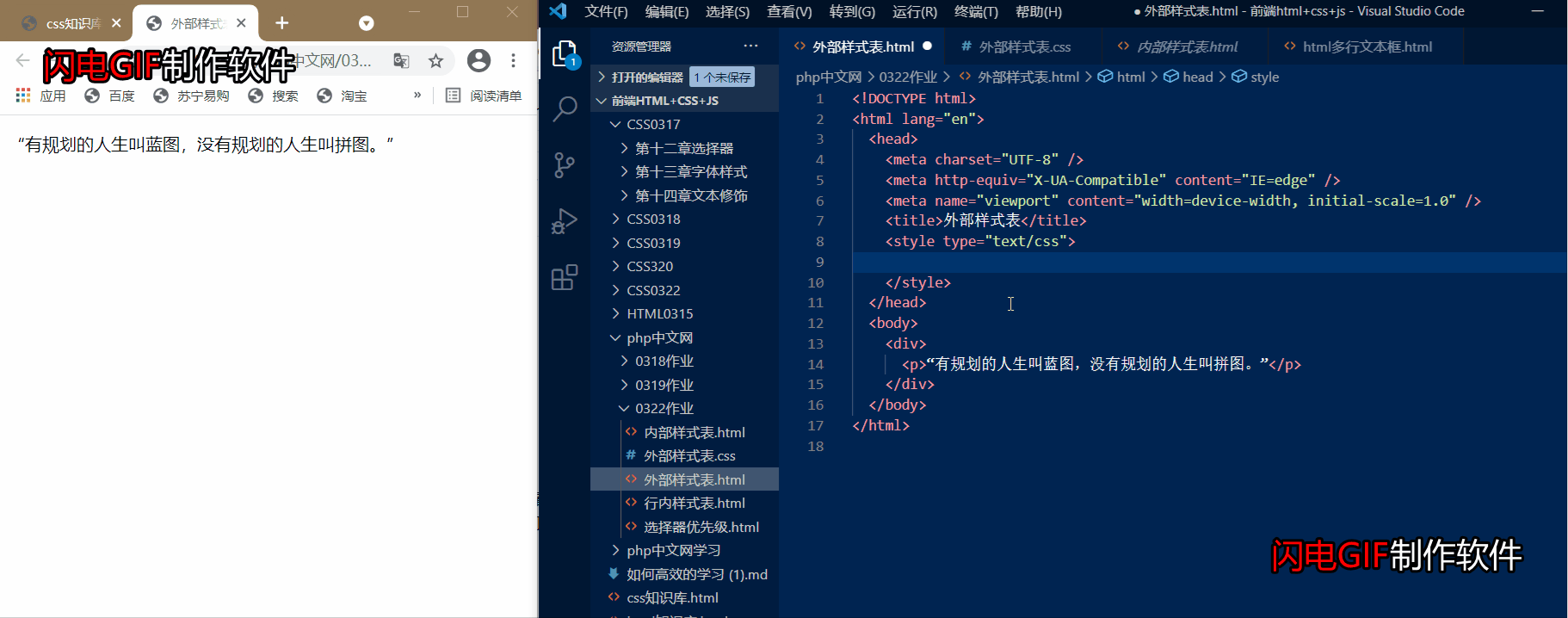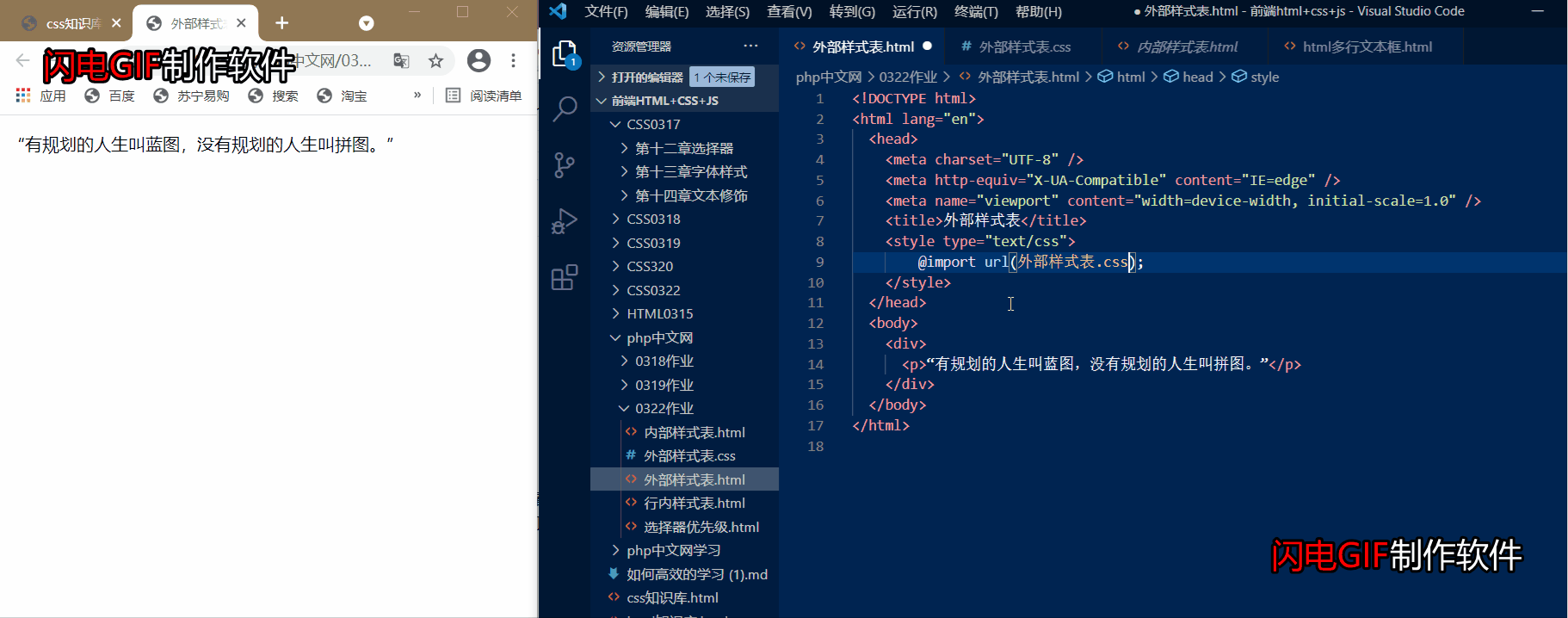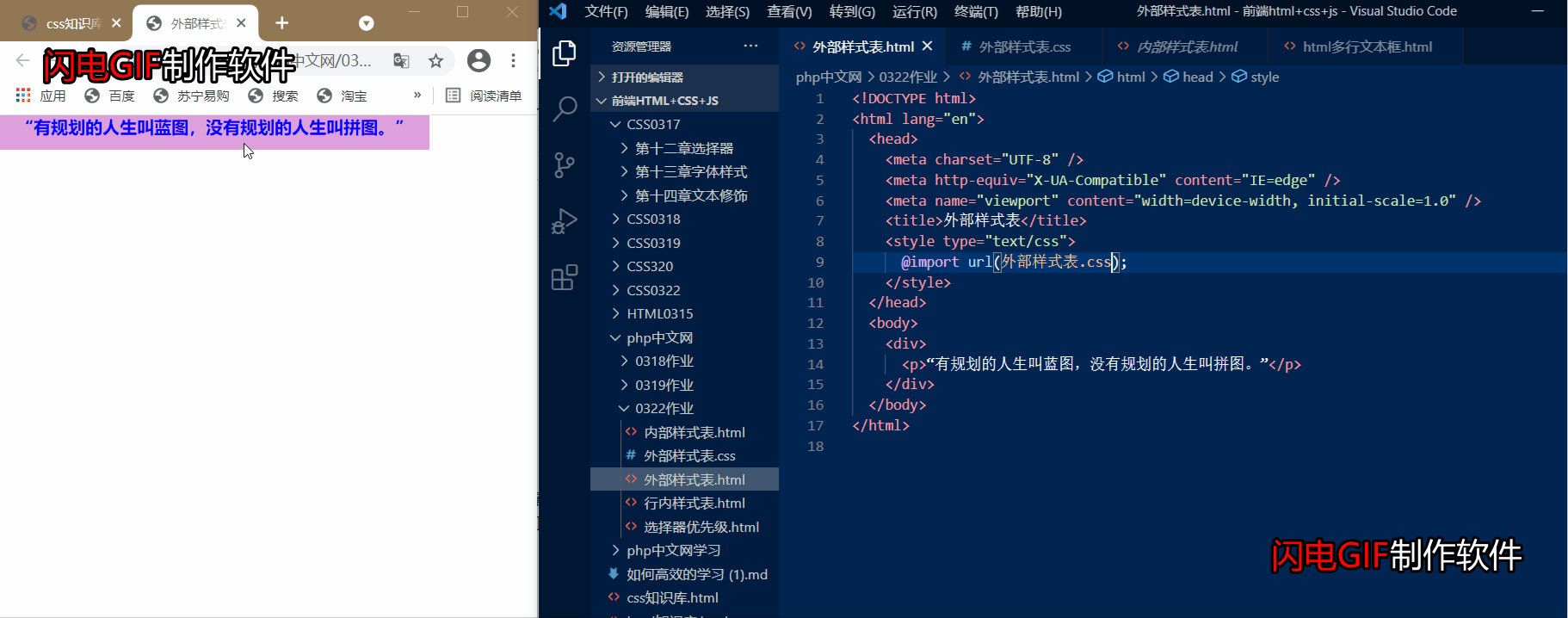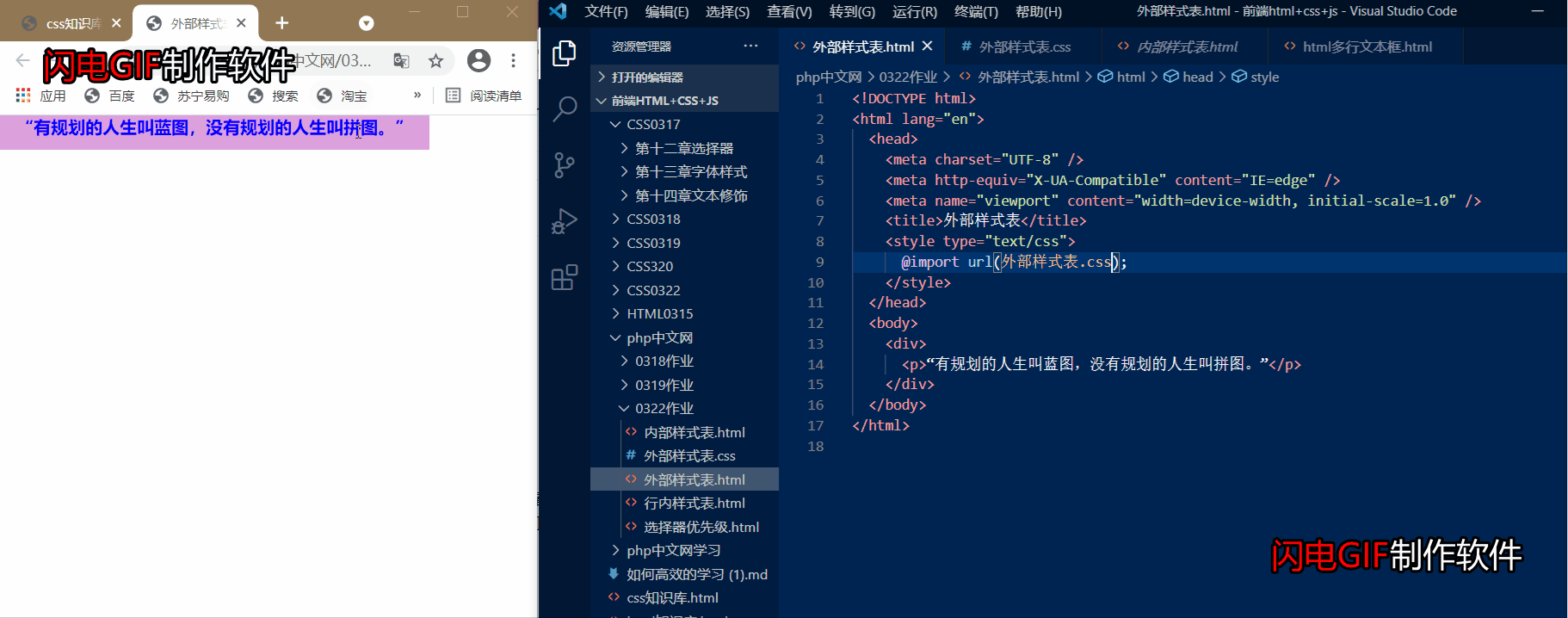
这里我们用@import url()引入外部的css文件,就可以把我们的样式给引入进去啦,这样代码看起来会更简洁!!!
3.代码块
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>外部样式表</title><style type="text/css">/* @imoprt url 引入外部css文件 */@import url(外部样式表.css);</style></head><body><div><p>“有规划的人生叫蓝图,没有规划的人生叫拼图。”</p></div></body></html>
三.常用伪类选择器的使用方式(模块化元素组件)
| 伪类 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| :nth-of-type(n) | 选择任何一个元素 |
| :first-of-type | 选择第一个元素 |
| :last-of-type | 选择最后一个元素 |
| :nth-last-of-type() | 选择倒数某一个元素 |
| :only-of-type | 唯一子元素的元素 |
1.:nth-of-type(n),选择任何一个元素
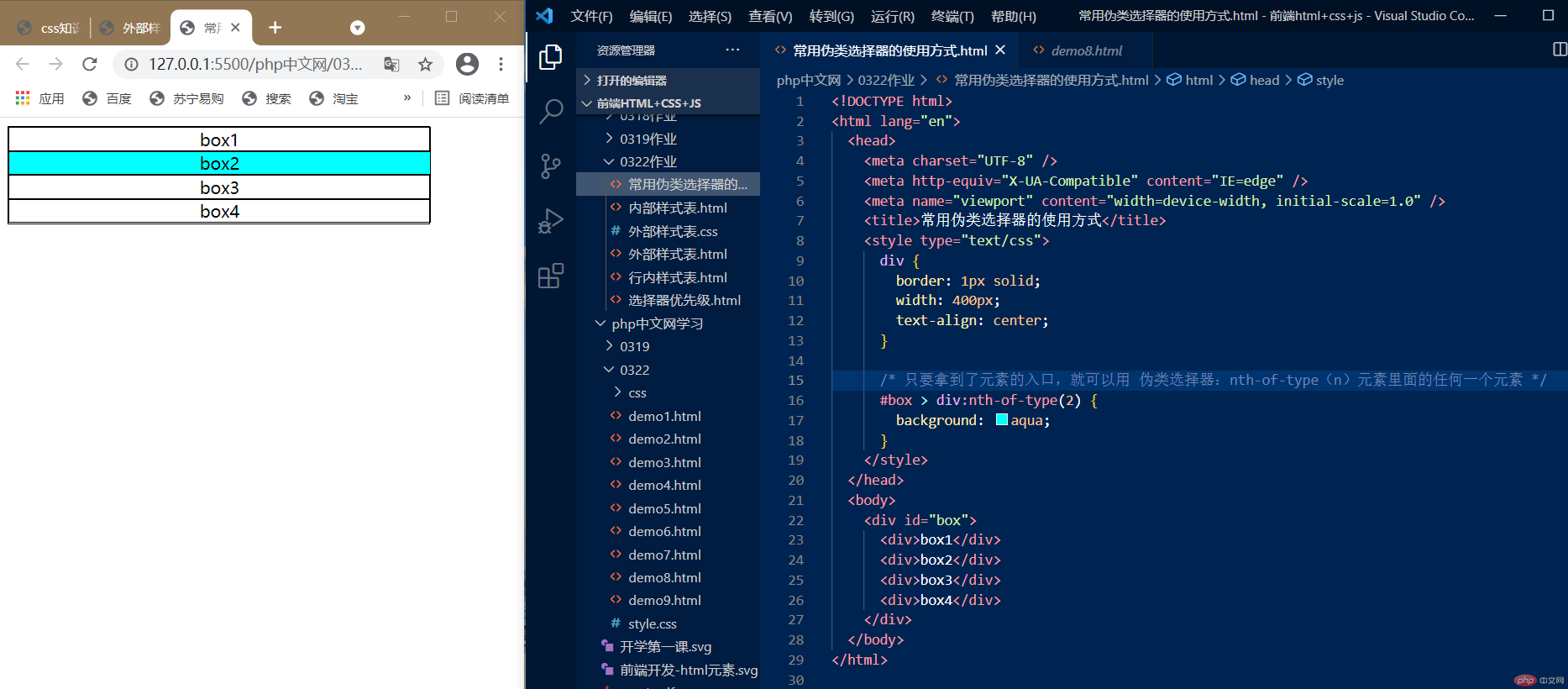
只要拿到了元素的入口,就可以用 伪类选择器:nth-of-type(n)元素里面的任何一个元素
2.:first-of-type,选择第一个元素
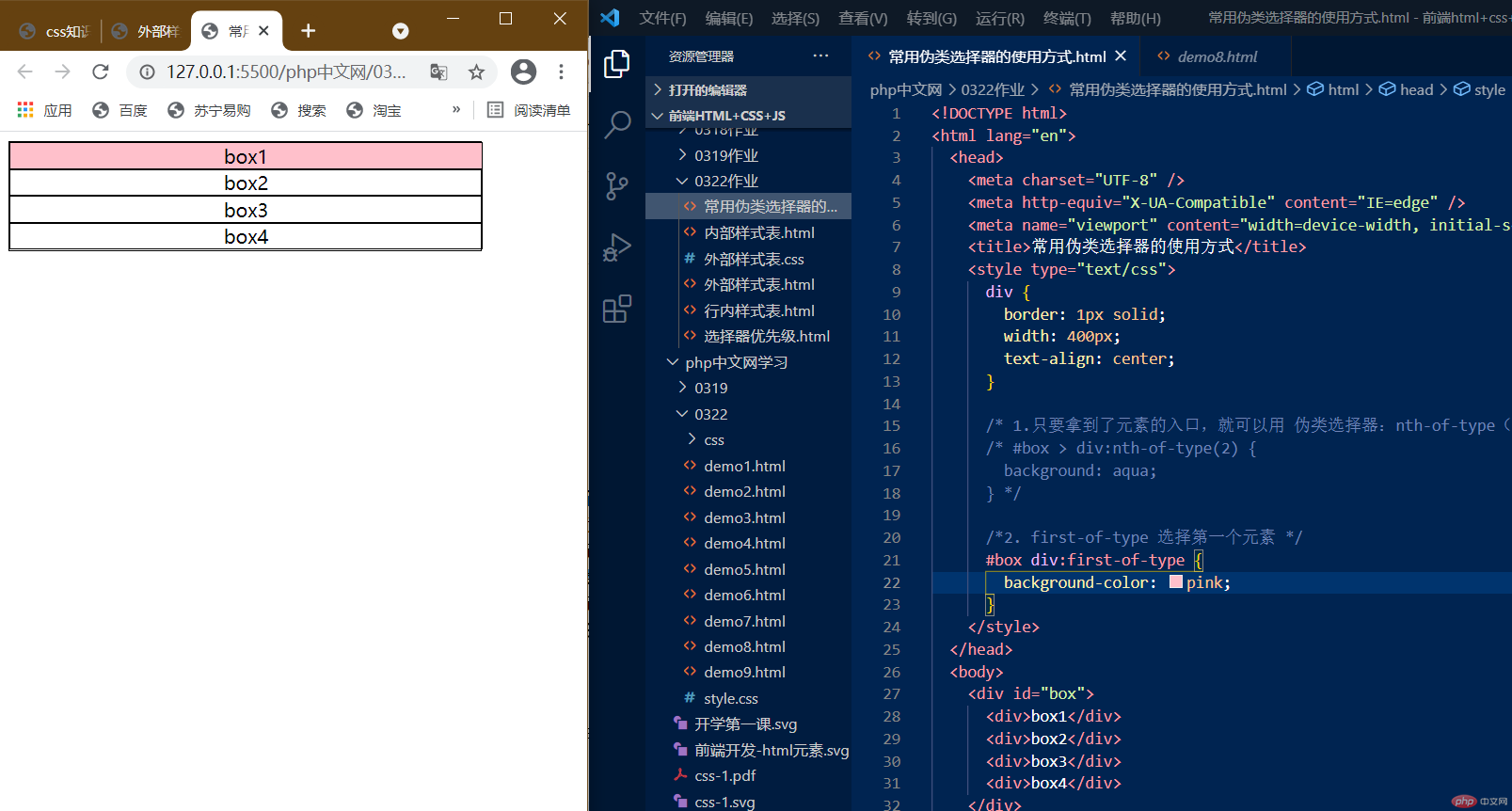
:first-of-type 选择第一个元素
3.:last-of-type,选择第最后一个元素
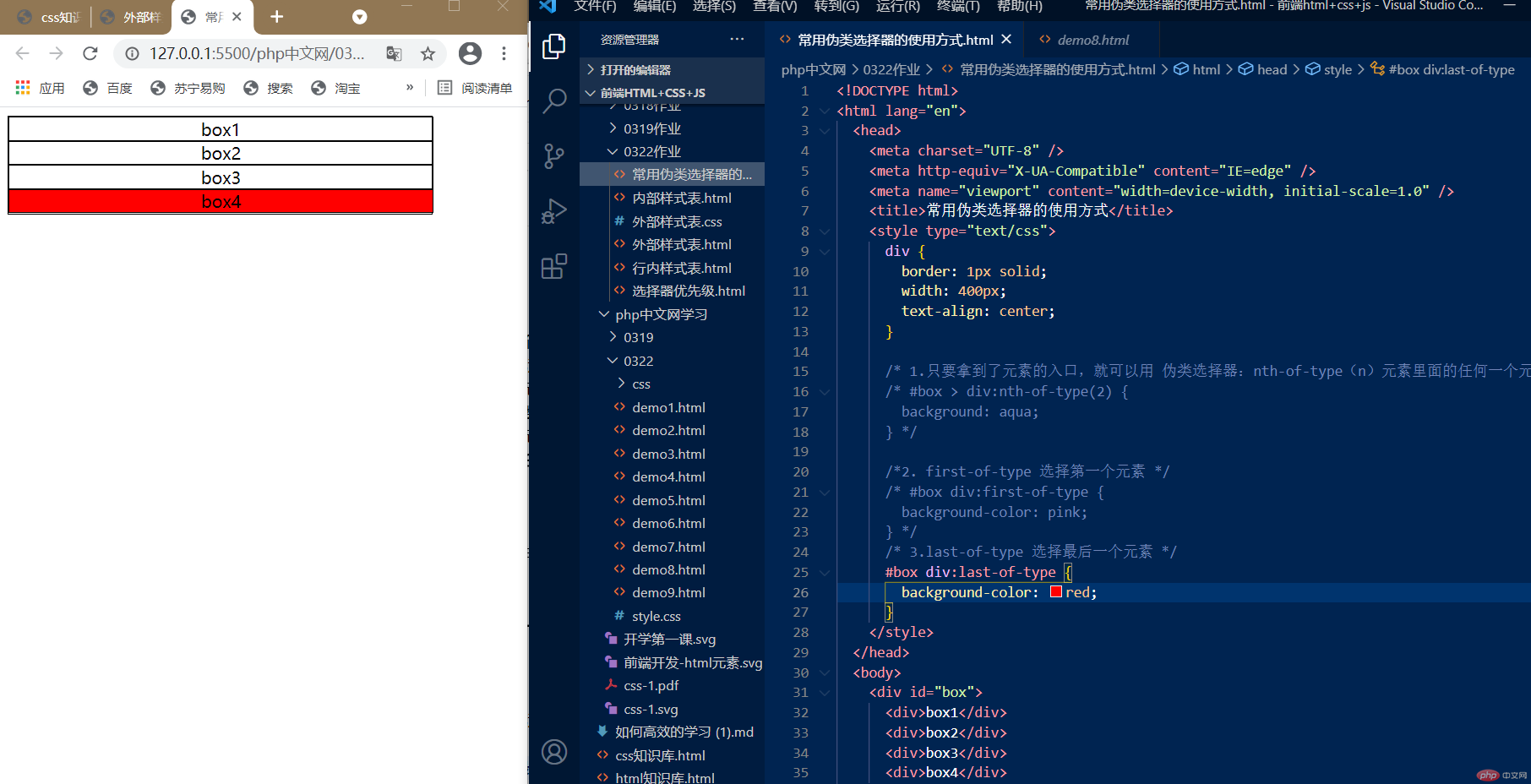
:last-of-type 选择最后一个元素
4.nth-last-of-type(),选择倒数某一个元素
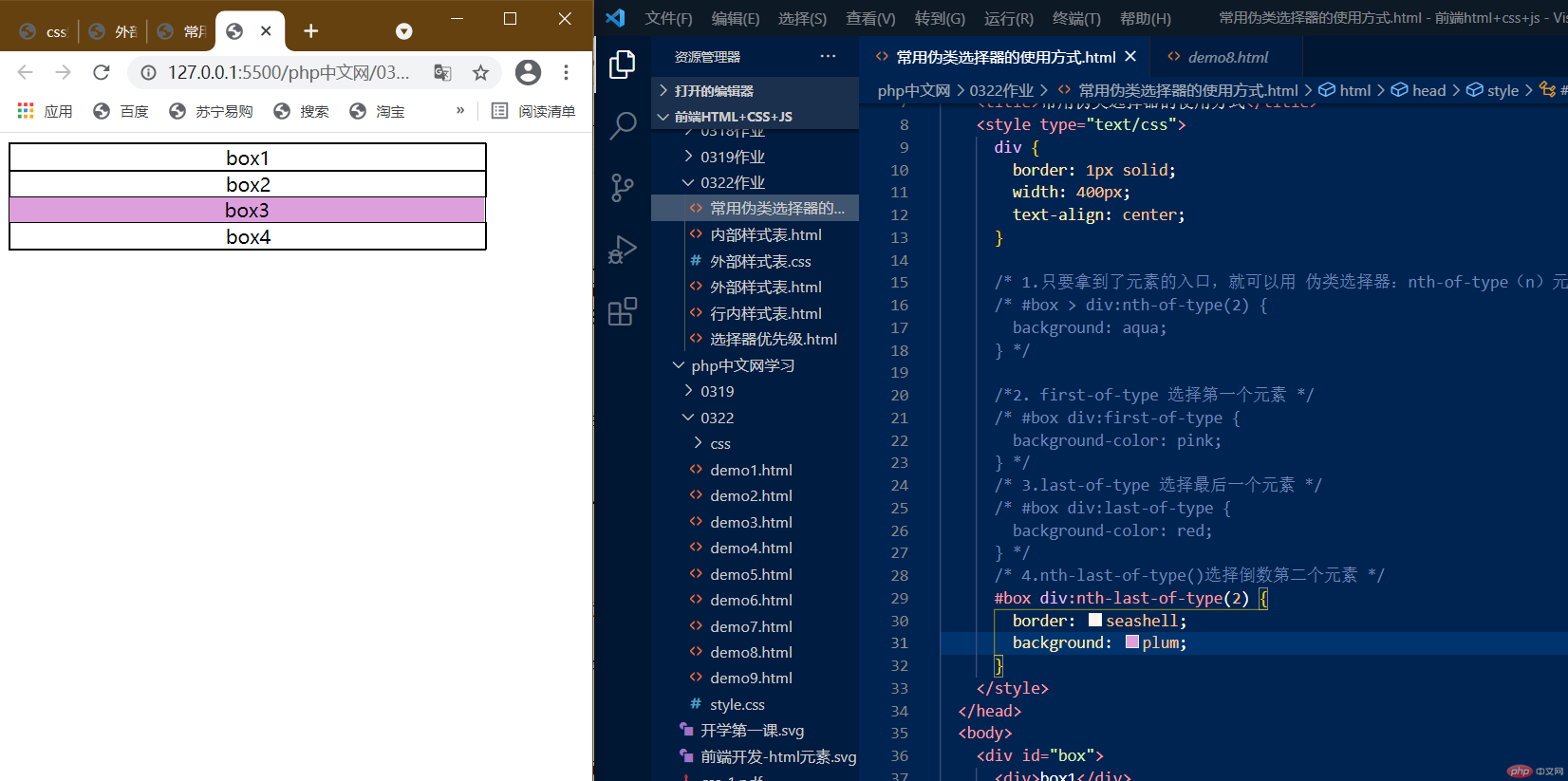
:nth-last-of-type(2)选择倒数第二个元素
4.:only-of-type,唯一子元素的元素
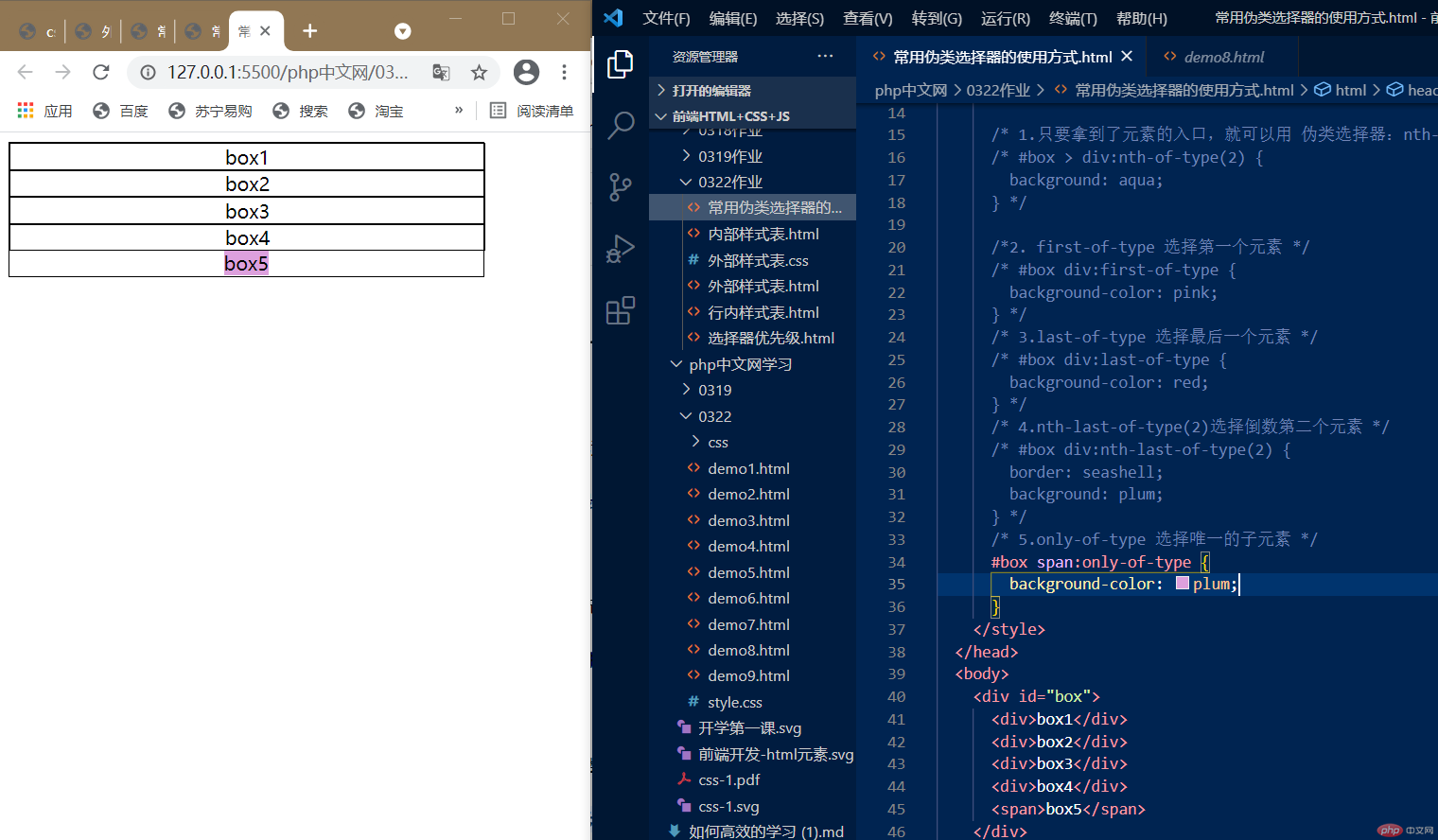
:only-of-type 选择唯一的子元素
5.:代码块
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>常用伪类选择器的使用方式</title><style type="text/css">div {border: 1px solid;width: 400px;text-align: center;}/* 1.只要拿到了元素的入口,就可以用 伪类选择器:nth-of-type(n)元素里面的任何一个元素 *//* #box > div:nth-of-type(2) {background: aqua;} *//*2. first-of-type 选择第一个元素 *//* #box div:first-of-type {background-color: pink;} *//* 3.last-of-type 选择最后一个元素 *//* #box div:last-of-type {background-color: red;} *//* 4.nth-last-of-type(2)选择倒数第二个元素 *//* #box div:nth-last-of-type(2) {border: seashell;background: plum;} *//* 5.only-of-type 选择唯一的子元素 */#box span:only-of-type {background-color: plum;}</style></head><body><div id="box"><div>box1</div><div>box2</div><div>box3</div><div>box4</div><span>box5</span></div></body></html>

