First of all, it is necessary to declare that the so-called "scope" is the "scope of information sharing", that is to say, the scope within which an information can be effective. The scopes of the four JSP built-in objects are: application, session, request, and page.
Recommended course: Java Tutorial.

The four major scopes of jsp are:
1, application function Domain
If you put a variable in application, it means that its scope is application and its effective scope is the entire application. The entire application refers to the start of the application to the end of the application. We don't say "from server startup to server shutdown" because a server may deploy multiple applications. Of course, if you shut down the server, all the applications on it will be shut down. Variables in the application scope have the longest survival time. If they are not manually deleted, they can always be used.
Object getAttribute(String name) //Get information from application;
void setAttribute(String name, Object value) //Set information to application scope.
2. Session scope
If you put a variable in the session, it means that its scope is the session and its valid scope is the current session. The so-called current session refers to the process from when the user opens the browser to when the user closes the browser.
Object HttpSession.getAttribute(String name) //Get information from session.
void HttpSession.setAttribute(String name,Object value) //Save information to the session.
HttpSessionHttpServletRequest.getSessio() //Get the session object where the current request is located.
session The session is considered started when the browser makes the first HTTP request. But it is difficult to judge the end, because the server will not be notified when the browser is closed, so it can only be judged by the following method: if the client does not respond within a certain period of time, the session is considered to be over. Tomcat's default value is 120 minutes, but this value can also be set through the setMaxInactiveInterval() method of HttpSession:
void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval)
If you want to actively end the session, for example, the user When clicking the "Logout" button, you can use the invalidate() method of HttpSession to force the end of the current session: void invalidate()
The time when the Session is deleted is:
1) Session Timeout: Timeout refers to the fact that the server does not receive the request from the client corresponding to the session for a certain period of time, and this time exceeds the maximum session timeout set by the server.
2) The program calls HttpSession.invalidate()
3) The server is shut down or the service is stopped
Note:
1) Access the static of *.html Because resources will not be compiled into Servlets, session issues are not involved.
2) When the JSP page does not explicitly prohibit sessions, the server will automatically create a session for it when opening the browser to request the jsp for the first time, and give it a sessionID, which will be sent to the client. terminal browser.
3) Since session consumes memory resources, if you do not plan to use session, you should close it in all JSPs.
4) The session will not be deleted when the browser is closed and can only be deleted through the above three methods.
Where is the session stored? -----------In memory on the server side.
3. Request scope
The variables in request can span the two pages before and after forward. But whenever the page is refreshed, they are recalculated.
Request forwarding: servlet.getRequestDispatcher("new.jsp").forward(req,resp);
Note:
1. Forwarding is a server behavior, and re- Targeting is client behavior.
2. No matter how it is forwarded on the server, the address of the original Servlet is still displayed in the browser address bar.
4. Page scope
The scope of the page object is limited to the current page requested by the user
The life cycles of request and page are short-lived The difference between them: a request can contain multiple pages (include, forward and filter).
The above is the detailed content of What are the four major scopes of jsp. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 jsp是属于前端还是后端Jan 28, 2023 pm 06:23 PM
jsp是属于前端还是后端Jan 28, 2023 pm 06:23 PMjsp属于后端。jsp的本质是一种servlet,而servlet又是服务器端的java应用程序,所以jsp是属于后端的技术。JSP部署于网络服务器上,可响应客户端发送的请求,并根据请求内容动态地生成HTML、XML或其他格式文档的Web网页,然后返回给请求者。JSP技术以Java作为脚本语言,为用户HTTP请求提供服务,并能与服务器上的其它Java程序共同处理复杂的业务需求。
 SpringBoot项目如何整合JSPMay 12, 2023 pm 07:40 PM
SpringBoot项目如何整合JSPMay 12, 2023 pm 07:40 PM新建好springboot项目以后目录如下:第一步:在项目的pom文件中加入配置jsp所需要的jar包代码:org.apache.tomcat.embedtomcat-embed-jasperprovided第二步:在main路径下新建目录webapp,在webapp下新建路径WEB-INF,在WEB-INF下新建路径jsp,在这个路径下放置我们要使用的jsp文件第三步:在主配置文件中配置jsp文件的访问路径和后缀代码:spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/sp
 jsp分页功能怎么实现Mar 04, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
jsp分页功能怎么实现Mar 04, 2024 pm 04:40 PM实现步骤:1、在JSP页面中引入JSTL标签库;2、从数据库中获取数据;3、对数据进行分页处理;4、在页面中显示分页导航条;5、根据当前页码和每页显示数量,从分页后的数据中获取对应的数据并显示在页面上即可。
 jsp和html区别在哪Jan 09, 2024 am 10:46 AM
jsp和html区别在哪Jan 09, 2024 am 10:46 AMjsp和html区别:1、运行机制;2、用途;3、与Java的关系;4、功能;5、与后端的关系;6、速度;7、可维护性和扩展性;8、学习和使用的难易程度;9、文件后缀和识别工具;10、社区和支持;11、安全性。详细介绍:1、运行机制,HTML是一种标记语言,主要用于描述和定义网页的内容,它运行在客户端,由浏览器解释执行,JSP是一种动态网页技术,运行在服务器端等等。
 jsp是什么格式的文件Jan 24, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
jsp是什么格式的文件Jan 24, 2024 pm 04:01 PMJSP是一种动态网页技术标准,其文件格式是在传统的网页HTML文件(.htm,.html)中插入Java程序段(Scriptlet)和JSP标记(tag),从而形成JSP文件(*.jsp)。
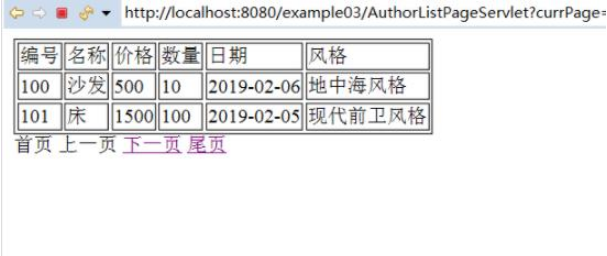 如何用jsp+mysql实现网页的分页查询May 30, 2023 pm 03:58 PM
如何用jsp+mysql实现网页的分页查询May 30, 2023 pm 03:58 PM一、实现分页查询的核心sql语句(1)查询数据库的记录总数的sql语句:selectcount(*)from+(表名);(2)每次查询的记录数的sql语句:其中:0是搜索的索引,2是每次查找的条数。select*from表名limit0,2;二、代码实现*上篇写过这两个类,DBconnection类:用于获取数据库连接,Author对象类。这两个类的代码点击连接查看。点击链接查看DBconnection类和Author对象类(1)登录页面:index.jsp。Inserttitlehere用户列
 Web开发的Java技术栈:了解Java EE、Servlet、JSP、Spring等常用于Web开发的技术Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:29 PM
Web开发的Java技术栈:了解Java EE、Servlet、JSP、Spring等常用于Web开发的技术Dec 26, 2023 pm 02:29 PMJavaWeb开发技术栈:掌握JavaEE、Servlet、JSP、Spring等用于Web开发的技术随着互联网的迅速发展,在当今的软件开发领域,Web应用的开发已经成为一种非常重要的技术需求。而Java作为一种广泛应用的编程语言,其在Web开发领域也有着重要的地位。JavaWeb开发技术栈涉及多项技术,如JavaEE、Servlet、JSP、Spr
 jsp中iframe是什么Aug 24, 2023 pm 04:02 PM
jsp中iframe是什么Aug 24, 2023 pm 04:02 PMjsp中iframe是一种用于嵌入其他网页或文档的HTML标签,可以实现页面的分割、动态加载、异步加载和跨域访问等功能。它为开发人员提供了更多的灵活性和交互性,可以提高网页的可用性和用户体验。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






