Web Pages folder
ASP.NET Web Pages - Folders
This chapter introduces knowledge about folders and folder paths.
In this chapter, you will learn:
Logical folder structure and physical folder structure
Virtual name and physical name
Web URL and Web path
##Logical folder structureThe following is Typical ASP.NET website folder structure:
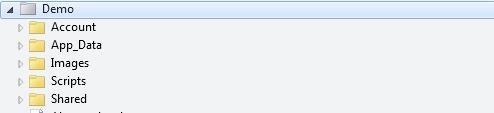
- "Account" folder contains login and security files
- "App_Data" Folder contains database and data files
- "Images" folder contains pictures
- "Scripts" folder contains browser scripts
- The "Shared" folder contains common files (such as layout and style files)
Physical folder structure The physical folder structure of the "Images" folder in the above website on your computer may be as follows: C:\Documents\MyWebSites\Demo\Images
Virtual Name and physical name Take the example above: The virtual name of the website image may be "Images/pic31.jpg". The corresponding physical name is "C:\Documents\MyWebSites\Demo\Images\pic31.jpg".
URL and path URL is used to access files in the website: http://www.w3cschool.cc/html/html-tutorial.htmlURL corresponds to the physical file on the server: C:\MyWebSites\w3cschool\html\html-tutorial.html
The root directory of the disk drive is written as C:, but the root directory of the website is / (slash).
The virtual path of the Web folder is usually different from the physical folder.
In your code, decide to use physical paths and virtual paths based on your coding needs.
ASP.NET folder paths have 3 tools: ~ operator, Server.MapPath method and Href method.
~ Operator
Use the ~ operator to specify virtual paths in programming code.
If you use the ~ operator, you can move your site to a different folder or location without changing any of your code:
var myStyleSheet = "~/styles/StyleSheet.css";
Server.MapPath method
Server.MapPath method Convert the virtual path (/) to a physical path that the server understands (C:\Documents\MyWebSites\Demo\default.html).
When you need to open a data file on the server, you can use this method (the data file can only be accessed by providing the complete physical path):
var fileName = Server.MapPath(pathName);
In the next chapter of this tutorial, you will learn more about reading Knowledge of fetching (and writing) data files on the server.
Href method
The Href method converts the path used in the code into a path that the browser can understand (the browser does not understand the ~ operator).
You can use the Href method to create paths to resources (such as image files and CSS files).
This method is generally used in the <a>, <img> and <link> elements in HTML:
<!-- This creates a link to the CSS file. -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="@Href(myStyleSheet)" />
<!-- Same as : -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/Shared/Site.css" />
The Href method is a method of the WebPage object.








